Teledyne API Ultrafine Particle Monitor - Model 651 |
|
| Primer on | |||
| ||||||
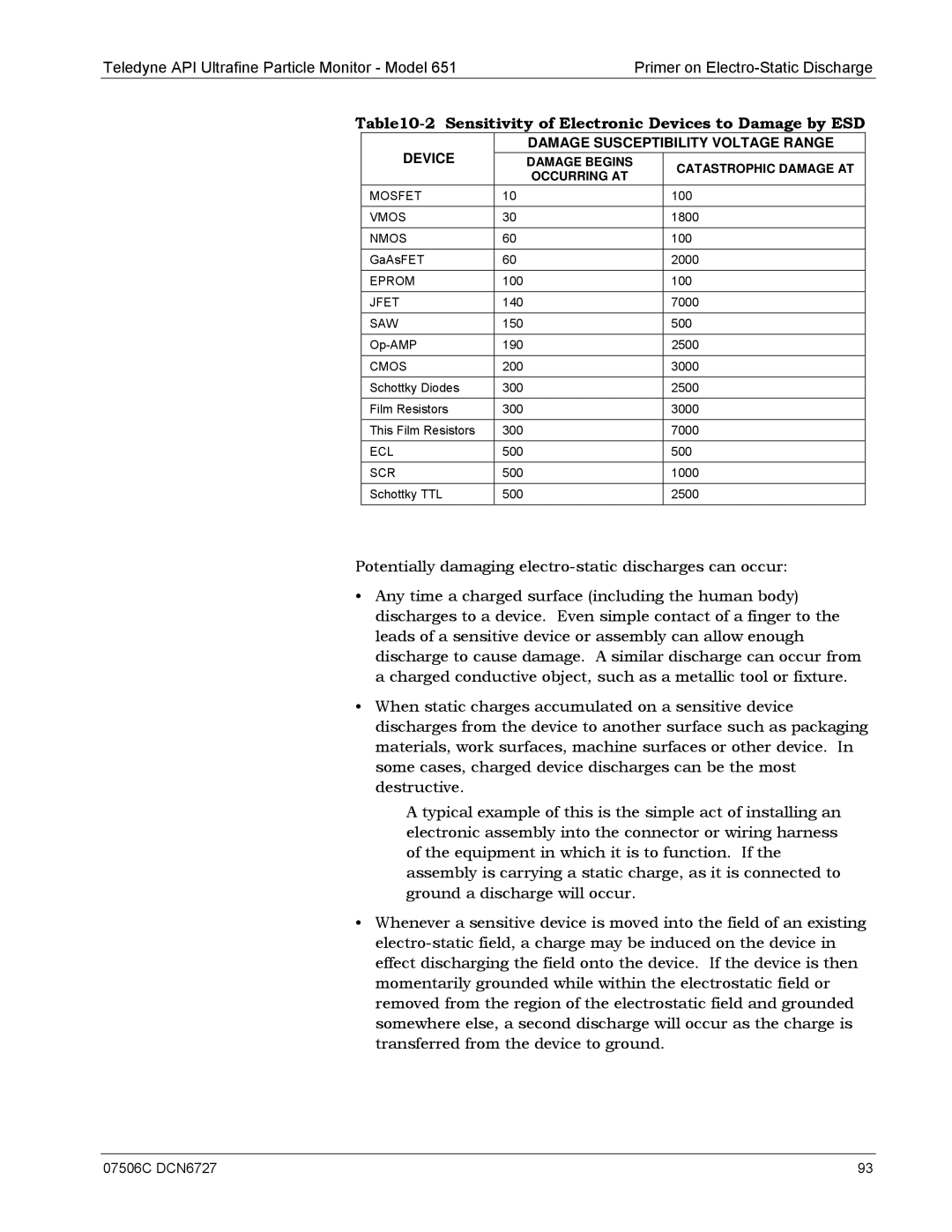
| DEVICE |
| DAMAGE SUSCEPTIBILITY VOLTAGE RANGE |
| ||
|
| DAMAGE BEGINS |
| CATASTROPHIC DAMAGE AT |
| |
|
|
| OCCURRING AT |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| MOSFET | 10 |
|
| 100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| VMOS | 30 |
|
| 1800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| NMOS | 60 |
|
| 100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| GaAsFET | 60 |
|
| 2000 |
|
| EPROM | 100 |
|
| 100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| JFET | 140 |
|
| 7000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SAW | 150 |
|
| 500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 190 |
|
| 2500 |
| |
| CMOS | 200 |
|
| 3000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Schottky Diodes | 300 |
|
| 2500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Film Resistors | 300 |
|
| 3000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| This Film Resistors | 300 |
|
| 7000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ECL | 500 |
|
| 500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SCR | 500 |
|
| 1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Schottky TTL | 500 |
|
| 2500 |
|
Potentially damaging
•Any time a charged surface (including the human body) discharges to a device. Even simple contact of a finger to the leads of a sensitive device or assembly can allow enough discharge to cause damage. A similar discharge can occur from a charged conductive object, such as a metallic tool or fixture.
•When static charges accumulated on a sensitive device discharges from the device to another surface such as packaging materials, work surfaces, machine surfaces or other device. In some cases, charged device discharges can be the most destructive.
A typical example of this is the simple act of installing an electronic assembly into the connector or wiring harness of the equipment in which it is to function. If the assembly is carrying a static charge, as it is connected to ground a discharge will occur.
•Whenever a sensitive device is moved into the field of an existing
07506C DCN6727 | 93 |