DI-1162 Remote Access Router
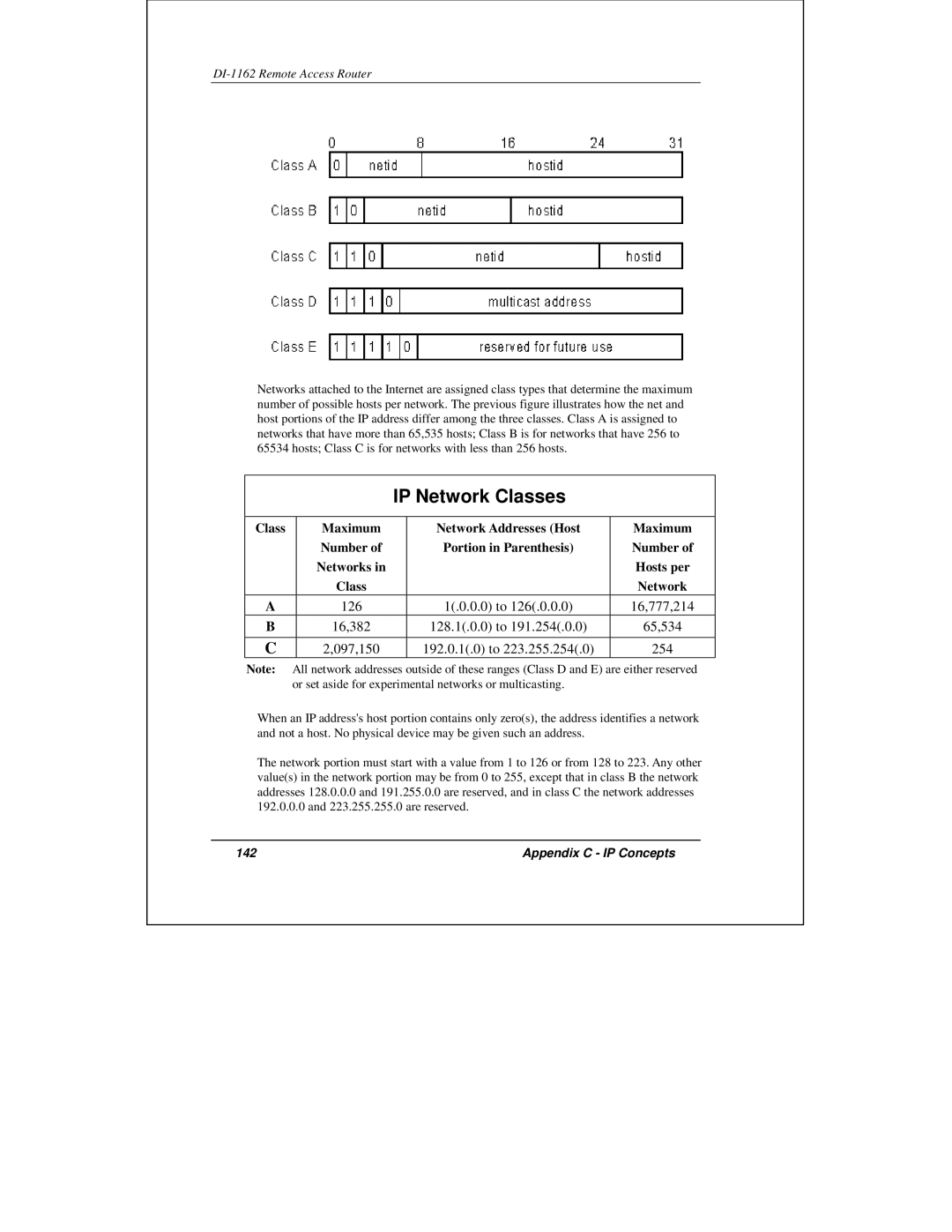
Networks attached to the Internet are assigned class types that determine the maximum number of possible hosts per network. The previous figure illustrates how the net and host portions of the IP address differ among the three classes. Class A is assigned to networks that have more than 65,535 hosts; Class B is for networks that have 256 to 65534 hosts; Class C is for networks with less than 256 hosts.
IP Network Classes
Class | Maximum | Network Addresses (Host | Maximum |
| Number of | Portion in Parenthesis) | Number of |
| Networks in |
| Hosts per |
| Class |
| Network |
A | 126 | 1(.0.0.0) to 126(.0.0.0) | 16,777,214 |
B | 16,382 | 128.1(.0.0) to 191.254(.0.0) | 65,534 |
C | 2,097,150 | 192.0.1(.0) to 223.255.254(.0) | 254 |
Note: All network addresses outside of these ranges (Class D and E) are either reserved or set aside for experimental networks or multicasting.
When an IP address's host portion contains only zero(s), the address identifies a network and not a host. No physical device may be given such an address.
The network portion must start with a value from 1 to 126 or from 128 to 223. Any other value(s) in the network portion may be from 0 to 255, except that in class B the network addresses 128.0.0.0 and 191.255.0.0 are reserved, and in class C the network addresses 192.0.0.0 and 223.255.255.0 are reserved.
142 | Appendix C - IP Concepts |