DMC-2x00
By Galil Motion Control, Inc
Using This Manual
Contents
Connecting Hardware
Communication
Iv Contents DMC-2X00
Application Programming
Troubleshooting 130
Contents y
Index 210
Overview
Specifications
Electrical Specifications
Mechanical Specifications
DMC- 2000 Family Part Number Definition
Environmental Specifications
Equipment Maintenance
Standard Servo Motor with +/- 10 Volt Command Signal
Overview of Motor Types
Stepper Motor with Step and Direction Signals
Amplifiers in Current Mode
Amplifiers in Velocity Mode
Overview of Amplifiers
DMC-2x00 Functional Elements
Microcomputer Section
Motor Interface
Communication
General I/O
System Elements
Motor
Amplifier Driver
Watch Dog Timer
Encoder
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Getting Started
DMC-2000 Daughter Board
Outline of the DMC-2000 Daughter Board
DMC-2200 Daughter Board
3B Outline of the DMC-2200 Daughter Board
Elements You Need
CABLE-USB-2M CABLE-USB-3M
Recommended System Elements of DMC-2100/DMC-2200
Installing the DMC-2x00
Determine Overall Motor Configuration
Standard Servo Motor Operation
Install Jumpers on the DMC-2x00
Master Reset and Upgrade Jumpers
Sinusoidal Commutation
Stepper Motor Operation
Configure DIP switches on the DMC-2000
Switch 4, 5 and 6 Main Serial Port Baud Rate
Switch 10 USB
Configure DIP switches on the DMC-2100
Configure DIP switches on the DMC-2200
Install the Communications Software
Connect AC Power to the Controller
Establish Communications with Galil Software
Communicating through the Main Serial Communications Port
Communicating through the Universal Serial Bus USB
Communicating through the Ethernet
Sending Test Commands to the Terminal
Determine the Axes to be Used for Sinusoidal Commutation
Make Connections to Amplifier and Encoder
DMC-2X00
Connect Standard Servo Motors
Inverting the Loop Polarity
BGA CR
ICM-2900
Example Sinusoidal Commutation Configuration using a DMC
Connect Sinusoidal Commutation Motors
Getting Started DMC-2X00
SHA
Connect Step Motors
Tune the Servo System
Design Examples
System Set-up
InstructionInterpretation
Instruction Interpretation
Profiled Move
Multiple Axes
Independent Moves
Position Interrogation
Absolute Position
Velocity Control
Operation in the Buffer Mode
Using the On-Board Editor
Operation Under Torque Limit
Interrogation
Motion Programs with Loops
Motion Programs with Trippoints
Line # Instruction Interpretation
Control Variables
Linear Interpolation
XQ #B
AMA
Circular Interpolation
LM ABC
BGS
VM AB
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Using Optoisolated Inputs
Limit Switch Input
Overview
Home Switch Input
Abort Input
Wiring the Opto-Isolated Inputs
Reset Input
Uncommitted Digital Inputs
Opto-Isolation Common Point
Using an Isolated Power Supply
Optoisolated Inputs
Analog Inputs
Amplifier Interface
Bypassing the Opto-Isolation
TTL Inputs
Auxiliary Encoder Inputs
TTL Outputs
General Use Outputs
Output Compare
Error Output
Extended I/O of the DMC-2x00 Controller
Interfacing to Grayhill or OPTO-22 G4PB24
Introduction
RS232 Ports
RS232 Main Port P1 Dataterm
RS232 Auxiliary Port P2 Dataset
RS-232 Configuration
RS422 Main Port P1
RS422 Auxiliary Port P2
Baud Rate Selection
Daisy-Chaining DMC-2000 only
Address
Ethernet Configuration DMC-2100/2200 only
Command Interpretation
Communication Protocols
Addressing
LED
DMC-2X00
Communicating with Multiple Devices
Using Third Party Software
Multicasting
Data Record
Data Record Map
DMC-2X00
Header Information Byte 0, 1 of Header
BIT
Axis Switch Information 1 Byte
Bytes 2, 3 of Header
General Status Information 1 Byte
Axis Status Information 2 Byte
Controller Response to Commands
QZ Command
Unsolicited Messages Generated by Controller
Galil Software Tools and Libraries
Command Syntax Ascii
Important All DMC-2x00 commands are sent in upper case
BG Abcd
BG Abcdefgh
BG D
BG S
Command Syntax Binary
Header Format
Binary Command Table
Datafields Format
Example
LE, VE
Controller Response to Data
Interrogation Commands
Summary of Interrogation Commands
Interrogating Current Commanded Values
Interrogating the Controller
Command Summary
=TPA
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Example Application Mode of Motion Commands
Independent Axis Positioning
VS,VA,VD
GA, GD
GP, GR
Command Summary Independent Axis
Operand Summary Independent Axis
Examples
Absolute Position Movement
Multiple Move Sequence
Position Tracking
20000
15000 10000
5000 Time ms 100
Command Description PT1
Example Motion
Example
Motion
Position vs. Time msec Motion
Velocity vs.Time Motion
Trip Points
Velocity cts/sec vs. Time msec with IT Motion
Command Summary Position Tracking Mode
Command Summary Jogging
Independent Jogging
Jog in X only
Joystick Jogging
AS a
#JOY
Linear Interpolation Mode
Specifying the Coordinate Plane
Specifying Linear Segments
Additional Commands
Specifying Vector Speed for Each Segment
Changing Feed Rate
#ALT
Command Summary Linear Interpolation
Operand Summary Linear Interpolation
Linear Interpolation Motion
Linear Move
LM CD
Position D
Vector Mode Linear and Circular Interpolation Motion
Multiple Moves
Specifying Vector Segments
Compensating for Differences in Encoder Resolution
Command Summary Coordinated Motion Sequence
Trippoints
Tangent Motion
Operand Summary Coordinated Motion Sequence
Tangent Axis
Operand
Coordinated Motion
BG ABC
AM ABC
SB0
Electronic Gearing
Ramped Gearing
Velocity cts/sec vs. Time msec Ramped Gearing
Command Summary Electronic Gearing
Electronic Gearing Over a Specified Interval
MO Z
GA Z, Z
Gantry Mode
Simple Master/Slave
Electronic Gearing
Electronic Cam
GA,A
DMC-2X00
3000 2250 1500 2000 4000 6000 Master a
Command Summary Electronic CAM
Command Description
Operand Summary Electronic CAM
Electronic CAM
Contour Mode
Specifying Contour Segments
336 288 240 192 Time ms
CMA
DT0CD0
Command Summary Contour Mode
Command Description CM Abcdefgh
General Velocity Profiles
Generating an Array
Contour Mode
#POINTS
Teach Record and Play-Back
Record and Playback Example
Virtual Axis
Ecam master example
Sinusoidal Motion Example
Monitoring Generated Pulses vs. Commanded Pulses
Stepper Motor Operation
Specifying Stepper Motor Operation
Stepper Motor Smoothing
Using an Encoder with Stepper Motors
Command Summary Stepper Motor Operation
Motion Complete Trip point
Stepper Position Maintenance Mode SPM
Operand Summary Stepper Motor Operation
Error Limit
Example SPM Mode Setup
Correction
SHX
Example Error Correction
#MOTION
Example Friction Correction
Dual Loop Auxiliary Encoder
Additional Commands for the Auxiliary Encoder
Backlash Compensation
Continuous Dual Loop
= Main Encoder Second Encoder
Motion Smoothing
Sampled Dual Loop
#DUALOOP
DE0
Using the IT and VT Commands
Using the KS Command Step Motor Smoothing
Trapezoidal velocity and smooth velocity profiles
Homing
Home Sensor Home Switch
Command Summary Homing Operation
High Speed Position Capture The Latch Function
Operand Summary Homing Operation
Input Function
#LATCH
AL B
#WAIT
JP #WAIT,ALB=1
Using the DOS Editor to Enter Programs DMC-2000 only
Application Programming
Edit Mode Commands
ED #BEGIN
Using Labels in Programs
Program Format
Special Labels
#START
No Command
Commenting Programs
REM Command
Executing Programs Multitasking
REM Half Circle Motion VP 0,3000 REM TOP Line
Trace Commands DMC-2100/2200 only
Debugging Programs
Error Code Command
Stop Code Command
RAM Memory Interrogation Commands
Program Flow Commands
Event Triggers & Trippoints
Command Function
DMC-2x00 Event Triggers
AS a B C D E F G H
Example- Multiple Move Sequence
Example- Set Output after Distance
Example- Repetitive Position Trigger
Example Start Motion on Input
Example Set Output when At Speed
Example Change Speed along Vector Path
Example- Define Output Waveform Using AT
Example Multiple Move with Wait
Conditional Jumps
Command Format JP and JS
Logical operators
Conditional Statements
Multiple Conditional Statements
Examples
If, Else, and Endif
JP#A
#BEGIN
Using the if and Endif Commands
Using the Else Command
Command Format IF, Else and Endif
Nesting if Conditional Statements
Subroutines
Stack Manipulation
Auto-Start Routine
Example Limit Switch
Automatic Subroutines for Monitoring Conditions
Example Position Error
Example Motion Complete Timeout
Example Input Interrupt
Example Command Error
Example Command Error w/Multitasking
Example Communication Interrupt
PAA=0
Example Ethernet Communication Error
Mathematical and Functional Expressions
Mathematical Operators
Bit-Wise Operators
Operator Function
Response from command MG len6 S4
Variables
Functions
Programmable Variables
Assigning Values to Variables
Assigning Variable Values to Controller Parameters
Example Using Variables for Joystick
Operands
Displaying the value of variables at the terminal
Special Operands Keywords
Arrays
Defining Arrays
Assignment of Array Entries
Time
Using a Variable to Address Array Elements
Uploading and Downloading Arrays to On Board Memory
Automatic Data Capture into Arrays
Command Summary Automatic Data Capture
Data Types for Recording
Operand Summary Automatic Data Capture
Example Recording into an Array
Input of Data Numeric and String
Deallocating Array Space
Input of Data
Example- Inputting Numeric Data
Operator Data Entry Mode
Keyword Function
Using Communication Interrupt
Output of Data Numeric and String
Inputting String Variables
Sending Messages
Specifying the Port for Messages
Formatting Messages
Using the MG Command to Configure Terminals
Summary of Message Functions
Displaying Variables and Arrays
Example Printing a Variable and an Array element
0000000009
LZ0
Local Formatting of Response of Interrogation Commands
Formatting Variables and Array Elements
Local Formatting of Variables
LZ1
Hardware I/O
Converting to User Units
Digital Outputs
Alph
Example- Set Bit and Clear Bit
Example- Output Bit
Example- Output Port
Example Turn on output after move
Example Using Inputs to control program flow
Example Start Motion on Switch
Input Interrupt Function
AI 1BGA
Analog Inputs
Example Position Follower Point-to-Point
TP AB
ST AB
Configuring the I/O of the DMC-2x00
Example Position Follower Continuous Move
PA VP
#CONT
Accessing Extended I/O
Saving the State of the Outputs in Non-Volatile Memory
Bit I/O Block Binary Decimal Value for Representation
Argument Blocks Bits Description
Wire Cutter
Example Applications
Interfacing to Grayhill or OPTO-22 G4PB24
Table Controller
JP #A
AMC
BGC AMC
BGS AMS
Speed Control by Joystick
Position Control by Joystick
Backlash Compensation by Sampled Dual-Loop
BGA JP #B
This page Left Blank Intentionally
Hardware Protection
Output Protection Lines
Software Protection
Input Protection Lines
Off-On-Error
Automatic Error Routine
Programmable Position Limits
#AJP #AEN
Limit Switch Routine
Troubleshooting
Installation
Communication
Stability
Operation
Theory of Operation
Level
Operation of Closed-Loop Systems
Velocity and Position Profiles
System Modeling
Functional Elements of a Motion Control System
Motor-Amplifier
Voltage Drive
Current Drive
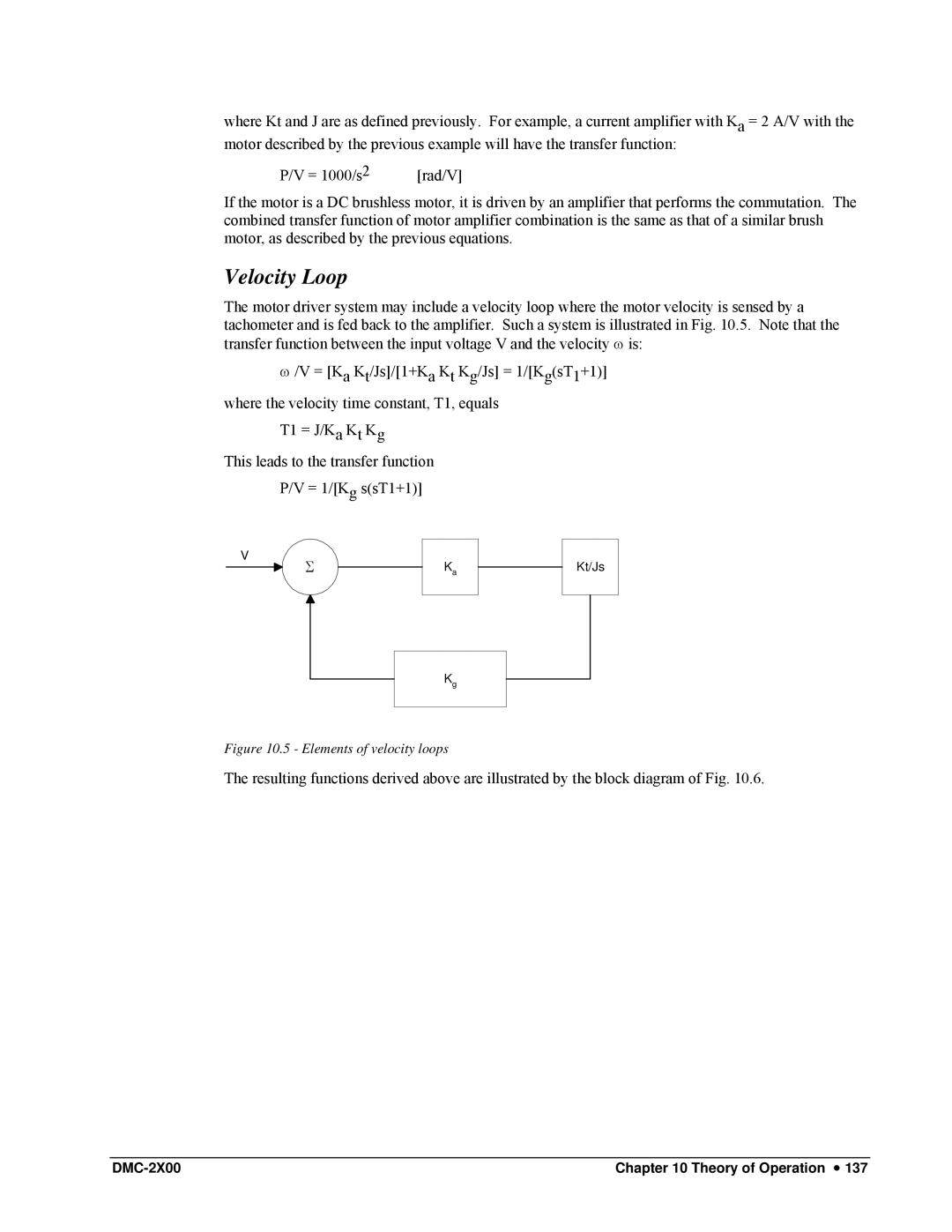
Velocity Loop
Elements of velocity loops
Voltage Source
DAC
Digital Filter
ZOH
System Analysis
Magnitude 200 2000 Rad/s
System Design and Compensation
Analytical Method
Theory of Operation DMC-2X00
Equivalent Filter Form
Electrical Specifications
Servo Control
Stepper Control
Input / Output
Performance Specifications
Power
Minimum Servo Loop Update Time
Normal
Fast Update Rate Mode
Connectors for DMC-2x00 Main Board
DMC-2x00 Axes A-D High Density Connector
DMC-2x00 Axes E-H High Density Connector
DMC-2x00 Auxiliary Encoder 36 Pin High Density Connector
DMC-2x00 Extended I/O 80 Pin High Density Connector
+5V
Pin Signal
RS-232-Main Port
RS-232-Auxiliary Port
USB USB Out
Standard RS-232 Specifications
Pin Serial Connector Male, D-type
Cable Connections for DMC-2x00
Ethernet
DMC-2x00 Serial Cable Specifications
Pin Male computer Pin female controller
Pin Female Computer Pin Female Controller
Pin Male terminal Pin male controller
Pin Female terminal Pin Male Controller
Pin-Out Description for DMC-2x00
Outputs
Inputs
Appendices DMC-2X00
Jumper Description for DMC-2x00
Jumper Label
Function If jumpered
Dimensions for DMC-2x00
Accessories and Options
DMCWIN16 DMCWIN32 SETUP16 SETUP32 KIT
ICM-2900 Interconnect Module
Description
Block 4 PIN Label Description
Error
Pwmx
Mocmdy
Signy
Reset
IN8
Xlatch
Ylatch
+MAZ
MAZ
+MBZ
MBZ
ICM-2900 Drawing
ICM
ICM-2908 Interconnect Module
ICM-2908 Drawing
ICM-2908
PCB Layout of the ICM-2900
Features
ISO OUT Power Error Reset CMP Mocmdw
ICM-1900 Interconnect Module
Terminal Label
DMC-2X00
100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107
AMP-19x0 Mating Power Amplifiers
ICM-1900 Drawing
MBW +INW
Specifications
Opto-Isolated Outputs for ICM-2900 / ICM-1900 / AMP
Standard Opto-Isolation and High Current Opto-isolation
Configuring the Amplifier Enable for ICM-2900 / ICM
Changing the Amplifier Enable Voltage Level
Laen Option
DMC-2000 ICM-1900 / ICM-2900
IOM-1964 Opto-Isolation Module for Extended I/O
Overview
Configuring Hardware Banks
Figure A-7
Input Circuit
High Power Digital Outputs
Figure A-10
Standard Digital Outputs
Figure A-12
Digital Inputs
Figure A-14
High Power Digital Outputs
Relevant DMC Commands
Standard Digital Outputs
Screw Terminal Listing
DMC-2X00
PWROUT32
PWROUT31
PWROUT30
PWROUT29
Connectors
CB-50-100 Adapter Board
Appendices DMC-2X00
JC6 50 PIN IDC J9 100 PIN High Density Connector
CB-50-100 Drawing
JC8 JC6
CB-50-80 Adapter Board
Figure A-16
JC8
JC6
CB-50-80 Drawing
CB-50-80 Outline
CB-50-80 Layout
TERM-1500 Operator Terminal
Figure A-19
Specifications Hand-Held
Figure A-20
Specifications Panel Mount
Keypad Maps Hand-Held
Single Key Output
Shift Key Output
Escape Commands
Cursor Movement Commands
Keypad Map Panel Mount 6 columns x 5 rows
Configuration
Default Configuration
Default Function Keys
Input/Output of Data DMC-2x00 Commands
Function Keys
Pin Modular Connector
Pin D Adaptor Male For P2
Ordering Information
Coordinated Motion Mathematical Analysis
Vs = Vx 2 + Vy
Lk = Xk 2 + Yk
Velocity
Example- Communicating with OPTO-22 SNAP-B3000
#CFGDOUT
MODULE=2
CFGVALUE=$180
NUMOFIO=4
Appendices DMC-2X00
DMC-2x00/DMC-1500 Comparison
DMC-2x00 DMC-1500
List of Other Publications
Training Seminars
Warranty
Contacting Us
Index
Limswi
PID
Poserr