Guidelines for handling electrostatic
A.2 Electrostatic charging
Charging
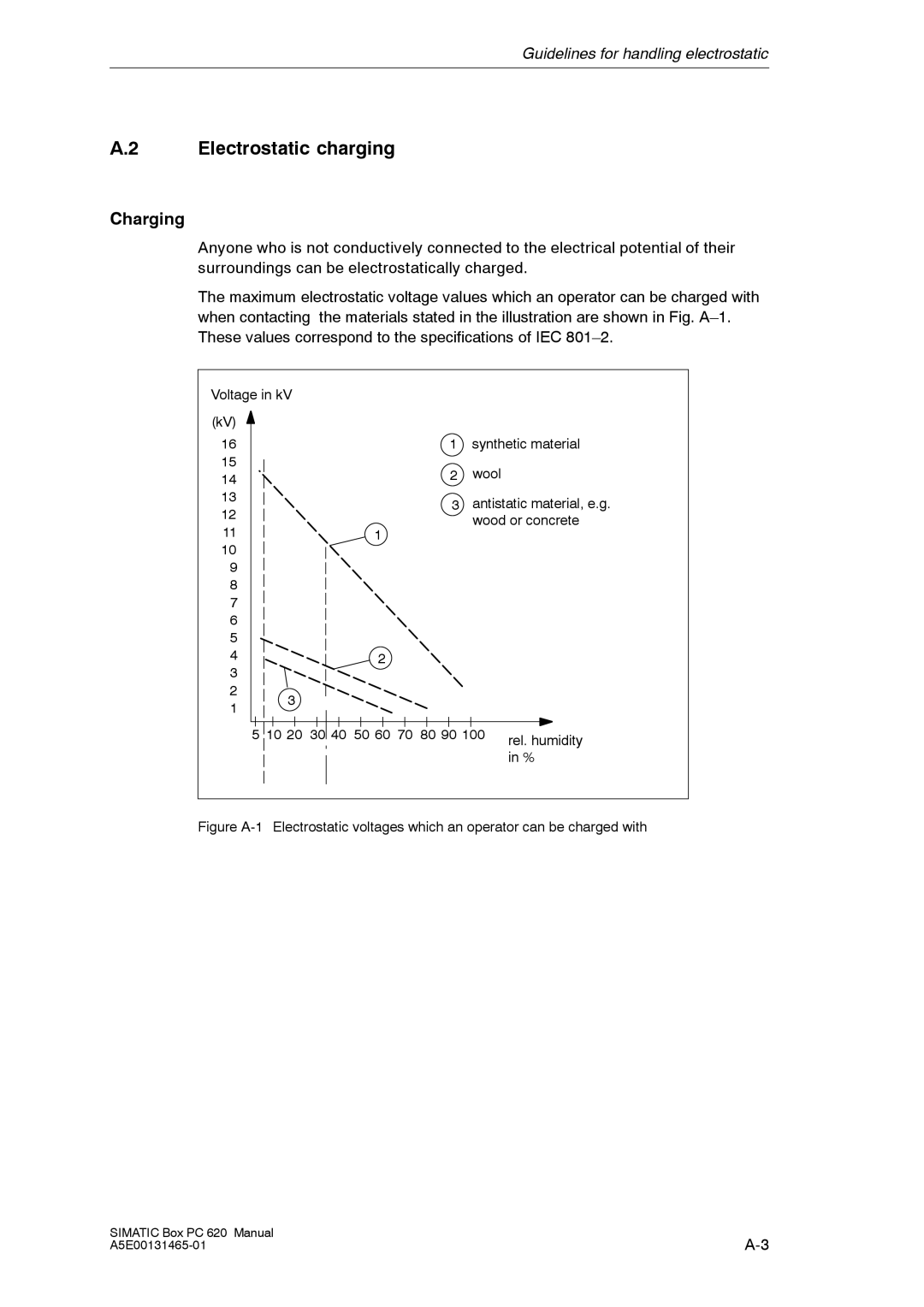
Anyone who is not conductively connected to the electrical potential of their surroundings can be electrostatically charged.
The maximum electrostatic voltage values which an operator can be charged with when contacting the materials stated in the illustration are shown in Fig.
Voltage in kV |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
(kV) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| 1 |
| synthetic material | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
16 |
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
15 |
| 2 |
| wool |
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
13 |
| 3 |
| antistatic material, e.g. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
12 |
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| wood or concrete | |||||
11 |
| 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
| 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
| 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| 5 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 | rel. humidity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| in % | |||
Figure A-1 Electrostatic voltages which an operator can be charged with
SIMATIC Box PC 620 Manual | |