Configuring Firewall Settings
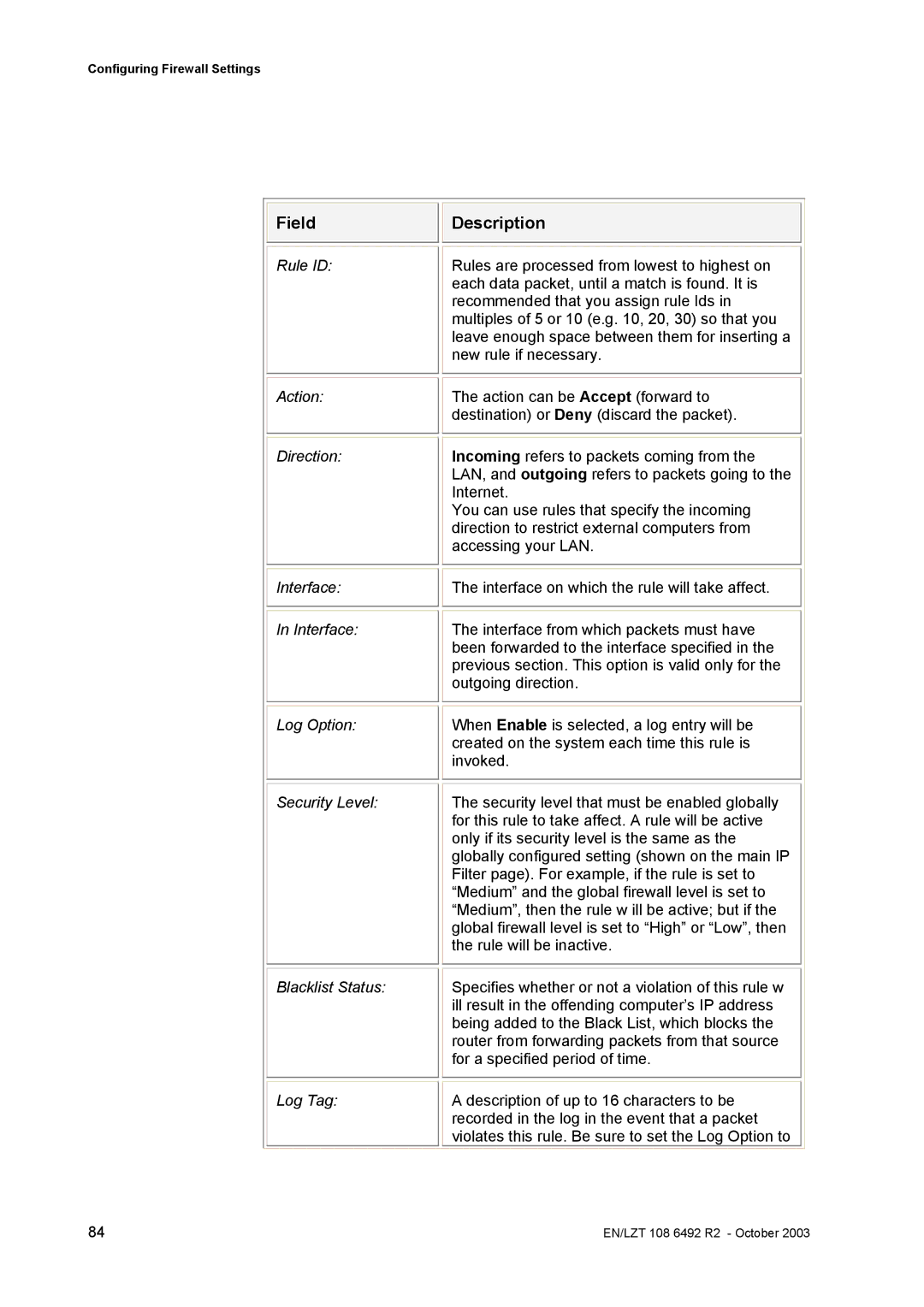
Field
Rule ID:
Action:
Direction:
Interface:
In Interface:
Log Option:
Security Level:
Blacklist Status:
Log Tag:
![]()
![]() Description
Description
Rules are processed from lowest to highest on each data packet, until a match is found. It is recommended that you assign rule Ids in multiples of 5 or 10 (e.g. 10, 20, 30) so that you leave enough space between them for inserting a new rule if necessary.
The action can be Accept (forward to destination) or Deny (discard the packet).
Incoming refers to packets coming from the LAN, and outgoing refers to packets going to the Internet.
You can use rules that specify the incoming direction to restrict external computers from accessing your LAN.
The interface on which the rule will take affect.
The interface from which packets must have been forwarded to the interface specified in the previous section. This option is valid only for the outgoing direction.
When Enable is selected, a log entry will be created on the system each time this rule is invoked.
The security level that must be enabled globally for this rule to take affect. A rule will be active only if its security level is the same as the globally configured setting (shown on the main IP Filter page). For example, if the rule is set to “Medium” and the global firewall level is set to “Medium”, then the rule w ill be active; but if the global firewall level is set to “High” or “Low”, then the rule will be inactive.
Specifies whether or not a violation of this rule w ill result in the offending computer’s IP address being added to the Black List, which blocks the router from forwarding packets from that source for a specified period of time.
A description of up to 16 characters to be recorded in the log in the event that a packet violates this rule. Be sure to set the Log Option to
84 | EN/LZT 108 6492 R2 - October 2003 |