MVP-8400i
AMX Limited Warranty and Disclaimer
AMX Software License and Warranty Agreement
FCC Information
Table of Contents
Upgrading MVP Firmware
EAP Security & Server Certificates
Commands
Text Effects Names 126 Button Query Commands 127
Panel Runtime Operations 137
Embedded codes 143 Panel Setup Commands 144
Appendix a Text Formatting 157
Appendix B Wireless Technology 163
Page
Overview
MVP-8400i Touch Panel
Specifications
MVP-8400i Specifications FG5965-04
Weight
Specifications
MVP-8400i LCD
Active Screen Area
Included Accessories
Other AMX Equipment
FG2255-07
MVP-BP Power Pack
Installing MVP-BP Batteries
MVP-BP Specifications
MVP-BP Specifications
If you are only using one battery, use Battery Slot #1
Installing the NXA-CFSP Compact Flash Card
Accessing the MVP’s Internal Components
Optional Compact Flash Upgrades
NXA-CFSP Compact Flash
Removing the Installed Card
Installing the Compact Flash Upgrade Card
Removing/installing a Compact Flash Memory card
Page
Panel Calibration
Calibrating the MVP Panels
Testing your Calibration
If Calibration Is Not Working
Configuring Communications
Modero Setup and System Settings
Wireless Settings Page Wireless Access Overview
Configuring a Wireless Network Access
Configure the Panel’s Wireless IP Settings
Wireless communication using a Dhcp Address
Wireless communication using a Static IP Address
Wireless Settings page IP Settings section
Simple versus Enterprise Configuration
Wireless Security Simple Mode window
Wireless Security Enterprise Mode window
Using the Site Survey tool
Wireless Site Survey
Configure the Card’s Wireless Security Settings
Configuration to a target WAP
Site Survey of available Waps Unsecured WAP shown selected
Automatically set Ssid
Manually set Ssid
Wireless Security Simple Mode window
WEP Key # Keyboard
Choose a Master Connection Mode
Protected Setup Select System Settings
System Settings page USB Connection
Configure a Virtual NetLinx Master using NetLinx Studio
Assigning Communication Settings for a Virtual Master
Mode Description Procedures
Ethernet
Master Connection to a Virtual Master via Ethernet
Connection Modes
These must match
Using G4 Web Control to Interact with a G4 Panel
G4 Web Control
Configuring Communications
Using your NetLinx Master to control the G4 panel
Web Control VNC installation and Password entry screens
Upgrading MVP Firmware
Upgrading the Modero Firmware via the USB port
Configure the panel for a USB Connection Type
Prepare Studio for communication via the USB port
Confirm and Upgrade the firmware via the USB port
Default Modero panel value is
Upgrading the Docking Station Firmware via USB
Prepare the Docking Station for firmware transfer via USB
Upgrade the Docking Station firmware via USB
Batteries
Device and System values
Upgrading MVP Firmware
Page
Setup Pages
Navigation Buttons
Setup Pages
Setup
WiFi/Wired icon
Navigation Buttons
Protected Settings
Information
Project Information
Project Information
Panel Information
Panel Information
RAM
Time & Date Settings
Time & Date Settings
Time Date Refresh/Set
Time Display fields
Audio Settings
Audio Settings
Set Date/Time
WAV files Supported sample rates
Supported WAV Sample Rates
Battery Settings
Battery Settings
Limit
Low Battery Warning
Battery Dock 1 Charge
Status Battery Dock 2 Charge
Battery Level Port
Protected Setup Pages
Protected Setup
System Recovery
Reboot / Shutdown
Device Information
Docking Station
Protected Setup Navigation Buttons
SIP
System Settings
System Settings Page Elements
Master Connection
System Settings
Wireless Settings
Wireless Settings
IP Settings
Access Point MAC
Address
Network Name Ssid WAP names
Simple/Enterprise
Wireless Security Simple Mode
Ssid
Wireless Security Enterprise Mode
Identity
Anon. Identity
Wireless Settings
Wireless Security Support
Open Settings
WEP Settings
Open Settings
WEP Settings
Generate Passphrase
Encryption key
WPA-PSK Settings
WPA-PSK Settings
EAP-LEAP Settings
EAP-LEAP Settings
EAP-FAST Settings
EAP-FAST Settings
Anonymous Identity
Automatic PAC
EAP-PEAP Settings
EAP-PEAP Settings
Been Disabled
EAP-TTLS Settings
EAP-TTLS Settings
Inner Authentication Type
Ssid Service Set Identifier
MSCHAPv2 default because its the most common
EAP-TLS Settings
EAP-TLS Settings
Client certificate configuration
Client Certificate Configuration
Certificates and their Extensions
Certificate Types Supported by the Modero Firmware
Calibrate
Calibration
G4 Web Control Settings
G4 Web Control Settings
G4 Web Control
Other Settings
Cache Settings
G4 Web Control Timeout
Cache Settings Page Elements
Image Cache Settings
Setting the image cache
Clearing the image cache
Checking image cache status
Password Settings
Password Settings
Panel Password
Change
SIP Settings
User Access
SIP Settings
Tools
Panel Connection Logs
Checking the Panel Connection Logs
Refreshing the Panel Connections Log
Clearing the Panel Connections Log
Panel Connection Logs
Panel Statistics
Panel Statistics
Checking the Panel Statistics
Refreshing the Panel Statistics
Clearing the Panel Statistics
Connection Utility
Using the Connection Utility
Connection Utility
WAP MAC
EAP Security & Server Certificates
EAP-TTLS EAP-TLS
Page
Panel Intercom Configuration
Setup
Setting the Intercom Session Timeout
Full Duplex Intercom
Setting Intercom Auto Answer
Advanced Setup
Allowing a panel to be monitored
Allowing a panel to monitor
Naming a panel
Sample Intercom
Sample Intercom
Name Description Channel Address Level PortCode
Panel Directory Room Name Name of a panel
Answering an incoming call
Answer Call
Advanced Setup
Creating Intercom Pages
More Time Popup
Answer Intercom Call Popup
Page
Commands
Commands
Programming
Button Assignments
@DPG
@PDR
@PHE
@PHP
@PPA
@PPM
@PPN
@PPT
@PPX
@PSP
@PST
Ppof
Ppog
Ppon
Programming Numbers
RGB triplets and names for basic 88 colors
RGB Values for all 88 Basic Colors
Index No Name Red Green Blue
102 MVP-8400i 8.4 Modero ViewPoint Touch Panel with Intercom
Default Font Styles and ID Numbers
Font Styles and ID Numbers
Font ID # Font type Size
Border Styles and Programming Numbers
Border Styles and Programming Numbers
TPD4 Border Styles by Name
Border styles
MVP-8400i 8.4 Modero ViewPoint Touch Panel with Intercom 105
Button Commands
Button Commands
ANI
APF
BAT
BAU
BCB
BCF
BCT
BDO
BFB
BIM
Entry is required
BLN
Sendcommand Panel,BMC-150,1,1,315,1,%BR%FT%TX%BM%IC%CF%CT
BMC
BMF
BMF-vt addr range,button states range,data
Cont
BMI
BML
BMP
BNC
BNN
BNP
BNT
BOR
BOS
BPP
BRD
BSF
BSM
BSO
BSP
BVN
BVP
BVT
BWW
DPF
DTO
ENA
FON
GDI
GIV
GLH
GLL
GRU
GSC
GSN
ICO
IRM
JSB
JSI
JST
MBT
MDC
RSS
SKT
SHO
STO
TEC
TOP
TXT
UNI
VTP
MVP Panel Lock Passcode commands
MVP Panel Lock Passcode Commands
Miscellaneous MVP Strings back to the Master
MVP Strings to Master
Text Effects Names
Text Effects
Button Query Commands
Custom Event Fields
Button Query Commands
?BCB
?BCF
?BCT
?BMP
?BOP
?BRD
?BRT
?BWW
?CHR
?DTO
?FBC
?FON
?ICO
?JSB
?JSI
?JST
?LOG
?MAC
?MUT
?STA
?STO
?TEC
Send Command Panel,?TEF-529,1
Send Command Panel,?TXT-529,1
?TEF
?TEF-vt addr range,button states range
Panel Runtime Operation Commands
Panel Runtime Operations
Akeyr
@AKP
@AKR
Beep
Setup
@EKP
Pkeyp
@PKP
@SOU
@SSL
@SST
@SWK
Input Commands
Input Commands
MPS
VKS
Embedded codes
Embedded Codes
Decimal numbers Hexidecimal values Virtual keystroke
Panel Setup Commands
Panel Setup Commands
Cfsm
CEX
ICM-TALK
ICM-LISTEN
ICM-SPEAKERLEVEL
ICM-MICLEVEL
MUT
@PWD
Dynamic Image Commands
Dynamic Image Commands
RAF, RMF Embedded Codes
RAF, RMF Embedded Codes
RMF
RSR
Escape Sequences
Escape Sequences
Intercom Commands
Intercom Commands
SIP Commands
SIP Commands
Msgwaiting
PHN-PRIVACY
PHN-REDIAL
Transferred
?PHN
PHN-DTMF
PHN-HANGUP
PHN-HOLD
SIP Setup Commands
PHN-SETUP Username
’PHN-SETUP-USERNAME,username’
Sendcommand Panel,’PHN-SETUP-USERNAME,6003’
Page
Appendix a Text Formatting
Text Formatting Codes for Bargraphs/Joysticks
Bargraph Text Code Inputs
Formatting Code Operations
Text Area Input Masking
Input mask character types
Character Types
Character Masking Rule
Input mask ranges
Input mask next field characters
Input mask operations
Input mask literals
Input mask output examples
Output Examples
Common Name Input Mask
URL Resources
Special escape sequences
Page
Appendix B Wireless Technology
Overview of Wireless Technology
Terminology
CERTIFICATES CA
MVP-8400i 8.4 Modero ViewPoint Touch Panel with Intercom 165
EAP Authentication
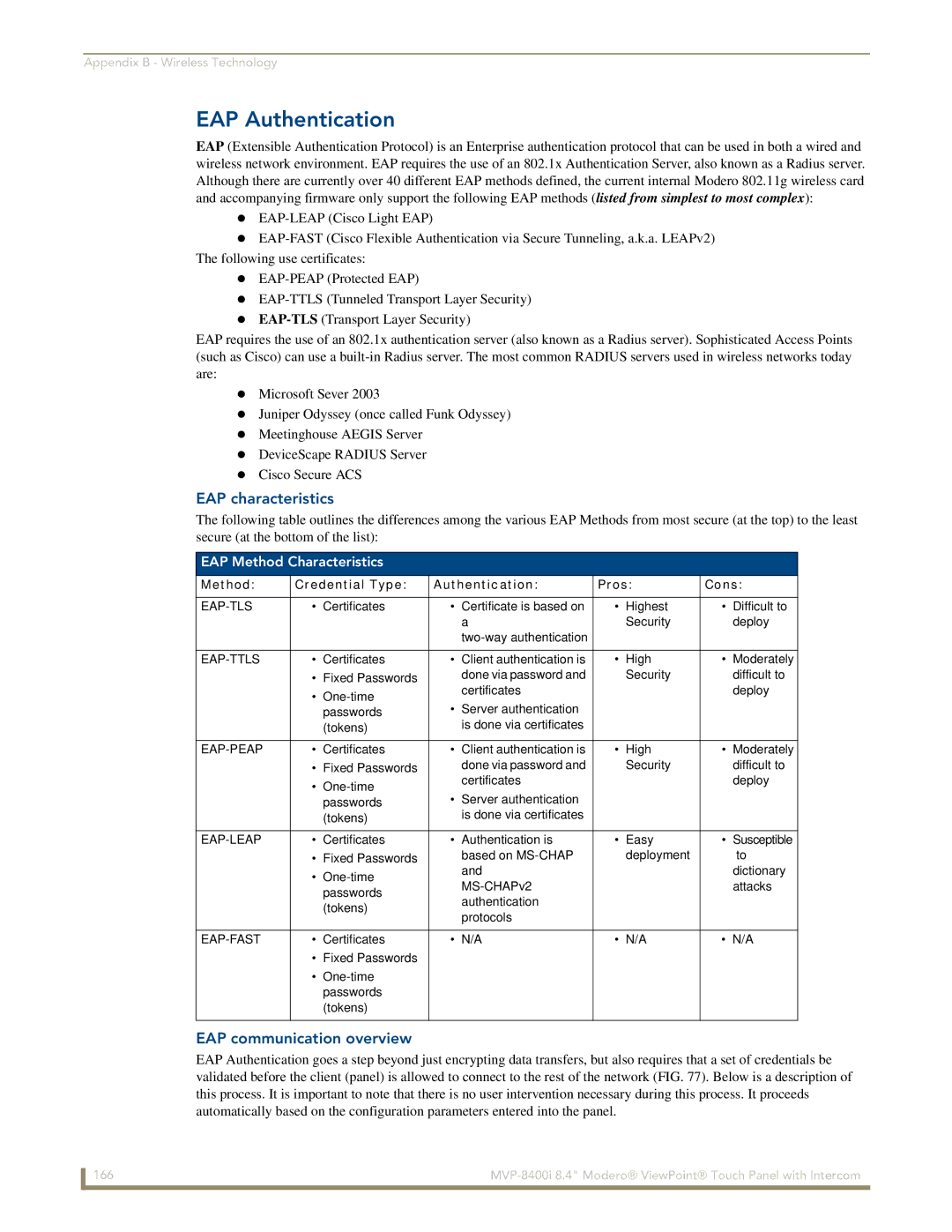
EAP characteristics
EAP Method Characteristics
Method Credential Type Authentication
AMX Certificate Upload Utility
Configuring your G4 Touch Panel for USB Communication
Setup the Panel and PC for USB Communication
Confirm the Installation of the USB Driver on the PC
How to Upload a Certificate File
Erasing All Certificates From the Touch Panel
Appendix C Troubleshooting
USB
Using USB for Virtual Master communication NetLinx Studio
Checking AMX Usblan Device Connections via NetLinx Studio
USB Driver
Panel Not in Listed as a Connected Device
Connection Status
Panel Doesn’t Respond to Touches
Batteries Will Not Hold or Take a Charge
Modero Panel Isn’t Appearing in The Online Tree Tab
MVP Can’t Obtain a Dhcp Address
My WEP Doesn’t Seem to Be Working
NetLinx Studio Only Detects One of My Connected Masters
Can’t Connect to a NetLinx Master
Only One Modero Panel in My System Shows Up
Panel Fails to Charge in MVP-WDS
Page
It’s Your World Take Control