Agilent Model 54835A/45A/46A Oscilloscopes
Ease of use with high performance
Trigger setup controls set mode and basic parameters
Service Policy
Display shows waveforms and graphical user interface
Power
Measurements
This Book
Contents
To check the keyboard To check the LEDs
Contents
No Display Trouble Isolation
To remove and replace the backlight inverter board
Replaceable Parts
To remove and replace the floppy disk drive
General Information
Instruments covered by this service guide
Oscilloscopes Covered by this Service Guide
Model Description
Accessories supplied
Accessories supplied
Options available
Options available
Option Number Description
Required when using 2 or more Agilent 1144A active probes
Accessories available
Accessories available
Agilent 1144A MHz Active Probe
Agilent
Specifications & characteristics
Specifications & characteristics
Acquisition
Specifications & characteristics Vertical
Whichever is larger
Horizontal
Offset Accuracy
Post-trigger
Specifications & characteristics Trigger
Specifications & characteristics Display
Measurements
Computer System/ Storage
CAT I and CAT II Definitions
Video Output
Rise Time figures are calculated from tr=.35/Bandwidth
Agilent Technologies 54835A/45A/46A general characteristics
Agilent Technologies 54835A/45A/46A general characteristics
General Characteristics
Agilent Technologies 54835A/45A/46A general characteristics
Recommended test equipment
Agilent Service software No substitution
Recommended test equipment
Agilent EPM Sensor 441A/Agilent 8482A
Preparing for Use
Preparing for Use
To inspect the instrument
To inspect the instrument
To connect power
To connect power
Three-wire Power Cable is Provided
To connect the mouse or other pointing device
To attach the optional trackball
To connect the mouse or other pointing device
To attach the optional trackball
To connect the keyboard
To connect to the LAN card
To connect the keyboard
To connect oscilloscope probes
To connect oscilloscope probes
To connect a printer
To connect a printer
To connect an external monitor
To connect the Gpib cable
To connect an external monitor
To tilt the oscilloscope upward for easier viewing
To tilt the oscilloscope upward for easier viewing
To power on the oscilloscope
To power on the oscilloscope
You Can Configure the Backlight Saver
To verify basic oscilloscope operation
Press the Default Setup key on the front panel
Graphical Interface Enable Button
Press the Autoscale key on the front panel
To clean the instrument
To clean the display monitor contrast filter
To clean the instrument
Testing Performance
Test Interval Dependencies
See Also
Let the Instrument Warm Up Before Testing
Clear Display
Averaging
To test the dc calibrator
Enable the graphical interface
Procedure
Connect the multimeter to the front panel Aux Out BNC
If the test fails
Set Aux Output to DC Set the output voltage
Selecting DC in the Calibration Dialog
To test input resistance
Input Resistance Equipment Setup
To test input resistance
25% accuracy Cables
Connect the equipment
Specification
To test voltage measurement accuracy
To test voltage measurement accuracy
Voltage Measurement Accuracy Equipment Setup
Acquisition Setup for Voltage Accuracy Measurement
Use the following table for steps 8 through
Scale Offset Supply Tolerance Limits
Select Channel 1 as the source for the Vavg measurement
Source Selection for Vavg Measurement
To Set Vertical Scale and Position
Set the scale from the table Set the offset from the table
To test offset accuracy
To test offset accuracy
Use the following table for steps 6 through
Volts/div Position Supply Tolerance Limits
To test offset accuracy
Real Time
Specification Equivalent Time
To test bandwidth
Equivalent Time Test
Calculate the response using the formula
Select Vamptd from the Voltage submenu of the Measure menu
Displayed. Note the Vamptd1 reading
Real Time Test
MΩ, 500 MHz Test on 54835A, 54845A, and 54846A
To test time measurement accuracy
Equivalent Time Mode Procedure
To test time measurement accuracy
Equivalent Time ≥16 averages
Horizontal Setup for Equivalent Time Procedure
Waveform for Time Measurement Accuracy Check
Acquisition Setup for Equivalent Time Procedure
Source Selection for Delta Time Measurement
Measurement Settings for Time Interval Measurement
For valid statistical data
New Measurement Settings for Delta Time Measurement
Real-Time Mode Procedure
Measurement Definitions for Real Mode Procedure
Click Close
Set horizontal time/div to 5 ns/div
Acquisition Setup for Trigger Sensitivity Test
To test trigger sensitivity
To test trigger sensitivity
Setting the Markers for a 0.5 Division Reference
Turn on Channel 1 and turn off all other channels
Procedure-Auxiliary Trigger Test
If a test fails
Page
Amplitude Input Channel Chan 4/Ext Resistance
Agilent Technologies 54835A/45A/46A Oscilloscope
Test Limits Results Vmax Vmin/5 =
Voltage Scale Coupling Supply Limits Channel
Channel 2 GSa/s
Realtime Channel 4 GSa/s
Channel 8 GSa/s
∆Time edge#101 Limits
Calibrating and Adjusting
Calibrating and Adjusting
Let the Oscilloscope Warm Up Before Adjusting
Loading New Software
To check the power supply
To check the power supply
Disconnect the oscilloscope power cord and remove the cover
Equipment Critical Specifications Recommended Model/Part
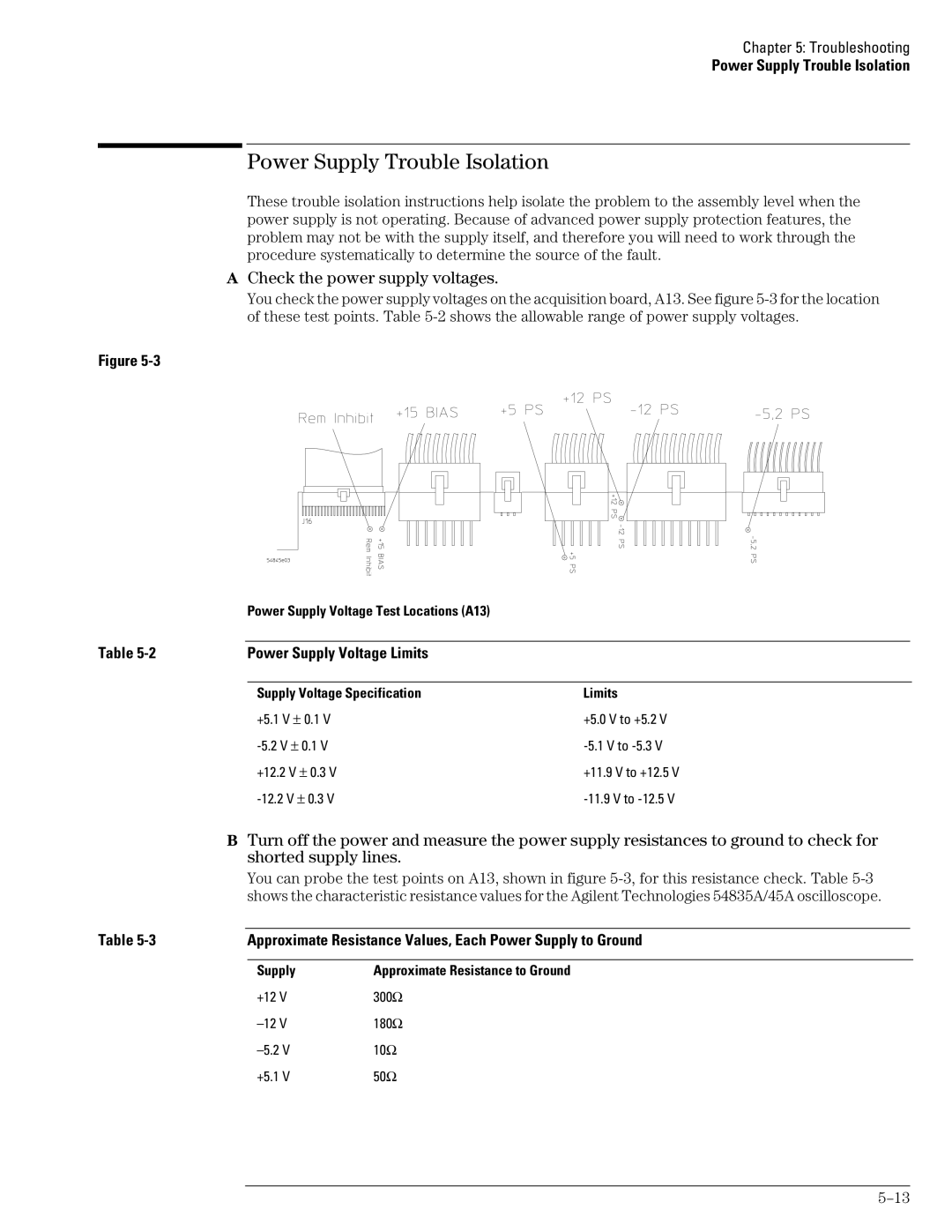
Power Supply Voltage Limits
Supply Voltage Specification Limits
Equipment Required
To check the flat panel display FPD
Flat-Panel Display Specifications
When to Use this Procedure
To check the flat panel display FPD
Click Start
Starting the Screen Test
Repeat steps 6 and 7 for all colors
Screen Test
Self calibration
To run the self calibration
To run the self calibration
Calibration time
If calibration fails
Click Start, then follow the instructions on the screen
Clear Cal Memory Protect to Run self calibration
Click here to start calibration
Page
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
To install the fan safety shield
To install the fan safety shield
Disconnect the instrument power cord and remove the cover
Installing the Fan Safety Shield
To troubleshoot the instrument
To troubleshoot the instrument
Primary Trouble Isolation Flowchart
Primary Trouble Isolation
Primary Trouble Isolation
Perform power-up
Power-on Display Default Graphical Interface Disabled
Check the display
Run oscilloscope self-tests
Check the front panel
Run the Knob and Key selftest and the LED selftest
No Display Trouble Isolation Flowchart
Check the fan connections
Remove the cabinet and install the fan safety shield
No Display Trouble Isolation
Sequence
Completed its power-on test LEDs do not come on,
Power-on
Power supply indicator Isolation flowchart
Configure the motherboard
Not, the problem may be with
Power to the instrument.
Solenoids are preset Normal operating pattern
Board video signals
Power Supply Trouble Isolation Flowchart
Power Supply Trouble Isolation
Power Supply Trouble Isolation
Check the power supply voltages
Approximate Resistance Values, Each Power Supply to Ground
Power Supply Distribution
Replace any shorted assembly
Override the Remote Inhibit signal
Power-up Sense Resistor Connection
Check +15 V Bias and Remote Inhibit cabling
Replace the power supply
Routing of +15 V Bias and Remote Inhibit Signals
Check for the oscilloscope display onscreen
To check probe power outputs
To check probe power outputs
Pin Supply +3V Offset Data Probe ID Ring Clk +12
To check the keyboard
When you are finished, click Close
Test Procedure
To check the keyboard
Troubleshooting Procedure
Re-assemble the instrument
Test by Rows
To check the LEDs
To check the LEDs
LED Test Screen
When you are finished, click Close
To check the motherboard, CPU, and RAM
To check the motherboard, CPU, and RAM
Messages Vary Slightly
Signal
To check the Svga display board video signals
To check the Svga display board video signals
Video Signals
Backlight Inverter Board Input Voltages Input Pin #
To check the backlight inverter voltages
To check the backlight inverter voltages
Backlight OFF Backlight on
Post Code Listing
Post Code Listing AMI Motherboard only
Post Code Listing AMI Motherboard only
Checkpoint Code Description
Color settings next
Keyboard BAT command is issued
Unblocking command
Next
Display memory read/write test next
Clearing the memory below 1 MB for the soft reset next
2Eh
2Fh
Winbios Setup next
Keyboard reset command next
Command next
After Winbios Setup next
9Ch
9Bh
Coprocessor text next
9Dh
To configure the motherboard jumpers and set up the Bios
To configure the motherboard jumpers and set up the Bios
Motherboard / floppy drive configurations Bios setup
To configure the motherboard jumpers and set up the Bios
Agilent Technologies Service Note Describes Upgrade Details
To configure the motherboard jumpers and set up the Bios
J37, J39
Configuring the AMI Series 727 Motherboard Jumpers
J46
Series 727 Motherboard Jumpers
MHz Clock Is Required
J2J21 J11 J12
J25J24 J37
Press F1 to run the Winbios setup
To configure the AMI Series 727 Winbios Parameters
System Keyboard Absent
Do the following within the setup program
Winbios Keyboard Commands
Do steps h-l only if Your System has 64 Mb RAM
Load Optimal Defaults
Exit the Setup program, saving the changes you made
Configuration Item Setting
Primary
Configuring the AMI Series 757 Motherboard for 200 MHz CPU
Series 757 Rev C Motherboard Jumpers
Pin
Do not Press F2
When to Do this Procedure
Series 757 System Bios Settings with 1.44 Mbyte floppy drive
Configuring the AMI Series 757 Motherboard for 300 MHz CPU
Series 757 Rev D Motherboard Jumpers
J14 J16
AMI Atlas-III PCI/ISA
Do the following within the setup program
Series 757 System Bios Settings with 120 Mbyte floppy drive
Off
FIC VA-503A Motherboard
Core S1-1 S1-2 S1-3 S1-4
Ratio S2-1 S2-2
Under the Power Management Setup, change these settings
Under the PnP/PCI Configuration, change these settings
To troubleshoot the acquisition system
Under Integrated Peripherals, change these settings
Isolating Acquisition Problems
To troubleshoot the acquisition system
Acquisition Trouble Isolation 1
Acquisition Trouble Isolation 2
Acquisition Trouble Isolation 3
To D Converter Failed
Return the Known Good Attenuator to Original Channel
Acquisition Trouble Isolation 4
Probe Board failed
Temperature Sense failed
Fiso failed
Offset DAC failed
Interpolator failed
Scroll Mode Counter failed
Timer failed
Timebase failed
To troubleshoot attenuator failures
To troubleshoot attenuator failures
Attenuator Click Test
Repeat steps 1 through 3 for the remaining input channels
Swapping Attenuators
Attenuator Connectivity Test
Attenuator Assembly Troubleshooting
Select About Infiniium... from the Help Menu
Enable the Graphical Interface
Software Revisions
Software Revisions
Page
Replacing Assemblies
Replacing Assemblies
Remove all accessories from the instrument
To return the instrument to Agilent Technologies for service
To remove and replace the cover
To remove and replace the cover
Cover Fasteners
To disconnect the cable
To disconnect and connect Mylar flex cables
To disconnect and connect Mylar flex cables
To reconnect the cable
To remove and replace the AutoProbe assembly
To remove and replace the AutoProbe assembly
Disconnect the power cable and remove the cover
Disconnecting W13
Avoid Damage to the Ribbon Cable and Faceplate
Pushing Out the AutoProbe Faceplate
Removing the Probe Power and Control Assembly
To remove and replace the probe power and control assembly
To remove and replace the probe power and control assembly
Avoid Interference with the Fan
To remove and replace the backlight inverter board
To remove and replace the front panel assembly
To remove and replace the backlight inverter board
Removing the Backlight Inverter Board
To remove and replace the front panel assembly
SMB Cable W18 and Comp Wire W19
Removing the BNC Nuts
Disconnecting W16, W20, and the Backlight Cables
Front Panel Side Screws
Keep Long Screws Separate for Re-assembly
Front Panel Cover Plate Screws
Removing the Cursor Keyboard
Removing the backlights
To remove and replace the acquisition board assembly
To remove and replace the acquisition board assembly
Removing the Acquisition Assembly
To remove and replace the LAN interface board
To replace the board, reverse the removal procedure
To remove and replace the LAN interface board
Removing the LAN Interface Board
To remove and replace the Gpib interface board
To remove and replace the Gpib interface board
Removing the Gpib Interface Board
Disconnect these cables from the Svga display board
Removing the Scope Interface and Svga Display Boards
To separate the scope interface board and Svga display board
To separate the scope interface board and Svga display board
To replace the card, reverse the removal procedure
To remove and replace the Option 200 sound card
To remove and replace the Option 200 sound card
To remove and replace the hard disk drive
To remove and replace the hard disk drive
Removing the Hard Disk Drive
To remove and replace the floppy disk drive
To remove and replace the floppy disk drive
To remove and replace the motherboard
Removing the Floppy Disk Drive Screws
Disconnect these cables from the motherboard
To remove and replace the motherboard
Removing the Motherboard Torx Screws
To remove and replace the motherboard
To remove and replace the power supply
To remove and replace the power supply
Removing Power Supply Cables
To remove and replace the fan
To install the fan, reverse this procedure
To remove and replace the fan
Removing Fan Fasteners
To remove and replace the CPU
To remove and replace the CPU
Removing the CPU
Removing and replacing SIMMs on the AMI motherboard
To remove and replace RAM SIMMs or Sdram DIMMs
To remove and replace RAM SIMMs or Sdram DIMMs
Removing RAM SIMMs
To remove and replace an attenuator
To remove and replace an attenuator
Do Not Remove the Attenuators from the Acquisition Board
If You Permanently Replace Parts
Removing an Attenuator
To reset the attenuator contact counter
To reset the attenuator contact counter
Self Test
Attenuator Relay Actuations Setup
Attenuator Channel box, select the channel you are changing
Repeat for each channel you need to change
To remove and replace an acquisition hybrid
To remove and replace an acquisition hybrid
To remove the acquisition hybrid
To replace the acquisition hybrid
Do not USE Excessive Force
Hybrid Connector
Removing the Hybrid Connector
Replaceable Parts
Unlisted Parts
Ordering Replaceable Parts
Listed Parts
Direct Mail Order System
Power Cables and Plug Configurations
Power Cables and Plug Configurations
Plug Type Cable Plug Description Length Color Country In/cm
MP61 MP17 MP62 or MP63 MP15 and MP49
Exploded Views
Exploded Views
Front Frame and Front Panel
Fan and Acquisition Assembly
Power Supply and PC Motherboard
A10 MP57
H12 H24 H25 MP55 MP60 H11
Exploded Views
A4A1W24/25 A4A4
Exploded Views
Exploded Views
FIC VA-503A Motherboard for PC Motherboard Configuration
W17W20 A15 W14 W11 A19 W16 A14 W24/25 W27 W22 A4A1
H23 A4A2
Exploded Views
MP12
Sleeve and Accessory Pouch
MP14 MP52 MP70 MP72
H10 MP20 MP13 H19 H26 MP19
Attenuator Assembly
Replaceable Parts List
Replaceable Parts List
Agilent Part Des Number
QTY
DRAM-SIMM 2MX32 8 MB Simm
DRAM-DIMM 16MX32 64 MB Dimm
Fans
Cables
Display BD. Jumper
Page
Theory of Operation
Theory of Operation
Power Supply Assembly
FPD Monitor Assembly
Block-Level Theory
Disk Drives
Acquisition System
Front Panel
Attenuators
Probe Power and Control
Svga Display Card
Gpib Interface Card
Acquisition Block Diagram
Attenuator Theory
Attenuator Theory
Acquisition Theory
Acquisition Board
Acquisition Theory
Acquisition Modes
Scope Interface Board
Page
Manufacturer’s Name
Manufacturer’s Address
Supplementary Information
Product Regulations
Restricted Rights Legend
Product Warranty