Problems and Solutions
Some of the more common problems are listed in Table 5‐1. This information is intended to be a check or verification that simple causes can be located and fixed. It is not an exhaustive “how to” for all types of problems. Procedures that require in depth knowledge or skills (like flashing the field) should be referred to a qualified generator service center.
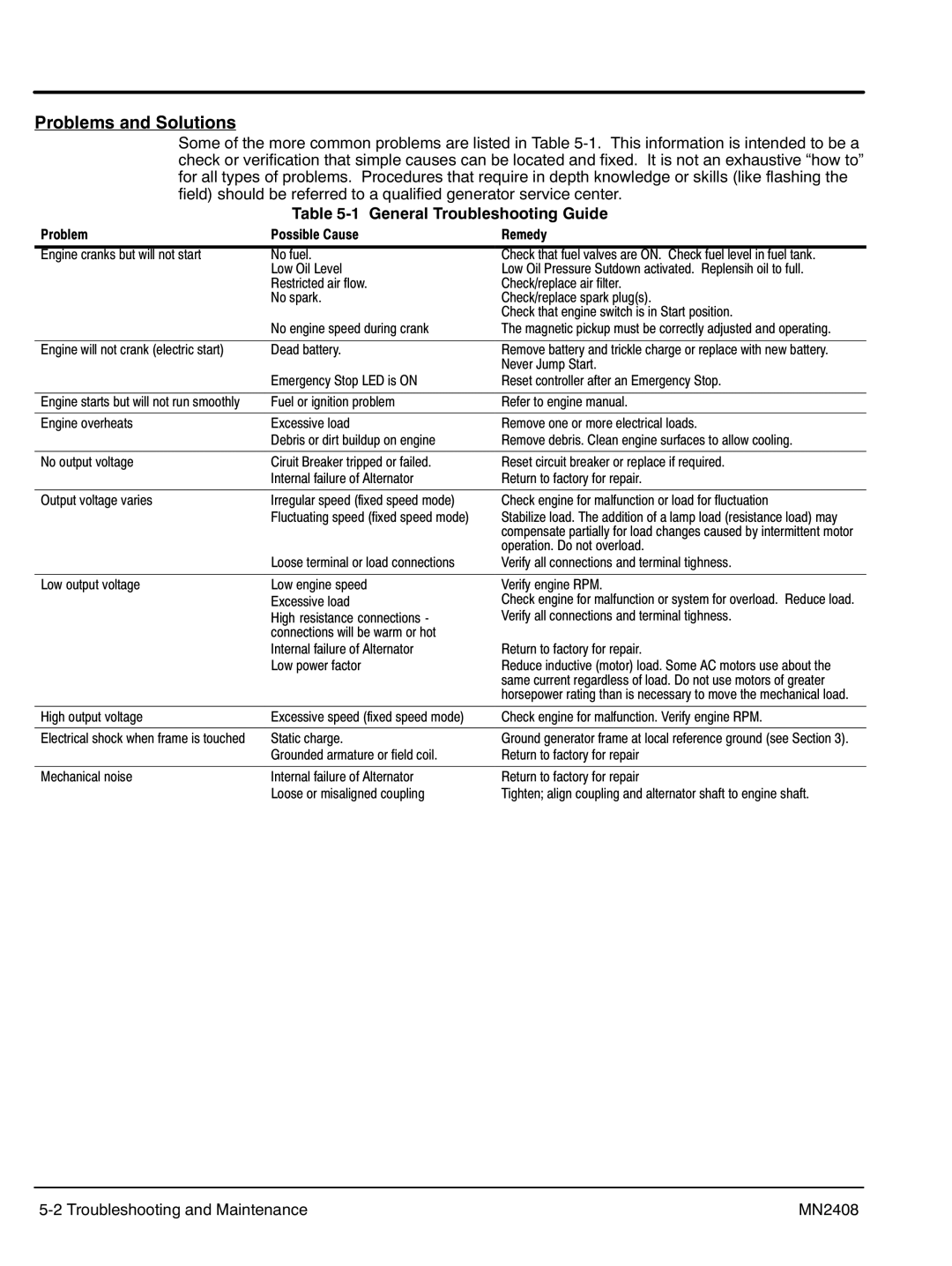
Table 5‐1 General Troubleshooting Guide
Problem | Possible Cause | Remedy |
Engine cranks but will not start | No fuel. | Check that fuel valves are ON. Check fuel level in fuel tank. |
| Low Oil Level | Low Oil Pressure Sutdown activated. Replensih oil to full. |
| Restricted air flow. | Check/replace air filter. |
| No spark. | Check/replace spark plug(s). |
|
| Check that engine switch is in Start position. |
| No engine speed during crank | The magnetic pickup must be correctly adjusted and operating. |
|
|
|
Engine will not crank (electric start) | Dead battery. | Remove battery and trickle charge or replace with new battery. |
|
| Never Jump Start. |
| Emergency Stop LED is ON | Reset controller after an Emergency Stop. |
|
|
|
Engine starts but will not run smoothly | Fuel or ignition problem | Refer to engine manual. |
|
|
|
Engine overheats | Excessive load | Remove one or more electrical loads. |
| Debris or dirt buildup on engine | Remove debris. Clean engine surfaces to allow cooling. |
|
|
|
No output voltage | Ciruit Breaker tripped or failed. | Reset circuit breaker or replace if required. |
| Internal failure of Alternator | Return to factory for repair. |
|
|
|
Output voltage varies | Irregular speed (fixed speed mode) | Check engine for malfunction or load for fluctuation |
| Fluctuating speed (fixed speed mode) | Stabilize load. The addition of a lamp load (resistance load) may |
|
| compensate partially for load changes caused by intermittent motor |
|
| operation. Do not overload. |
| Loose terminal or load connections | Verify all connections and terminal tighness. |
Low output voltage | Low engine speed |
| Excessive load |
| High resistance connections - |
| connections will be warm or hot |
| Internal failure of Alternator |
| Low power factor |
Verify engine RPM.
Check engine for malfunction or system for overload. Reduce load. Verify all connections and terminal tighness.
Return to factory for repair.
Reduce inductive (motor) load. Some AC motors use about the same current regardless of load. Do not use motors of greater horsepower rating than is necessary to move the mechanical load.
High output voltage | Excessive speed (fixed speed mode) | Check engine for malfunction. Verify engine RPM. |
Electrical shock when frame is touched | Static charge. | Ground generator frame at local reference ground (see Section 3). |
| Grounded armature or field coil. | Return to factory for repair |
|
|
|
Mechanical noise | Internal failure of Alternator | Return to factory for repair |
| Loose or misaligned coupling | Tighten; align coupling and alternator shaft to engine shaft. |
5‐2 Troubleshooting and Maintenance | MN2408 |