CAT System Computer Control
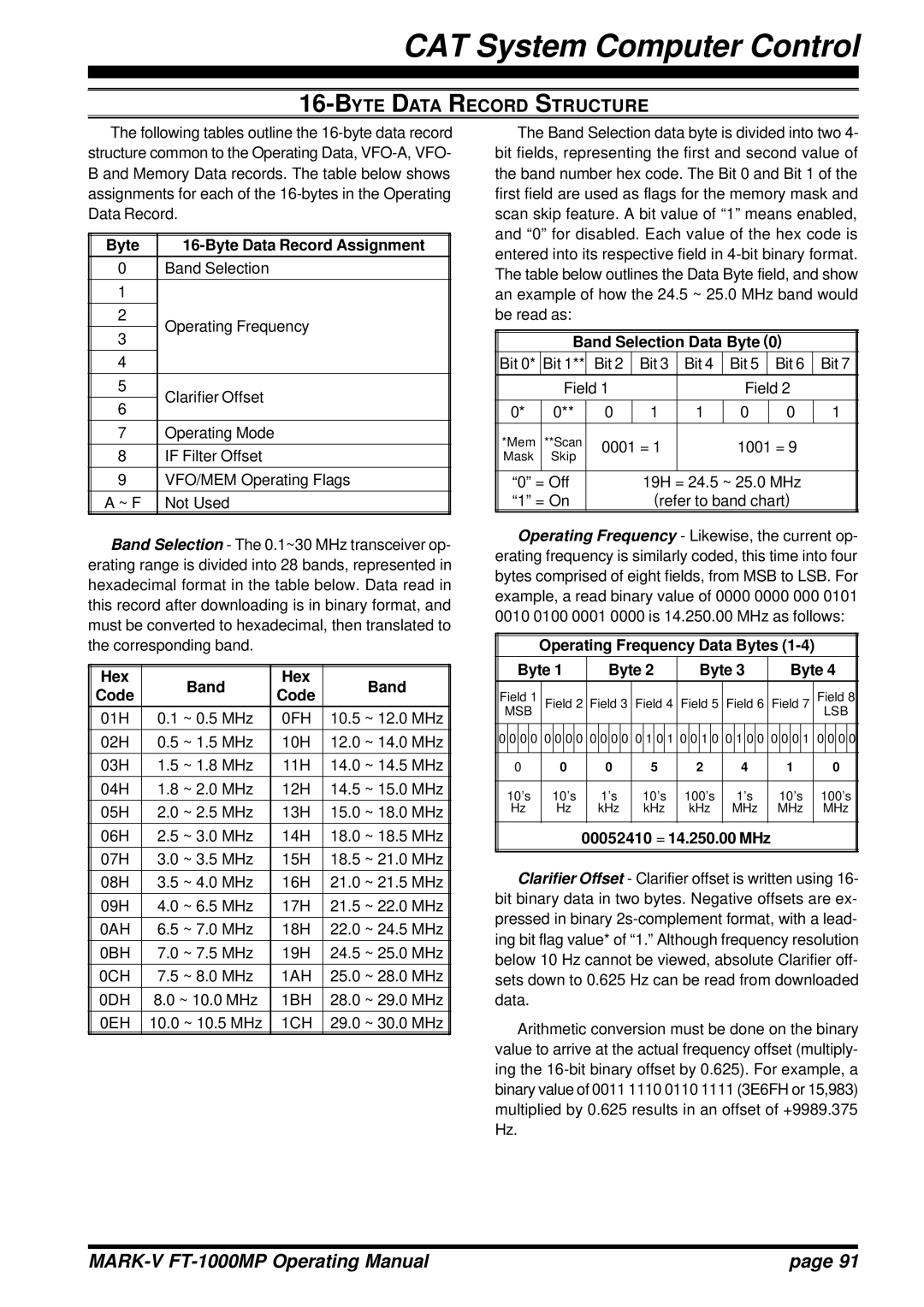
16-BYTE DATA RECORD STRUCTURE
The following tables outline the
Byte |
|
0Band Selection
The Band Selection data byte is divided into two 4- bit fields, representing the first and second value of the band number hex code. The Bit 0 and Bit 1 of the first field are used as flags for the memory mask and scan skip feature. A bit value of “1” means enabled, and “0” for disabled. Each value of the hex code is entered into its respective field in
2
3
4
5
6
Operating Frequency
Clarifier Offset
be read as:
Band Selection Data Byte (0)
Bit 0* | Bit 1** | Bit 2 | Bit 3 | Bit 4 | Bit 5 | Bit 6 | Bit 7 |
| Field 1 |
|
| Field 2 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0* | 0** | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7Operating Mode
8IF Filter Offset
9VFO/MEM Operating Flags A ~ F Not Used
Band Selection - The 0.1~30 MHz transceiver op- erating range is divided into 28 bands, represented in hexadecimal format in the table below. Data read in this record after downloading is in binary format, and must be converted to hexadecimal, then translated to the corresponding band.
| Hex | Band | Hex | Band |
| Code | Code | ||
|
|
| ||
| 01H | 0.1 ~ 0.5 MHz | 0FH | 10.5 ~ 12.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 02H | 0.5 ~ 1.5 MHz | 10H | 12.0 ~ 14.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 03H | 1.5 ~ 1.8 MHz | 11H | 14.0 ~ 14.5 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 04H | 1.8 ~ 2.0 MHz | 12H | 14.5 ~ 15.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 05H | 2.0 ~ 2.5 MHz | 13H | 15.0 ~ 18.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 06H | 2.5 ~ 3.0 MHz | 14H | 18.0 ~ 18.5 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 07H | 3.0 ~ 3.5 MHz | 15H | 18.5 ~ 21.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 08H | 3.5 ~ 4.0 MHz | 16H | 21.0 ~ 21.5 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 09H | 4.0 ~ 6.5 MHz | 17H | 21.5 ~ 22.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0AH | 6.5 ~ 7.0 MHz | 18H | 22.0 ~ 24.5 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0BH | 7.0 ~ 7.5 MHz | 19H | 24.5 ~ 25.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0CH | 7.5 ~ 8.0 MHz | 1AH | 25.0 ~ 28.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0DH | 8.0 ~ 10.0 MHz | 1BH | 28.0 ~ 29.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0EH | 10.0 ~ 10.5 MHz | 1CH | 29.0 ~ 30.0 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
*Mem | **Scan | 0001 = 1 | 1001 = 9 |
Mask | Skip |
|
|
|
| ||
“0” = Off | 19H = 24.5 ~ 25.0 MHz | ||
“1” = On | (refer to band chart) | ||
Operating Frequency - Likewise, the current op- erating frequency is similarly coded, this time into four bytes comprised of eight fields, from MSB to LSB. For example, a read binary value of 0000 0000 000 0101
0010 0100 0001 0000 is 14.250.00 MHz as follows:
Operating Frequency Data Bytes
| Byte 1 |
| Byte 2 |
|
| Byte 3 |
|
| Byte 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Field 1 |
| Field 2 | Field 3 |
| Field 4 | Field 5 |
| Field 6 | Field 7 |
| Field 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MSB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LSB | ||||||
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
| 0 |
| 0 |
|
| 5 |
| 2 |
|
| 4 |
| 1 |
|
| 0 |
| ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10’s |
| 10’s |
| 1’s |
| 10’s | 100’s |
|
| 1’s | 10’s |
| 100’s | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hz |
|
| Hz | kHz |
|
| kHz |
| kHz |
| MHz | MHz |
| MHz | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00052410 = 14.250.00 MHz
Clarifier Offset - Clarifier offset is written using 16- bit binary data in two bytes. Negative offsets are ex- pressed in binary
Arithmetic conversion must be done on the binary value to arrive at the actual frequency offset (multiply- ing the
| page 91 |