Product Overview
Overview
Bit Timer/Counter
Pins
Bit Basic Timer
Watch Timer
Block Diagram
KS57C2308
INT1
INT4
INT0
INT2
Test signal input must be connected to V SS
Test
PIN Circuit Diagrams
Pin Circuit Type E P4, P5
General-Purpose Program Memory
Address Spaces
Overview
Vector Addresses
EMB ERB
GENERAL-PURPOSE Memory Areas
Vector Address Area
PC9 PC8 PC7 PC6 PC5 PC4 PC3 PC2 PC1 PC0
+ Programming TIP Defining Vectored Interrupts
+ Programming TIP Using the REF Look-Up Table
Instruction Reference Area
Data Memory RAM
Data Memory Addressing Modes
Memory Banks 0, 1,
F80H-FFFH
Working Registers
RMCL1 @HL,A Incs SMB
+ Programming TIP Clearing Data Memory Banks 0
Ramclr SMB
RMCL0 @HL,A Incs
Working Registers
Working Register Map
Working Register Banks
Paired Working Registers
Special-Purpose Working Registers
SRB
+ Programming TIP Selecting the Working Register Area
INT0 Push
Incs WX,EA YZ,EA POP
SP7 SP6 SP5 SP4
Stack Pointer SP
SP3 SP2 SP1
+ Programming TIP Initializing the Stack Pointer
Call Instructions
Push Operations
Push Instructions
Interrupt Routines
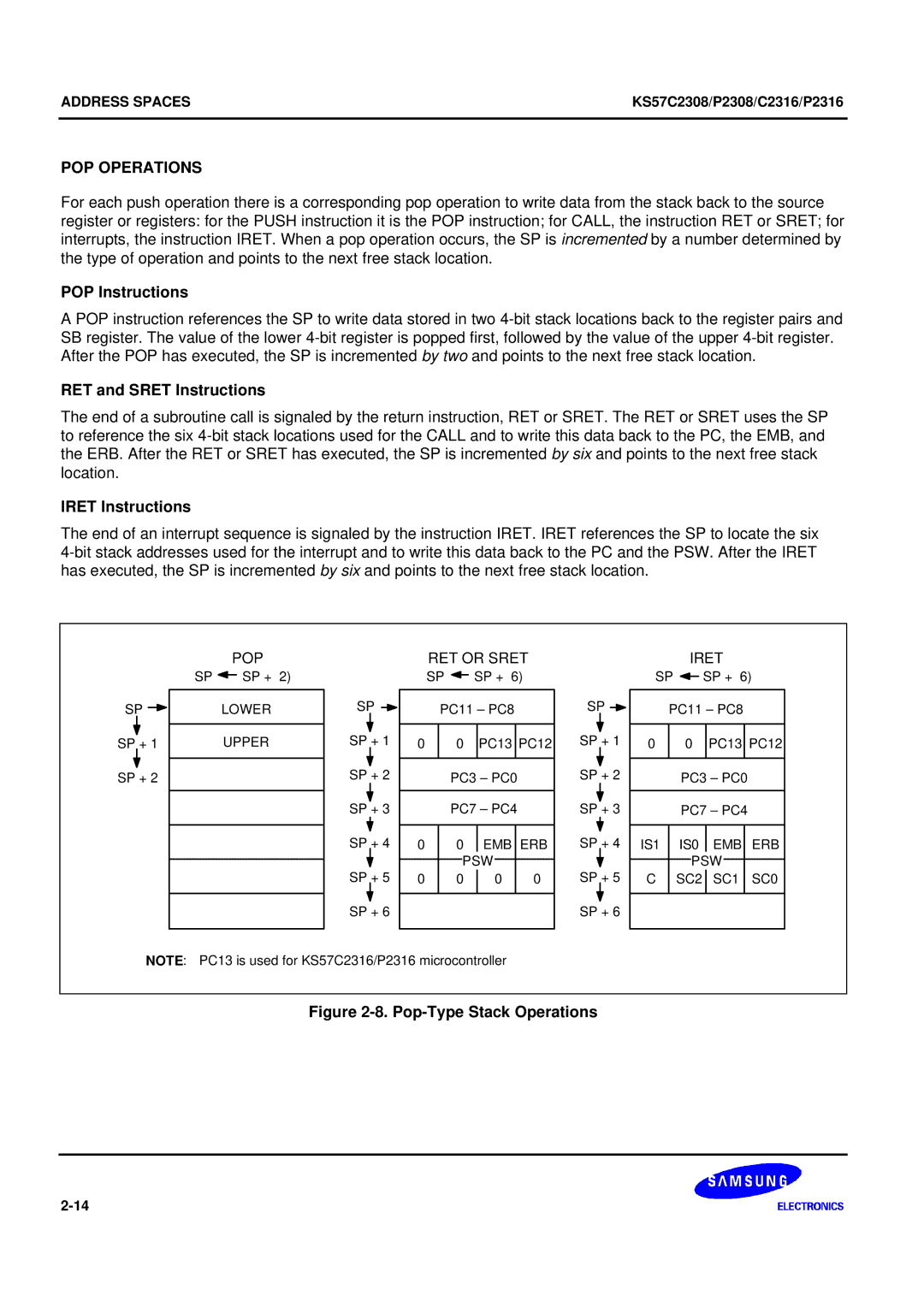
RET and Sret Instructions
POP Operations
POP Instructions
Iret Instructions
BSC Register Organization Name Address Bit
Program Counter PC
MSB LSB FB0H IS1 IS0 EMB ERB FB1H SC2 SC1 SC0
Interrupt Status Flags IS0, IS1
Interrupt Status Flag Bit Settings
IS1 IS0
+ Programming TIP Using the EMB Flag to Select Memory Banks
EMB Flag EMB
ERB Flag ERB
HL,EA
Carry Flag C
Skip Condition Flags SC2, SC1, SC0
Valid Carry Flag Manipulation Instructions Operation Type
ADC EA,HL
HL,#0AAH
Band
Address Spaces
Addressing Modes
RAM Address Structure
EMB and ERB Initialization Values
Reset Bitr EMB
+ Programming TIP Initializing the EMB and ERB Flags
EMB =
Enable Memory Bank Settings
EMB-Independent Addressing
Select Bank Register SB
Select Memory Bank SMB Instruction
BIT Addressing
Direct and Indirect Addressing
Bank Mapping
Bit Indirect Addressing
Adata EQU
@HL
@WL
Bdata EQU 8EH SMB
Cpse @HL
Bdata EQU
HL,#BDATA WX,#ADATA Comp @WL
Sret Decs Comp RET
Xchd @HL
Bit Indirect Addressing Example
HL,#BDATA WX,#ADATA Trans @WL
SMB HL,#BDATA WX,#ADATA Trans @WL
BDATA,EA
EA,P4
SMB ADATA,EA
Bdata EQU 8EH SMB EA,P4
HL,#ADATA EA,@HL
SMB HL,#ADATA EA,@HL
Memory MAP
MAP for Hardware Registers
I/O Map for Memory Bank Addressing Mode Register Bit
Fbah INT B IEW Irqw
FB7H Scmod
FB8H INT a IE4 IRQ4 IEB Irqb
Fbch INT C IET0 IRQT0
Register Descriptions
Register Description Format
Read/Write Bit Addressing Basic Timer Restart Bit
Bmod Basic Timer Mode Register
Bit Identifier
FD0H
Clmod Clock Output Mode Register
Clock Source and Frequency Selection Control Bits
Fbeh
IE0, 1, IRQ0, 1 INT0, 1 Interrupt Enable/Request Flags
IE1 IRQ1 IE0 IRQ0
Fbfh
IE2, IRQ2 INT2 Interrupt Enable/Request Flags
IE2 IRQ2
FB8H
IE4, IRQ4 INT4 Interrupt Enable/Request Flags
IEB, Irqb Intb Interrupt Enable/Request Flags
IE4 IRQ4 IEB Irqb
Fbdh
IES, Irqs Ints Interrupt Enable/Request Flags
Ints Interrupt Enable Flag
IES Irqs
Fbch
IET0, IRQT0 INTT0 Interrupt Enable/Request Flags
INTT0 Interrupt Enable Flag
IET0 IRQT0
Fbah
IEW, Irqw Intw Interrupt Enable/Request Flags
Intw Interrupt Enable Flag
IEW Irqw
External Interrupt Mode Control Bits
IMOD0 External Interrupt 0 INT0 Mode Register
FB4H
IMOD1.0
IMOD1 External Interrupt 1 INT1 Mode Register
FB5H
External Interrupt 1 Edge Detection Control Bit
IMOD2.2 IMOD2.1 IMOD2.0
IMOD2 External Interrupt 2 INT2 Mode Register
FB6H
External Interrupt 2 Edge Detection Selection Bit
FB2H
Interrupt Master Enable Bit
IPR Interrupt Priority Register
IME
F8EH
LCD Clock Output Disable/Enable Bit
Lcon LCD Output Control Register
Read/Write Bit Addressing LCD Bias Selection Bit
LCD Clock Lcdck Frequency Selection Bits
Lmod LCD Mode Register
F8DH, F8CH
Duty and Bias Selection for LCD Display
FB3H
Pcon Power Control Register
Read/Write Bit Addressing CPU Operating Mode Control Bits
CPU Clock Frequency Selection Bits
PMG1 Port I/O Mode Flags Group 1 Port 3
FE9H, FE8H
FEDH, Fech
PMG2 Port I/O Mode Flags Group 2 Port 2, 4, 5,
PM7 PM5 PM4 PM2
PNE N-Channel Open-Drain Mode Register
FD7H, FD6H
FB1H, FB0H
PSW Program Status Word
SC2-SC0 SC1 IS1 IS0 EMB ERB
FDDH, Fdch
Pumod Pull-Up Resistor Mode Register
PUR7 PUR6 PUR5 PUR4 PUR3 PUR2 PUR1 PUR0
FB7H
Scmod System Clock Mode Control Register
1Bit
Smod Serial I/O Mode Register
FE1H, FE0H
Enable/Disable Timer/Counter 0 Bit
TMOD0 Timer/Counter 0 Mode Register F91H, F90H
Timer/Counter 0 Input Clock Selection Bits
Clear Counter and Resume Counting Control Bit
TOE0
TOE Timer Output Enable Flag Register
Timer/Counter 0 Output Enable Flag
Bit3
F9AH
Wdflag Watchdog Timer Counter Clear Flag Register
Watchdog Timer Counter Clear Flag
Wdtcf
Wdmod
Wdmod Watchdog Timer Mode Register F99H, F98H
Watchdog Timer Enable/Disable Control
5AH
Wmod Watch Timer Mode Register F89H, F88H
Instruction SET Features
SAM47 Instruction SET
Instruction Reference Area
Reducing Instruction Redundancy
Bitr EMB
Instructions Which Have Skip Conditions
Flexible Bit Manipulation
Instructions Which Affect the Carry Flag
ADC A,@HL
ADC and SBC Instruction Skip Conditions
SBC A,@HL
Instruction Operand Notation Symbol Definition
Symbols and Conventions Data Type Symbols
Register Identifiers Full Register Name
Opcode Definitions Indirect Register
Opcode Definitions
Opcode Definitions Direct Register
@HL @WX @WL
HIGH-LEVEL Summary
Cpse
Idle
Stop
EA,RR
Xchi @HL
XCH
EA,DA
DA,A
ADS
COM
ADC @HL
SBC @HL
Btstz
Bitr
Binary Code Summary
SCF RCF CCF
First Byte Condition
PC13-8 ← SP + 1 SP
Ra,#im Ra ← im RR,#imm RR ← imm
EA,RR EA ← EA or RR
EA,RR EA ← EA and RR
EA,RR EA ← EA XOR RR
← a + HL + C
Skip if C =
Second Byte Bit Addresses
FB0H-FBFH FF0H-FFFH
LDB
Instruction Descriptions
Operation Operand Operation Summary Bytes Cycles
ADC Add With Carry
ADC
Operand Binary Code Operation Notation
#8H ← 8H
ADS EA,HL
ADS Add And Skip On Overflow
ADS
JPS YYY
EA ← 0C3H + 12H = 0D5H
Logical
SMB Band
Band Bit Logical
Band
Band C,P1.@L
Flag EQU
Band @H+FLAG
FF1H-FF9H
Bitr Bit Reset
Bitr
Bitr P2.0
BP2 Bitr
Incs BP2
Bits
Bits Bit Set
Bits P2.0
BP2 Bits
BOR Bit Logical or
BOR
BOR @H+FLAG
LABEL2
Btsf Bit Test and Skip on False
Btsf
LABEL3
BP2 Btsf
RET Incs BP2
Btst Bit Test and Skip on True
Btst
BP2 Btst
Btstz
Btstz Bit Test and Skip on True Clear Bit
BP2 Btstz
Btstz @H+FLAG
Bits @H+FLAG
Bxor
Bxor Bit Exclusive or
RCF Bxor C,P1.0
Bxor @H+FLAG
Call Operation
Call Call Procedure
Operand Operation Summary Bytes Cycles
Calls Play
Calls Call Procedure Short
Calls Operation
0FFH 0FEH EMB, ERB 0FDH 0FCH 0FBH 0FAH
CCF Complement Carry Flag
CCF
COM
COM Complement Accumulator
COM a
Cpse
Cpse Compare and Skip if Equal
Cpse EA,HL RET
Decs HL
Decs Decrement and Skip on Borrow
Decs
Call PLAY1
DI Disable Interrupts
EI Enable Interrupts
Idle
Idle Idle Operation
Idle NOP
Incs
Incs Increment and Skip on Carry
Incs @HL
IS1 IS0 EMB ERB
Iret Return From Interrupt
Iret
SC2 SC1 SC0
ADR14
JP Jump
JP Operation
Jump to direct address 14 bits
ADR12
JPS Jump Short
JPS Operation
Jump direct in page 12 bits
JR Jump Relative Very Short
EA,WX ADS WX,EA
JR KK
JPS AAA BBB CCC DDD
JPS YYY XXX LD
LD Load
Description Operand Binary Code Operation Notation
Instruction Operation Description and Guidelines
Examples Instruction Operation Description and Guidelines
LDB Load Bit
LDB
Flag EQU 20H.3 RCF
Flag
LDB @H+FLAG
LDB @H+FLAG,C
Call Display JPS Main ORG
LDC Load Code Byte
LDC
Display LDC
ORG 01FDH
Display LD
01FFH LDC
LDD Load Data Memory and Decrement
LDD Operation
LDI Operation
LDI Load Data Memory and Increment
HL,#2FH LDI @HL
NOP
NOP No Operation
Stop NOP
Or Logical or
Or EA,@HL
POP
POP Pop From Stack
POP HL
Push
Push Push Onto Stack
Push HL
RCF Reset Carry Flag
RCF
Operation
REF Reference Instruction
Operand Operation Summary Bytes Cycles Memc Reference code
BBB EA,#FFH CCC Call SUB1 DDD SUB2
BBB EA,#FFH CCC Tcall SUB1 DDD TJP SUB2
AAA LD
Tcall SUB1
Opcode Symbol Instruction
HL,#0FH
TJP SUB2 ORG
RET
RET Return From Subroutine
PSW ← EMB,ERB
RRC
RRC Rotate Accumulator Right Through Carry
RRC a
SCF SBC EA,HL
SBC Subtract With Carry
SBC
RCF SBC EA,HL
#8H
RCF SBS EA,HL
SBS Subtract
SBS
SCF SBS EA,HL
SCF Set Carry Flag
SCF
Addresses Register Areas Bank
SMB Select Memory Bank
SMB
Format Binary Code Operation Notation
SRB Select Register Bank
ERB Setting SRB Settings Selected Register Bank
SRB
Sret Return From Subroutine and Skip
Sret
Stop Stop Operation
Stop
Vent Load EMB, ERB, and Vector Address
VENTn
VENTn Example The instruction sequence
XCH
XCH Exchange a or EA with Nibble or Byte
XCH EA,@HL
Xchd Operation
Xchd Exchange and Decrement
YYY Xchd @HL
HL,#2FH
Xchi Exchange and Increment
Xchi Operation
YYY Xchi @HL
XOR
XOR Logical Exclusive or
XOR EA,HL
SAM47 Instruction SET
Oscillator Circuits Interrupts Power-Down
Page
Oscillator Circuits
CPU Clock Notation
Using a Subsystem Clock
Clock Control Registers
Clock Circuit Diagram
STO
Main System Oscillator Circuits
Subsystem Oscillator Circuits
PCON.1 PCON.0
Power Control Register Pcon
Pcon Bit Settings Resulting CPU Operating Mode
SCMOD.0 =
PCON,A
+ Programming TIP Setting the CPU Clock
Instruction Cycle Times
SCMOD.3 SCMOD.2 SCMOD.0
System Clock Mode Register Scmod
FB7H SCMOD.3 SCMOD.2 SCMOD.0 Scmod
Fx Oscillation Fxt Oscillation
Oscillator CIRCUITSKS57C2308/P2308/C2316/P2316
KS57C2308/P2308/C2316/P2316OSCILLATOR Circuits
Switching the CPU Clock
Elapsed Machine Cycles During CPU Clock Switch
CLMOD.1 CLMOD.0
Clock Output Mode Register Clmod
Result of CLMOD.3 Setting
Clock Source Frequency
Clock Output Procedure
Clock Output Circuit
PMG2,EA
+ Programming TIP CPU Clock Output to the CLO Pin
CLMOD,A
INT0, INT1, INT4
Interrupt Types and Corresponding Port Pins Interrupt Name
Interrupts
INTB, INTT0, Ints
Software-Generated Interrupts
Power-Down Mode Release
Vectored Interrupts
Multiple Interrupts
Interrupt Execution Flowchart
Interrupt Control Circuit Diagram
Multiple Interrupts
Two-Level Interrupt Handling
Multi-Level Interrupt Handling
Result of IPR Bit Setting
Standard Interrupt Priorities Default Priority
Interrupt Priority Register Settings
Interrupt Priority Register IPR
IMOD0 IMOD0.3 IMOD0.1 IMOD0.0
IMOD1 IMOD1.0
INT1 IMOD0
External INTERRUPT0 and INTERRUPT1 Mode Registers
INT0 Noise Filter Edge Clock Selector
IRQ0 IRQ1 Edge IMOD1
Effect of IMOD2 Settings
External Interrupt 2 Mode Register IMOD2
IMOD2 Register Bit Settings
FB6H IMOD2.2 IMOD2.1 IMOD2.0
Circuit Diagram for INT2 and KS0-KS7 Pins
Interrupt Flags
IME IPR.2 IPR.1 IPR.0
Interrupt Request Flags IRQx
Intb Btstz Irqb
+ Programming TIP Enabling the Intb and INT4 Interrupts
Iret INT4 Bitr IRQ4
POWER-DOWN
Stop Idle
CPU
Idle Mode Timing Diagrams
Timing When Idle Mode is Released by Reset
Stop Mode Timing Diagrams
Timing When Stop Mode is Released by Reset
IMOD2,A
Keyclk Call MA2SUB
P2,EA
SMB Bitr Irqw IRQ2 Bits IEW IE2 CLKS1 Call Watdis
Port PIN Configuration for POWER-DOWN
P3.0/LCDCK
Recommended Connections for Unused Pins
P3.1/LCDSY
SEG0-SEG23
POWER-DOWN
Timing for Oscillation Stabilization After Reset
Data Memory RAM
Hardware Register Values After Reset
Program Status Word PSW
Clocks
Watchdog Timer
Basic Timer
Timer/Counters 0
LCD Driver/Controller
KS57C2308/P2308/C2316/P2316
Channel Open-Drain Mode Register PNE
Port Mode Flags
Pull-Up Resistor Mode Register Pumod
10 I/O Ports
P6,EA
PULL-UP Resistor Mode Register Pumod
Port Mode Flags PM Flags
Pumod ID
LCD Output Segments Bit Output Pins
Channel OPEN-DRAIN Mode Register PNE
LMOD.7 and LMOD.6 Setting for Port 8 Output Control
PIN Addressing for Output Port
1FAH SEG26
SEG24
SEG25
1FBH SEG27
Port 0 Circuit Diagram
Port 0 Circuit Diagram
Port 1 Circuit Diagram
IMOD0 IMOD1
Port 2 Circuit Diagram
Port 2 Circuit Diagram
Port 3 and 6 Circuit Diagram
Port 3 and 6 Circuit Diagram
Port 4 and 5 Circuit Diagram
Port 4 and 5 Circuit Diagram
Port 7 Circuit Diagram
Port 7 Circuit Diagram
10-12
KS57C2308/P2308/C2316/P2316 Timers and TIMER/COUNTERS
Watchdog Timer Function
Interval Timer Function
Oscillation Stabilization Interval Control
RAM
Basic Timer Register Overview Type Description Size
Addressing Reset Name Mode
Wdtcf
Basic Timer Input Clock Interval Time
Basic Timer Mode Register Bmod
Basic Timer Mode Register Bmod Organization
BMOD.3
Basic Timer Counter Bcnt
Basic Timer Operation Sequence
+ Programming TIP Using the Basic Timer
Watchdog Timer Counter Clear Flag Wdtcf
Watchdog Timer Mode Register Wdmod
Watchdog Timer Counter Wdcnt
Bmod
Reset Bits EMB SMB
+ Programming TIP Using the Watchdog Timer
BMOD,A Main Bits Wdtcf
BIT TIMER/COUNTER 0 TC0
TC0 Function Summary
TC0 Component Summary
TC0 Circuit Diagram
TC0 Register Overview Type Description Size
Enable Timer/Counter
TC0 ENABLE/DISABLE Procedure
Disable Timer/Counter
TC0 Programmable TIMER/COUNTER Function
TC0 Operation Sequence
TMOD0.5 TMOD0.4
TMOD0 Settings for TCL0 Edge Detection
TC0 Event Counter Function
TCL0 Edge Detection
TREF0,EA EA,#4CH TMOD0,EA
+ Programming TIP TC0 Signal Output to the TCLO0 Pin
TC0 Clock Frequency Output
Bits TOE0
TC0 Serial I/O Clock Generation
TC0 External Input Signal Divider
TREF0,EA EA,#0CH TMOD0,EA
TC0 Mode Register TMOD0
Resulting Counter Source and Clock Frequency
TMOD0.6, TMOD0.5, and TMOD0.4 Bit Settings
TMOD0.6 TMOD0.5 TMOD0.4
+ Programming TIP Restarting TC0 Counting Operation
TC0 Timing Diagram
TC0 Counter Register TCNT0
MSB LSB
TC0 Output Enable Flag TOE0
TC0 Reference Register TREF0
TC0 Output Latch TOL0
+ Programming TIP Setting a TC0 Timer Interval
TREF0,EA
Real-Time and Watch-Time Measurement
Using a System or Subsystem Clock Source
Clock Source Generation for LCD Controller
Check Subsystem Clock Level Feature
Timing Tests in High-Speed Mode
Buzzer Output Frequency Generator
Watch Timer Circuit Diagram
Watch Timer Mode Register Wmod
WMOD,EA Bits IEW
+ Programming TIP Using the Watch Timer
Clock Btstz Irqw
LCD CONTROLLER/DRIVER
Data BUS LCD Controller Driver
LCD Circuit Diagram
LCD Circuit Diagram
LCD RAM Address Area
LCON.0 LMOD.3 COM0-COM3 SEG0-SEG31
LCON.0 and LMOD.3 Bit Settings
LCD Control Register Lcon
P8.0-P8.7
LMOD.5 LMOD.4
LCD Mode Register Lmod
LMOD.3 LMOD.2 LMOD.1 LMOD.0
GND
LCD Power Supply Static Mode Bias
LCD Drive Voltage
LCD Voltage Dividing Resistors
Voltage Dividing Resistor Circuit Diagrams
Common COM Signals
LCD Common Signal Waveform Static
LCD Common Signal Waveform at 1/2 Bias 1/2, 1/3 Duty
LCD Common Signal Waveform at 1/3 Bias 1/3, 1/4 Duty
SEG
Segment SEG Signals
Select/No-Select Signals for LCD Static Display Mode
Select No-select
Select/No-Select Signals for LCD 1/2 Bias Display Mode
Select Non-select
Select/No-Select Signals for LCD 1/3 Bias Display Mode
10. Select/No-select Bias Signals in 1/3 Bias Display Mode
11. LCD Signal Waveforms in Static Mode
COM0 SEG11 SEG12 VLC0 VSS +VLCD 0 Vlcd
12. LCD Connection Example in Static Mode
13. LCD Signal Waveforms at 1/2 Duty, 1/2 Bias
COM0 COM1 SEG9
14. LCD Connection Example at 1/2 Duty, 1/2 Bias
15. LCD Signal Waveforms at 1/3 Duty, 1/2 Bias
COM0 COM1 COM2 SEG12
16. LCD Connection Example at 1/3 Duty, 1/2 Bias
17. LCD Signal Waveforms at 1/3 Duty, 1/3 Bias
18. LCD Connection Example at 1/3 Duty, 1/3 Bias
19. LCD Signal Waveforms at 1/4 Duty, 1/3 Bias
COM0 COM1 COM2 COM3 SEG13
20. LCD Connection Example at 1/4 Duty, 1/3 Bias
12-24
Serial I/O Interface
Serial I/O Operation Sequence
Serial I/O Interface Circuit Diagram
SMOD.1
Serial I/O Mode Register Smod
SMOD.0
SMOD.2
Serial I/O Timing Diagrams
SIO Timing in Transmit/Receive Mode
Bitr EMB EA,TDATA
Serial I/O Buffer Register Sbuf
SBUF,EA EA,#0EEH SMOD,EA
SBUF,EA EA,#4FH SMOD,EA
XCH EA,SBUF
SBUF,EA EA,#8FH SMOD,EA
Bits IES Ints Push
Bits SMOD.3
SBUF,EA EA,#0FH SMOD,EA
High Speed SIO Transmission
13-8
Electrical Data
Standard Electrical Characteristics
Stop Mode Characteristics and Timing Waveforms
Miscellaneous Timing Waveforms
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Parameter Symbol Conditions Rating Units
D.C. Electrical Characteristics
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Output low
D.C. Electrical Characteristics Concluded
Stop mode DD = 5 V ± 10% CPU = fx/4, Scmod = 0100B
Main System Clock Oscillator Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Condition Min Typ Max Units
Subsystem Clock Oscillator Characteristics
Input/Output Capacitance
A.C. Electrical Characteristics
Input Width
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Released by Reset 17/fx Time Released by interrupt
Timing Waveforms
A.C. Timing Measurement Points Except for XIN and Xtin
TCL0 Timing
10. Serial Data Transfer Timing
QFP-1420C Package Dimensions
Mechanical Data
15-2
16 KS57P2308/P2316 OTP
KS57P2308/KS57P2316
REG
Operating Mode Characteristics
Test
16-4
16-5
KS57P2308/P2316 OTPKS57C2308/P2308/C2316/P2316
16-7
16-8
16-9
16-10
Timing Waveforms
16-12
16-13
11. Serial Data Transfer Timing
12. OTP Programming Algorithm
KS57P2308/P2316 OTP KS57C2308/P2308/C2316/P2316 16-16
SASM57
Shine
Sama Assembler
HEX2ROM
Smds Product Configuration SMDS2+ 17-2
TB572308A/16A Target Board
Xtal MDS
SMDS2/SMDS2+
Idle LED
XTI
Stop LED
Pin Connectors for TB572308A/16A
DIP
KS57 Series Mask ROM Order Form
Page
Customer Risk Order Agreement
KS57 Series Request for Production AT Customer Risk
Risk Order Information
Order Quantity and Delivery Schedule
Page
Prom
KS57C2308 Mask Option Selection Form
Attachment Check one
Customer Checksum Company Name Signature Engineer
Page
KS57C2316 Mask Option Selection Form
+ What is the purpose of this order?
KS57 Series OTP Factory Writing Order Form 1/2
Page
+ Are you going to continue ordering this device?
KS57P2308 OTP Factory Writing Order Form 2/2
Device Number
If so, how much will you be ordering? PCS
Page
KS57P2316 OTP Factory Writing Order Form 2/2

![]()
![]() SP + 2)
SP + 2)![]() SP + 6)
SP + 6)