Snmp
Page
FCC Requirements
Safety Requirements
Warranty
Warranty Product Returns
Page
Contents Access Bank II Snmp
Chapter Electrical Installation
Chapter Physical Installation
Remote Monitor
Chapter Initialization Basic Configuration
Chapter Battery Reversal FXS & Dial Pulse Origination Card
Chapter FXS-ID Configuration
Chapter Channel FXO & Dial Pulse Termination Card
Chapter Wire E&M/TO Configuration
Xvi
Chapter Diagnostics Troubleshooting
Chapter Snmp Management & Command Line Interface
Chapter Maintenance
Xviii
Xix
Page
General System Overview
About This Chapter
Software Programmable Functions
Features, Functions, and Options
Standard Features
Dual T1/CSU Network Interfaces
2 RS-232 Data Port
Analog Line Interfaces FXS, & FXO, and 4-Wire E&M
Digital Data Ports
1 V.35 DCE Port
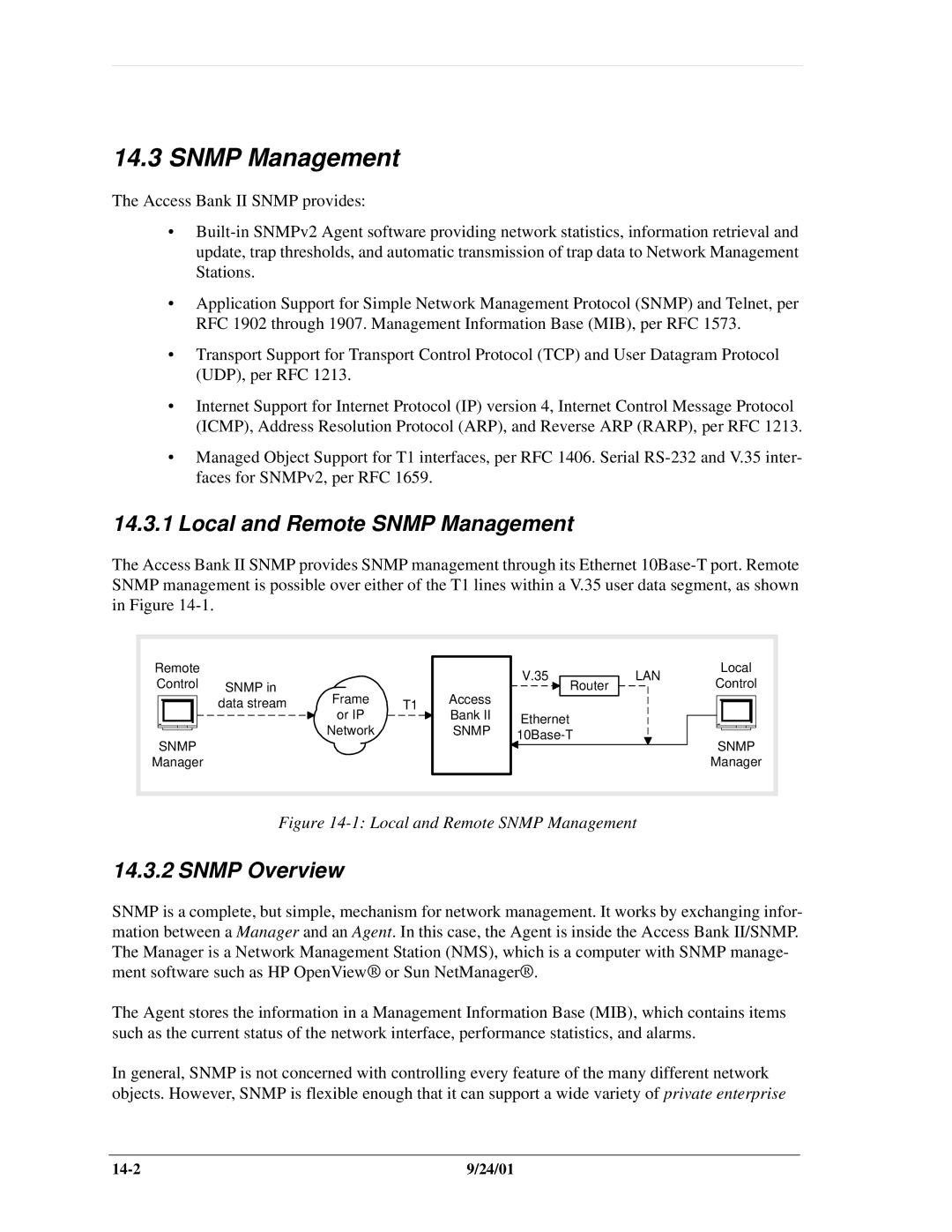
Local and Remote Network Management
Local/Remote Mode Selection
Snmp Management
Local and Remote Snmp Management
Snmp Overview
Local and Remote CLI Management
Command Line Interface
Local and Remote Telnet CLI Management
Windows-Based GUI Management Software
Local and Remote GUI Management
Design Philosophy
Product Description
Physical Characteristics
Control Panel Interface Connectors
LED Test and Status Indicators
Control Panel DIP Switches
Access Bank II Snmp Top Cover Installation Guide
Technical Specifications
Line Codes
T1-to-T1 Delay
T1 Channel Service Units CSUs
Dual T1 Network Line Interfaces
2 RS-232 Remote Management/Data Port
Analog Line Interfaces
FXS Voice Card
1 V.35 Serial Port
12 4-Wire E&M/TO Voice Card
11 FXO/DPT Voice Card
Network Management
Alarms
Control Panel I/O Connectors
Standards Compliance
Power
Physical Dimensions
Environmental
Installation
24/01
Installation Check List
Physical Installation
Description
Access Bank II Snmp Packing Materials List
Chassis Mounting
Rack Mounting
Wall Mounting
Surface Mounting
Rack Mounting with Brackets Shipped with Unit
Mounting with Heavy-Duty Brackets
Wall-Mounting the Access Bank II Snmp
Mounting the Power Converter
2Rack Mounting on a 19 Rack Using Small Brackets
Rack Mounting on a 19 Rack Using Heavy-Duty Brackets
4Optional Heavy Duty Brackets
24/01
Electrical Installation
DCE-MF
Installing Cables and Adapters
1 RJ-48C Jacks for T1 Span 1 and Span
Snmp Connector
3 V.35 DCE Data Port Connector
DC Power Connector Input
Tip & Ring Jack female
Connecting the Voice Circuits
Connecting the Dual T1 Lines
Customer Premises Installations
T1 Line Interface on RJ-48C-T1 Modular 8-Pin Jack
V.35 DCE Data Port Connections
Abam 600 T1 Cable
3 24 AWG Twisted-Pair
Pin Assignments for CAC V.35 Data Cables
Micro-D Signal Winchester Paired Pin male Signals + Shield
Access Bank II Snmp V.35 DCE Data Port Connections
Access Bank II Snmp V.35 DCE Port female
1 RS-232 DCE Management Cable Local Management Cable
RS-232 Management
CAC Local Management Adapter Cable Pin Assignments
Null Modem Adapter
7Null Modem Adapter Pin Assignments
Straight Adapter
Connecting the Power and Ground
Power Connector Pinout Assignments
CAC Straight Adapter Pin Assignments
24/01
Connecting to the Access Bank
Initialization Basic Configuration
AB-II Snmp in an Example Network
Configuring the Access Bank
Check the system clocking configuration
Check the time information
Check the configuration of T1 port #1
To set Snmp configurations, if required examples given below
Nicholas Jones, 203-555-8897, PIN #33345
24/01
Remote Monitor
Remote Monitor Software Program
Message Traffic
Overview
Hardware Requirements
Online Help
Remote Monitor Screen Hierarchy
Initialization for Basic Operation in the Remote Mode
FXS-ID Voice Card
FXS-ID Configuration
Signaling Types
FXO Switch to AB2 FXS A/B Signaling
Wink-Start to Loop-Start or Ground-Start
Wink Delay
Setting the FXS Transmit and Receive Levels
FXS Transmit and Receive Level Option Settings
Option Switch Signaling Number
FXS Signaling Summary
Option Switches A, B, and C
Setting the FXS Signaling Options
FXS Signaling Options
FXS Signaling Option Descriptions
Option 2. Wink-Start to Ground-Start Conversion
Option 3. E&M Immediate-Start-to-Loop-Start Conversion
Option 4. E&M Immediate-Start-to-Ground-Start Conversion
Option 7. Customized Signaling
TP Busy/Idle Switch
FXS Voice Channel Monitoring and Testing
FXS Backplate LEDs
FXS Backplate Switches
Self Test Loopbacks
Busying Out Individual FXS Channels
FXS Voice Channel Monitoring and Testing
24/01
Description of the BRFXS/DPO Card
Battery Reversal FXS & Dial Pulse Origination Card
Overview of Operation
DPO
BRFXS/DPO Applications
Transmit and Receive Attenuation Switch Values
Setting the Transmit and Receive Levels
Brfxs V
OFF
BRFXS/DPO Configuration Settings
BRFXS/DPO Back Plate LEDs
Busying Out Individual BRFXS/DPO Channels
Setting Brfxs and DPO
Battery Reversal FXS Loop-Start
BRFXS/DPO Voice Channel Monitoring and Testing
Self Test Loopbacks
24/01
Description of the FXO Card
Channel FXO & Dial Pulse Termination Card
Termination Options and Switch Settings for the FXO/DPT
Termination Options
Foreign Exchange Office FXO Termination
Termination Options
Dial Pulse Termination DPT
Channel Attenuation Options
FXO V
10-6
Functional Description
11.2 4-Wire E&M/TO Voice Card
Physical Description
Typical Applications
Signaling Conventions
11.4 E&M Signaling Conventions
48V
Detector-Driver Functions
5E&M Signaling Type
Programming E&M Signaling Types
Jumper Switch Settings
Jumper Connections by Type and Mode
4-Wire E&M Signaling Options
Detector Configuration
Normal and Tandem Cables
Configuring Signaling Types and Trunk Processing
E&M T1 Signaling
Normal and Tandem Mode Cables for 4-wire E&M/TO Card
Transmit Analog-to-Digital Gain
TP Busy/Idle Switch
Setting Transmit and Receive Gain
4-Position DIP Switch Settings
11.13 E&M Voice Channel Monitoring
11.14 E&M Normal mode cable
Call Progress LED Indicators
Receive Digital-to-Analog Gain
Markings
Common Connector
Telco Connectors
Cable Type
E&M Normal Mode Cable
11.15 E&M Tandem Mode Cable
E&M Tandem Mode Cable
Normal Mode Telco Connector a Telco Connector B
7Part 1 Connector Pinouts for Cable P/N
Part 2 Connector Pinouts for Cable P/N
Part 1 Connector Pinouts for Cable P/N
11-17
11-18
Diagnostic Switches
Diagnostics Troubleshooting
Self Test 1
Local Mode OFF = No Test Tone, on = Ringback Tone
Voice Channel LED is RED during Self Test
Self Test Fault Indications
Card Self Test Signaling States
Card Self Test
Standard Digital Milliwatt Signal
12.5 1 kHz Digital Milliwatt Test Signal
Remote Mode Ringback Tone or 1 Digital Milliwatt
Local Mode No Network Loopback or Network Loopback Enabled
Ansi T1.403 Remote Payload Loopback
Remote Mode Remote T1 Line or Payload Loopbacks
Ansi T1.403 Remote T1 LLB
Illustrations of Loops and Self-Tests
Loopback Legend
Self-Test
Equipment Loopback Payload
Equipment Loopback
DS-1 Network Loopback Payload
12.9.4 DS-1 Network Loopback
Sending DS-1 CSU Loopback
Receiving DS-1 CSU Loopback
12.9.9 V.35 Equipment Loopback
Sending DS-1 Bert Pattern
Sending V.54 Loopback
12.9.10 V.35 Network Loopback
Disabling an External Alarm
Receiving V.54 Loopback
Sending FX Ring or Tone
T1 Line Status LEDs for T1 Span 1 and T1Span
50-Pin Tip & Ring Jack
Fault Isolation Procedures
T1 Test LEDs for T1 Span 1
V.35 Status LED
Control Panel LED Indications
All Voice Channel LEDs flash RED
Other Fault Indications
Back Plate Indications
Voice Channel LED is RED during a Self Test
Access Bank II Snmp Shuts Down for No Apparent Reason
12-18
Maintenance
Replacing a Voice Card
Replacing the Controller Card
Accessing the Voice Cards
Removing the Chassis Tray
Replacing the Controller Card
13-6
Local/Remote Mode Selection
Snmp Management Command Line Interface
Snmp Management
Local and Remote Snmp Management
Snmp Overview
Protocols
Protocol Hierarchy Used In Access Bank II Snmp
Supported Management Information Bases
Commands
Management Information Bases
Statistics
Traps
Command Line Interface CLI
Maintenance
Local and Remote CLI Management
14.4.2 RS-232 CLI Operation
Command Line Interface CLI
Context Sensitive Help
Context sensitive help, type ? at any time
CommandLineInterfaceHelp.Forimmediate
Code ipaddr path .Load app code path from Tftp server
DPT
DSX
Ring
Disable any Current Loopback General Loopback Usage
Display/Set Optional Data RS-232 Port
Echo Echo Telnet output on serial line Off Disable Enable
14.4.4.1 aco
Configuration Commands
Alarms
Boot
14.4.4.3 aps
Config
14.4.4.5 clk
Connections
Date
Craft
14.4.4.10dni
14.4.4.11dialout
14.4.4.12 ds1
Event
Exit
14.4.4.15 ip
Make
Kill
Loop
14.4.4.18 mac
Password
Name
Ping
Telnet
14.4.4.23 rs232
Screen height
Snmp
Trap
Status Commands
14.4.4.30
14.4.5.1equipment
14.4.5.2 log
Statistics
Status
14-30
Glossary
Channel Service Unit See DSU/CSU
ESF Extended Superframe Format
PBX Private Branch Exchange Performance Report Message PRM
Trunk Processing TP