5.1.1 Out-of-band management
It is common to provide a (physically) separate management interface for all of the devices and to carry only management traffic. This is referred to as
sometimes a separate Ethernet connection (path 1) or a whole different physical connection such as the console port (path 2).
Management Module (Path 1)
The IBM Eserver BladeCenter comes with at least one Management Module. The Management Module supports an external Ethernet interface, which is used to manage the
Blade servers, Ethernet switches, and the Management Module itself. Within the
IBM Eserver BladeCenter, management traffic flows through a different bus, the I2C bus, as shown in the Figure
On the Nortel GbESM, the Ethernet management (MGT1 and MGT2) ports which connect the switch to the Management Module are placed in VLAN 4095. It is not possible to change this. It is also not possible to reach VLAN 4095 from any of the other internal or external ports on the switch. This is a deliberate design constraint. It is intended to enforce isolation of the Management Module network (VLAN) from any other networks (VLANs) that are configured on the switch. This implies that the Blade servers should not be on the same VLAN nor the same IP subnet as the Management Module. Placing the servers on the same subnet as the Management Module can have unexpected and undesirable results.
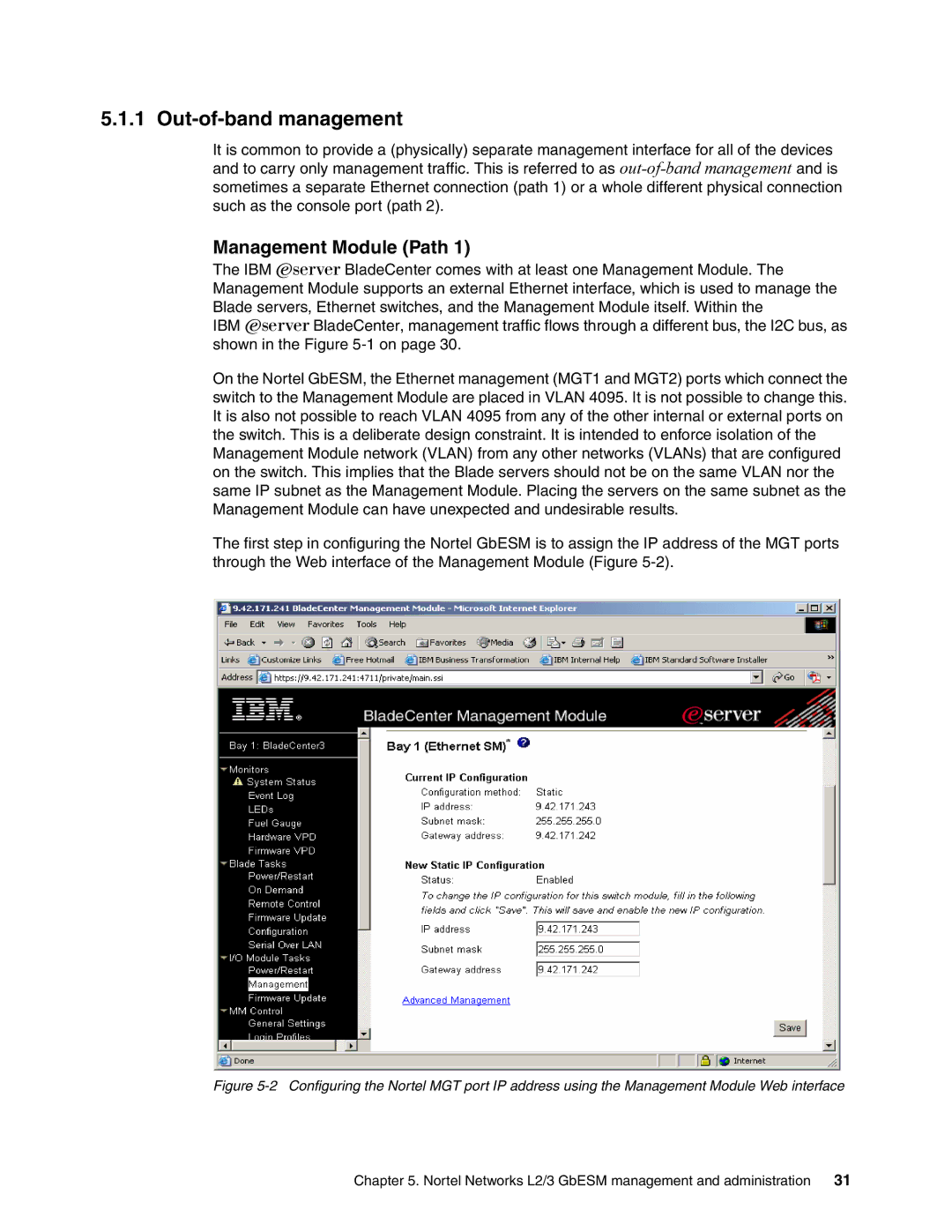
The first step in configuring the Nortel GbESM is to assign the IP address of the MGT ports through the Web interface of the Management Module (Figure
Figure 5-2 Configuring the Nortel MGT port IP address using the Management Module Web interface
Chapter 5. Nortel Networks L2/3 GbESM management and administration 31