05/2000 6GK1970-5CA20-0AA1 Release
Simatic NET Profibus Networks Manual
Qualified Personnel
Safety Guidelines
Correct Usage
Trademarks
Symbols
Symbols
Contents
Active Components for RS-485 Networks
Passive Components for RS-485 Networks
Testing Profibus
Active Components for Wireless Networks
Passive Components for Electrical Networks
Passive Components for PROFIBUS-PA
Installing LAN Cables
Installing Network Components in Cubicles
Dimension Drawings
Index Index-1
Glossary-1
Page
Profibus Networks
Distributed Systems
Communication Systems
Simatic NET
Overview of the Simatic NET System
AS-Interface
Industrial Ethernet/Fast Ethernet
Attachable Systems
Basics of the Profibus Network
Transmission Media
Standards
Token BUS/Master-Slave Method
Access Techniques
Active and Passive Nodes
Transmission Techniques
Transmission Techniques According to EIA Standard RS-485
EIA Standard RS-485
Advantages
Properties of the RS-485 Transmission Technique
Restrictions
Transmission Techniques for Optical Components
Profibus User Organization Guideline
Integrated Optical Interfaces, OBT, OLM
OBT
Characteristics of the Optical Transmission Technique
Transmission Technique for Wireless Infrared Technology
Characteristics of the IEC 61158-2 Transmission Technique
Transmission Technique for PROFIBUS-PA
IEC 61158-2 Standard
Page
Topologies of Simatic NET Profibus Networks
Transmission Rate
Topologies of RS-485 Networks
LAN Cable
Node Attachment
Components for Transmission Rates up to 1.5 Mbps
Connecting Segments Using RS-485 Repeaters
Components for Transmission Rates up to 12 Mbps
Interfacing Electrical and Optical Networks/Components
Topologies of Optical Networks
Topology with Integrated Optical Interfaces
Topologies with OLMs
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT
OLMs
Example of a Bus Topology with OLMs
Bus Topologies
Optical Channels
Star Topologies with OLMs
Redundant Optical Rings using OLMs
Monitoring FO Links
Mixed Structure
Topologies of Simatic NET Profibus Networks
Alternative Cabling Strategy
Combination of Integrated Optical Interfaces and OLMs
Maximum Length of a Link
Topologies of Wireless Networks
Point-to-Point Link
Infrared Link Module ILM
Point-to-Point Link with Two Profibus ILMs
Point-to-Multipoint Link
ILM Profibus
Topologies with PROFIBUS-PA
Field Device Power Supply via PROFIBUS-PA
Bus and Star Topology
SpliTConnect System
Expansion
Total Cable
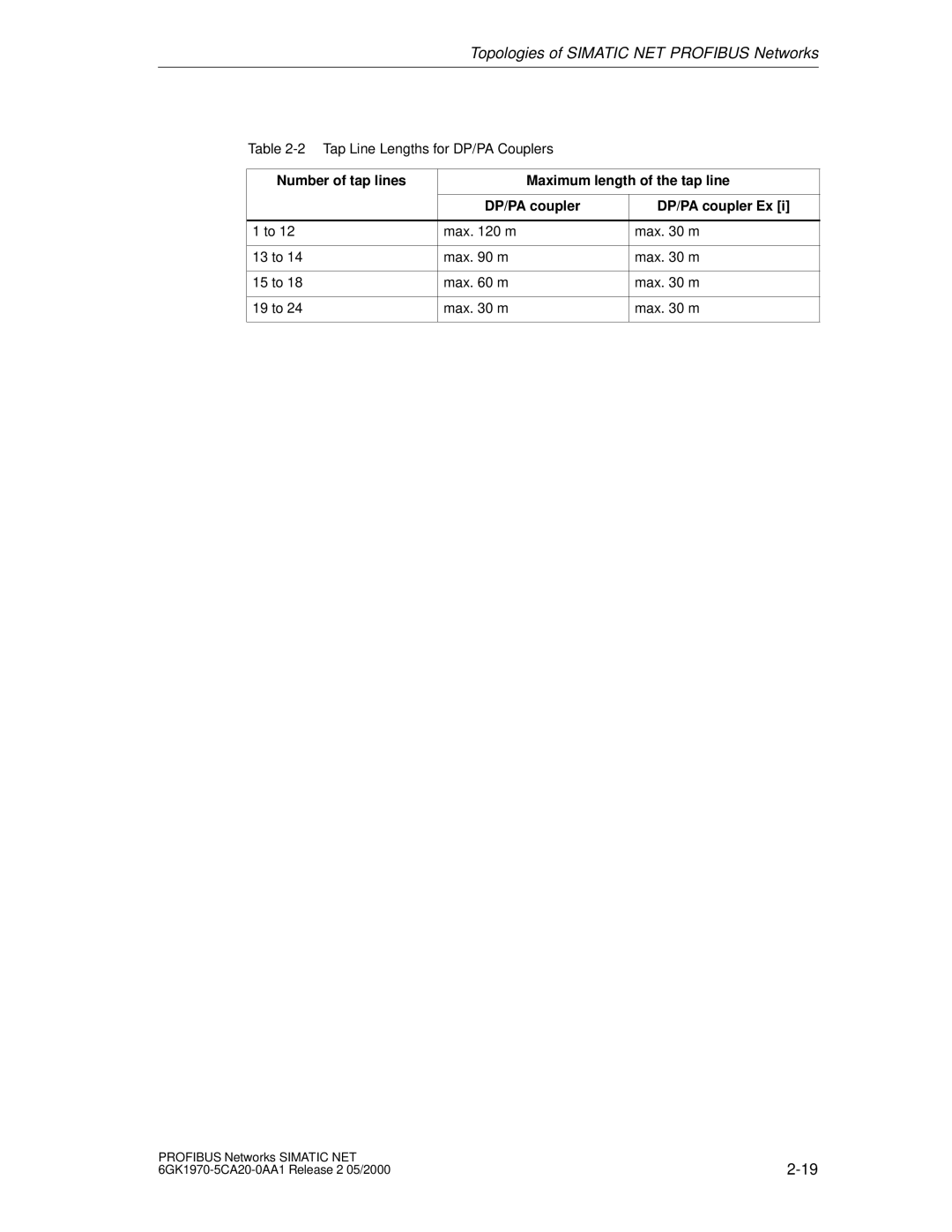
Tap Line
Tap Line Lengths for DP/PA Couplers
Uses
Connectivity Devices 1 DP/DP Coupler
Parameter Assignment
How the DP/DP Coupler Works
DP/PA Bus Coupling
Connecting to PROFIBUS-PA
Uses of the DP/PA Coupler
3 DP/PA Coupler
Configuring the DP/PA Coupler
Properties of the DP/PA Coupler General
Properties of the DP/PA Coupler Ex
4 DP/PA Link
Definition
DP/PA Link
How the DP/PA Link Works
Properties
DP/PA Link
PA master
Rules
18 DP/RS-232C Link for PROFIBUS-DP
Connecting PROFIBUS-DP to RS-232C
Device
How the DP/RS-232C Link Works
20 DP/AS-Interface Link
Connecting with the DP/AS-Interface Link
DP/AS-Interface Link
How the DP/AS-Interface Link 65 Works
22 DP/AS-Interface Link
23 Example of a Configuration with DP/AS-Interface Link
How the DP/AS Interface Link 20 Works
24 DP/EIB Link
Connecting PROFIBUS-DP to instabus EIB
Industrial Automation
Building Automation
S7-300 ET 200M
How the DP/EIB Link Works
Instabus EIB
Configuring
Page
Configuring Networks
Configuring Electrical Networks
Profibus Networks
Parameters
Transmission Rates up to a Maximum of 500 Kbps
Segments for Transmission Rates up to a Maximum of 500 Kbps
Length of the Tap Lines
Segments for a Transmission Rate of 1.5 Mbps
Transmission Rate 1.5 Mbps
Node Attachments at 1.5 Mbps
Value Factors
Rules
Between two DTEs 10 m
Transmission Rate up to a Maximum of 12 Mbps
Segments for Transmission Rates up to a Maximum of 12 Mbps
RS-485 Repeater
Configuring Electrical Networks with RS-485 Repeaters
Configuring
Configuration Parameters for Optical Networks
Configuring Optical Networks
Introduction
How a Fiber-Optic Cable Transmission System Works
Transmission Path
Transmitter
Attenuation
Receiver
Optical Power Budget
Optical Power Budget of a Fiber-Optic Transmission System
Plastic and PCF FO Cables
Power Budget
Glass FO Cables
Splices
Work Sheet
Link Power Margin
Fiber-optic cable
Cable Lengths for Plastic and PCF FO Paths
For 1 Network =
Lengths between two Nodes in m
Calculation Examples
Mixing Plastic Fiber-Optic and PCF Fiber-Optic
Attenuation of the transmission path
Link power margin
AFOC =
Number * aSpl
12 dB
10.0 dB
Blank form for a power budget using OLMs
Transmission Delay Time
Creating a System Overview
Configuring Optical Buses and Star Topologies with OLMs
Properties Profibus Dialog
Setting the Profibus Properties
Options Cables Tab
Entering the Cabling Configuration
Bus Parameters Adapted to the System
Checking the Bus Parameters
Configuring Redundant Optical Rings with OLMs
Configuration of a Non-existent Node
Raising the Retry Value to at Least the Value
Checking and Adapting the Slot Time
Transmission Rate
Example of Configuring the Bus Parameters in Step
Structure of the Network Example
Transmission rate Minimum slot Time
Entering the Bus Parameters
Calculation of the Slot Time
Bus Parameters/User-Defined Dialog
Passive Components for RS-485 Networks
Simatic NET Profibus Cables
Profibus Cables
Overview
LAN Cables for Profibus
UV resistance
Sienopyr FR
Passive Components for RS-485 Networks
FC Standard Cable 6XV1 830-0EH10
FC Standard Cable
LAN Cable with Halogen-free Outer Sheath 6XV1 830-0LH10
FC-FRNC Cable LAN cable with halogen-free outer sheath
FC Food Cable 6XV1 830-0GH10
FC Food Cable
FC Robust Cable 6XV1 830-0JH10
FC Robust Cable
Profibus flexible cable 6XV1 830-0FH10
Profibus Flexible Cable
Properties
FC Underground Cable
FC Underground Cable 6GK1 830-3FH10
Filler
Trailing Cable 6XV1 830-3EH10
FC Trailing Cable
Properties
Segment Lengths
Example of Using the Profibus Trailing Cable in a Drag Chain
Passive Components for RS-485 Networks
Festoon Cable 6XV1 830-3GH10
Profibus Festoon Cable
10 Installation of the Profibus Festoon Cable Schematic
Passive Components for RS-485 Networks
11 Use of the Profibus Cable for Festoons
Installation Guidelines
SIENOPYR-FR Marine Cable
SIENOPYR-FR Marine Cable 6XV1830-0MH10
Inner sheath
Uses
FastConnect System
FastConnect Bus Connector
Designed for Industry
Functions
OLM
Order numbers 6ES7 0BA50-0XA0 0BB50-0XA0 6GK1 0FC00
Technical Specifications
Bus Connector with PG Socket
Disconnecting a Station
Pinout of the Sub-D Male Connector
Pin Signal Meaning Name
Passive Components for RS-485 Networks
Using the FastConnect Stripping Tool for Preparing FC Cables
OFF
Bus Connectors
FMS/DP
Appearance
6ES7 972-0BB40-0XA0 0BA30-0XA0 500-0EA02
Order 6ES7 972-0BA11-0XA0 6ES7 972-0BA40-0XA0 6GK1 Numbers
PG socket
Disconnecting a Station
Siemens
Appearance 6ES7 972-0B.11
First and last station on Further stations on the bus
Connecting Up the LAN Cable
Passive Components for RS-485 Networks
Appearance 6ES7 972-0BA30-0XA0
18 Bus Connector order number 6ES7 972-0BA30-0XA0
Cable guides Insulation displacement terminals
Appearance 6ES7 972-0B.40
Connecting the LAN Cable to Bus Connector 6ES7 972-0B.40
23 Connecting the LAN Cable to Bus Connector 6ES7 972-0B.40
Appearance 6GK1500-0EA02
Installing the Bus Connector with Axial Cable Outlet
Fitting the Bus Connector
Removing the Bus Connector
Plugging the Bus Connector into the Module
Possible disturbance of data traffic on the bus
Bus terminal RS-485 Bus terminal 12 M
Bus Terminals for RS-485 Networks Versions
Bus Terminal RS-485
Design and Functions of the RS-485 Bus Terminal
RXD/TXD-P
28 RS-485 Bus Terminal with Additional PG Interface
Additional PG Interface
29 12M Bus Terminal BT12M
Design and Functions of the 12M Bus Terminal
30 Operator Controls
Bus terminal 12 M
Termination
Restriction when using the 12M bus terminal at 500 Kbps
Mounting/Attaching the LAN Cables
31 Drilling Diagram for the Bus Terminal
Passive Components for RS-485 Networks
Passive Components for RS-485 Networks
Grounding
33 Ways of Installing and Grounding the Bus Terminal
Wall Mounting
Technical Data of the RS-485 Bus Terminal
Technical Data of the RS-485 Bus Terminal
Technical Data of the 12M Bus Terminal
Technical Data of the 12M Bus Terminal
Electromagnetic Compatibility
Climatic Conditions
Mechanical Conditions
Construction
Test Marks
Cable Connection without Bus Connection Elements
Cable Connections Cable Connections to Network Components
All-round shielding of the LAN cable must be retained
Avoid accidental shield contact with the environment
Keep to the permitted ambient conditions
Function
Preassembled Connecting Cables 1 830-1T Connecting Cable
Simatic NET 830-1T connecting cable
35 830-2 Connecting Cable
2 830-2 Connecting Cable
Simatic NET 830-2 connecting cable
Active Components for RS-485 Networks
Using the RS-485 Repeater 6ES7 972-0AA01-0XA0
What is an RS-485 Repeater?
RS-485 Repeater
Design of the RS-485 Repeater
Layout of the Repeater Function
Pinout of the Sub D Connector PG/OP Connector
Technical Specifications
Layout Pin no Signal name Meaning
Block Diagram of the RS-485 Repeater
Block Diagram
Possible Configurations with the RS-485 Repeater
Terminating Resistor On/Off
Off
Segment 1 Terminated, Segment 2 Connected Through
Segments 1 and 2 Terminated
Segment
Terminating resistor
Terminating resistor Bus segment 2 off
Segments 1 and 2 Connected Through
Installing and Uninstalling the RS-485 Repeater
Installing the RS-485 Repeater on an S7-300 Rail
Installation on an S7-300 Rail
Installation on a Standard Rail
Removing the Repeater from an S7-300 Rail
Removing the RS-485 from the Standard Rail
Ungrounded Operation
Ungrounded Operation of the RS-485 Repeater
Connecting the Power Supply
Connecting the Power Supply
Cable Type
Connecting the Profibus Cable
Connecting the LAN Cable
Profibus Terminator
What is a Profibus Terminator?
Order number
Design of the Profibus Terminator
Lists the technical data of the Profibus terminator
Standard cable 6XV1 830-0EH10
Page
Passive Components for PROFIBUS-PA
PVC outer sheath
FC Process Cable
SpliTConnect Tap
How the SpliTConnect Tap Works
Produktinformation
Simatic NET
Personnel qualification requirements
Insert the strand holder 6 onto the not stripped off strands
Grounding
Hinweis
SpliTConnect Coupler
SpliTConnect Terminator
Technische Daten /Technical Data
Passive Components for Electrical Networks
Fiber-Optic Cable FO
Fiber-Optic Cables
Plastic Fiber-Optic Cables
Plastic Fiber-Optic Cables
Properties of Fiber-Optic Cables
Properties of Fiber-Optic Cables
Plastic Fiber Optic, Duplex Cord
Plastic FO Cable, Duplex Cord 6XV1821-2AN50
Core Cladding Jacket buffer
Simatic NET Profibus Plastic Fiber Optic, Duplex Cord
Fiber-Optic Cables
Plastic FO Cable, Standard Cable 6XV1821-0A
Plastic Fiber-Optic, Standard Cables
Simatic NET Profibus plastic fiber-optic, standard cable
Standard lengths
PCF Fiber-Optic Cables
PCF FO Cable, Standard Cable 6XV1821-1B
PVC outer jacket Kevlar strain relief PCF fibers
Simatic NET Profibus PCF fiber-optic cable
Passive Components for Electrical Networks
Glass Fiber-Optic Cables
Simple Configuration
Simatic NET Standard Fibers
Guidelines for Laying Cables
TB3 Frnc or
Cable Type Fiber-Optic Standard Cable Indoor Fiber-Optic
Cable Type Fiber-Optic Indoor Fiber-Optic Standard Cable
Cable Type Flexible Fiber-Optic
Trailing Cable Duplex Fiber-Optic Marine Cable
13.3 ±
Fiber-Optic Standard Cable
Fiber-Optic Standard Cable
Indoor Fiber-Optic Cable
Indoor Fiber-Optic Cable
Flexible Fiber-Optic Trailing Cable
Flexible Fiber-Optic Trailing Cable
Uses
Passive Components for Electrical Networks
Sienopyr Duplex Fiber-Optic Marine Cable 6XV1 830-0NH10
Sienopyr Duplex Fiber-Optic Marine Cable
Ordering
Special Cables
Special Cables
Fiber Types
Cable Structures
Ordering
Fiber-Optic Connectors
Connectors for Plastic Fiber-Optic Cables
Requirements
Order Numbers
Accessories
Cable Lengths
Instructions for Assembling Plastic Fiber-Optic Cables
Installing Plastic Fiber-Optic Cables
Bfoc Connectors for OLMs
Connectors for Glass Fiber Cables
Bfoc Connectors for Glass Fiber-Optic Cables
Preassembled Cables
Fitting Connectors On-Site
Page
Active Components for Optical Networks
Optical Bus Terminal
Optical Bus Terminal OBT
6GK1 500-3AA00
Operating Instructions
Optical Link Module OLM
Design
Functions
Profibus OLM/P11
Page
Active Components for Wireless Networks
Infrared Link Module ILM
Profibus ILM
Ordering Data
Page
Testing Profibus
Hardware Test Device BT200 for PROFIBUS-DP Possible Uses
Area of Application
Logging Functions
Figure A-1 Hardware Test Device BT200 for Profibus DP
Design
Functions
Checking the Accessibility of Nodes
Checking the Profibus Cable
Checking the RS-485 Interface of a Slave
How the Unit Functions
Ordering Data
Testing FO Transmission Paths Necessity of a Final Test
Optical Power Source and Meter
Test Methods
Evaluating the Results of the Attenuation Measurements
Arrangement for Measuring Attenuation
Figure A-3 Optical Time Domain Reflectometer Otdr
Optical Time Domain Reflectometer Otdr
Figure A-4 How an Otdr Functions
How an Otdr Functions
Otdr provides the measurement results graphically
Otdr Evaluation
Checking the Optical Signal Quality with Profibus OLM
OLM/G12
Page
Page
Protecting LAN Cables from Lightning
Why Protect Your Automation System From Overvoltage?
Further Literature
Bus Cables within Buildings
Coarse Protection
LAN Cables between Buildings
PLC PLC
Instructions for Installing Coarse Protection
Instructions for Installing Fine Protection
Page
Page
Installing LAN Cables
LAN Cables as Important Plant Connections
LAN Cables in Automation Systems
Keep the Overall System Concept in Mind
Networking Simatic with Simatic NET
Power Supply Voltage
Electrical Safety
DC Power Supply
Protection from External Electrical Influences
Mechanical Protection of LAN Cables
Protection of Electrical and Optical LAN Cables
Mechanical Protection
Do not kink or crimp the trailing and festoon cables
Redundant LAN Cables
Install LAN cables separately
Electromagnetic Compatibility of LAN Cables
Measures to Counter Interference Voltages
Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC
Using the Shields of Electrical LAN Cables
Installation and Grounding of Inactive Metal Parts
Grounding
Cable Shields
Handling the Shield
Equipotential Bonding
When do potential differences occur?
When and why is equipotential bonding necessary?
How do you avoid potential differences?
Rules for Equipotential Bonding
Installing LAN Cables
Cable Categories and Clearances
Routing Electrical LAN Cables
How to Read the Table
Conditions
Clearance Table
Cables for Lay
Within closets
Outside closets
Cabling within Buildings
Cabling within Closets
Cabling outside Buildings
Fiber-optic cables should be given preference
EMC Rules for Electrical LAN Cables
Power Supply for Programming Devices
Connecting Switched Inductances to Suppressors
Special Noise Suppression Measures
Underground Cabling
Cabinet Lighting
Electromagnetic Compatibility of Fiber-Optic Cables
Pull Cables Using Cable Grips and Protect Connectors
Temperatures
General
Storage and Transportation
Pressure
Fitting Strain Relief
Torsion
Do not twist trailing cables and festooned cables
Installing other Cables
Avoid Loops
Attachments to Profibus Cables
Additional Instructions on Installing Fiber-Optic Cables
Attaching Profibus Fiber-Optic Cables
Page
Page
Installation Instructions for Simatic NET
Simatic NET
Copyright Siemens AG All Rights Reserved
Personnel qualification requirements
Page
Page
Setting the Cutting Depth of the Cable Knife
Page
Separating the Simatic NET Plastic Fiber Optic Duplex Cord
Removing the Buffer
Fitting Simplex Connectors
Connector must be towards the center
Simatic NET Profibus Plastic Fiber Optic, standard cable
Simatic NET Profibus Plastic Fiber Optic, duplex cord
Simatic NET Profibus Plastic Fiber Optic Stripping Tool Set
Plug adapter
Other commercially available accessories
Simatic NET
Personnel qualification requirements
Page
Setting the Cutting Depth of the Cable Knife
Foil working from the end of the cable
Separating the Simatic NET Plastic Fiber Optic Duplex Cord
Removing the Buffer
Crimping the Bfoc Connector
Grinding and Polishing Bfoc Connectors
Page
Simatic NET Profibus Plastic Fiber Optic Duplex cord
Simatic NET Profibus Plastic Fiber Optic Standard cable
Simatic NET Profibus Plastic Fiber Optic Bfoc crimping tool
Simatic NET Profibus Plastic Fiber Optic Bfoc polishing set
Other commercially available accessories
Simatic NET Profibus PCF Fiber Optic Standard Cable
Personnel qualification requirements
Simatic NET Profibus PCF Fiber Optic Standard Cable
Using the Pulling Loop
Marking Simatic NET Profibus PCF Fiber Optic Standard Cable
For connecting OLM/P
Assembled with 2 x 2 Bfoc connectors
Simatic NET Profibus PCF Fiber Optic, standard cable
Simatic NET Profibus PCF Fiber Optic cable
Installing Network Components Cubicles
IP Degrees of Protection
IEC 60529, EN
Code Contact and Solid Body Water Protection Number
Degree of Protection
Simatic NET Components
Outdoor Installation
Ventilation Openings
Heat Dissipation
Standards
Dimension Drawings
Figure F-2 Bus Connector to IP 20 6ES7 972-0BA30-0XA0
Dimension Drawings of the Bus Connectors
On OFF Siemens
Figure F-6 FastConnect Bus Connector 6GK1 500-0FC00
Figure F-7 RS-485 Repeater on Standard Rail 125
Dimension Drawings of the RS-485 Repeater
Figure F-9 Profibus Terminator 40.3 44.5
Dimension Drawing of the Profibus Terminator
Figure F-10 RS-485 Bus Terminal on 15 mm high Standard Rail
Dimension Drawings of the RS-485 Bus Terminal
Figure F-11 BT12M Bus Terminal on 15 mm high Standard Rail
Dimension Drawings of the BT12M Bus Terminal
Dimension Drawings of the Optical Bus Terminal OBT
Simatic NET
Sieme N S
Dimension Drawings Infrared Link Module ILM
Dimension Drawings Optical Link Module OLM
Dimension Drawings
Page
Operating Instructions ILM / OLM / OBT
Operating Instructions ILM / OLM / OBT
Simatic NET
Attenzione
Simatic NET Profibus ILM
Personnel qualification requirements
General
Installation and Startup
Modes and Settings
Installing the Profibus ILM
Signaling Contact Displays
Help With Problems During Operation
Product
Symbols
Introduction
Description of the Device
Siemens Profibus ILM
Topologies
Transmission Rate
Point-to-Point Link with Two Profibus ILMs Slave
Point-to-Point-Link
Infrared Link Modul ILM 6ZB530-3AC30-0BA1
Slave
Page
ILM
Point-to-Multipoint Link
Infrared transmission link 2 0.5 to 15 m
Signal Regeneration
Monitoring the Received Optical Level
Constant Light Monitoring
Monitoring the Optical Link
Monitoring the Optical Receive Activity
Monitoring the Optical Link with an Acknowledgment Pulse
Infrared Link Modul ILM 6ZB530-3AC30-0BA1
Modes and Settings
Setting the Terminating Resistor
Setting the Transmission Rate
Operation With Acknowledgment Pulse
3 4 5 6 7 8 Setting
Operation with Signaling Contact
3 4 5 6 7
Installation and Startup
General Notes on Installation and Startup
6ZB5530-3AC30-0BA1 Infrared Link Modul ILM
Installing the Profibus ILM
6ZB5530-3AC30-0BA1 Infrared Link Modul ILM
Thickness of sheet Approx mm depending on
Siemens
ILM
Screw M6 x By turning
Connecting the Electrical RS 485 Bus Cables
6ZB5530-3AC30-0BA1 Infrared Link Modul ILM
Connecting the Power Supply and the Signaling Contact
20 to 30 Max Max mA Max a NEC Class
Displays
Status Displays for Incorrect Operation
LED Display Possible Causes Signaling Contact
LOW LED
6ZB5530-3AC30-0BA1 Infrared Link Modul ILM
Errors Due to Incorrect Network Configuration
Delay Time of the Profibus ILM
Delay Time of Further Active Profibus Network Components
Transmission Delay Time TTD
Technical Specifications
6ZB5530-3AC30-0BA1 Infrared Link Modul ILM
Infrared Link Modul ILM 6ZB530-3AC30-0BA1
Illumination Range
LOW LED displays critical receive levels
Appendix
References
Product name
Installation Guidelines
EMC 89/336/EEC
Area of application
Copyright by Siemens
OLM/P11
Qualified personnel
Safety Instructions
Certified usage
Trademarks
Contents
Order Numbers
Introduction
OLM
Operating mode related functions
Non operating mode related functions
Line monitoring with echoes
General Functions Operating mode related functions
Send echo
Monitor echo
Please note
Line topology
� Monitoring mechanisms
Line topology without optical fiber link monitoring
Network structure in an optic star topology
Star topology
Network structure in a redundant optical ring topology
Redundant optical ring
� Monitoring mechanisms
Safety notice
OLM/G11-1300
OLM/G12-1300
General information about setting up
DIL switch S7 compatibility in Position
Setting the compatibility
Operating mode Electrical Port without segment monitoring
Setting the operating mode
Setting the operating mode of the optical ports CH2, CH3
Operating mode Line without optical fiber link monitoring
Operating mode Redundant optical ring
Installation Connecting the optical lines
Mounting the modules
Mounting on a hat rail
Mounting on a mounting plate
Observe the following safety notice
Connecting the electric RS 485 bus lines
Connecting the signaling contact lines
Connecting the power supply
Measuring sockets
Defining the receiving level of the optical ports
LED Indicators
LED Indicators and Troubleshooting
What the LED indicators and signaling contacts mean
Fault indicated on the system LED
Troubleshooting
Fault indicated on CH1
Fault indicated on CH2 / CH3
Version 1.0 8/00
Configuration of redundant optical rings
Configuration of optical line and star topologies
Constants for calculating the slot time at DP standard
Signal transmission
Voltage/power supply
Retimer
Safety
Electromagnetic compatibility EMC
Climatic ambient conditions
Mechanical ambient conditions
CE Designation
List of abbreviations
Literature notes
Measuring sockets
Function not guaranteed
Simatic Training Centers
Simatic NET Support and Training
Simatic Customer Support Hotline
Nuremberg Nürnberg Johnson City Singapore Singapur
Simatic Customer Support On-line Services
Source for special cables
Further support
Page
Manual
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT
Copyright Siemens AG 1998 All rights reserved
Installation and Startup
10-1
Network Topology
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT C79000-G8976-C122-02
OBT
Introduction
Operating Mode
Power Supply
Connections
Sensitivity
Simatic NET Profibus OBT Product
Supplied
Not supplied
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT C79000-G8976-C122-02
Optoelectric Signal Conversion and Signal Regeneration
Functional Description
Interfaces
Automatic Transmission Rate Detection
Supported FO Fiber Types
Displays
CH1, CH2 , CH3 channel 1 to 3, yellow
+ 24V green
Operator Controls
Optical Bus
Network Topology
OLM/G11 OBT
Using Long Fiber Optic Sections
Example of Attaching RS-485 Segments
Attaching RS-485 Segments
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT C79000-G8976-C122-02
Installation and Startup
Installation and Startup
Precedure for Installation
Installing the Profibus OBT
Installation
Installing a Module on a Mounting Plate
Installation on a Mounting Plate
PE M L+ NEC CLASS2
C D
Connecting the Optical Cables
Connecting the Electrical RS-485 Cable
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT C79000-G8976-C122-02
LED Display Possible Cause of Problem
Troubleshooting
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT C79000-G8976-C122-02
Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT C79000-G8976-C122-02
Product Name
Installation Instructions
EU Directive EMC 89/336/EEC
Information for Manufacturers of Machines
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT
Siemens AG
References
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT C79000-G8976-C122-02
ISO/OSI
Abbreviations
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT C79000-G8976-C122-02
Simatic NET A&D PT2
Profibus Optical Bus Terminal OBT C79000-G8976-C122-02
Abbreviations/Acronyms
General Information
General Information
Standards, Manuals and Further Information
References
Order Numbers
Further Information
Page
Simatic Training Center
Simatic NET Support and Training
Simatic Customer Support Hotline
Nuremberg Johnson City Singapore Simatic Basic Hotline
Ordering Special Cables, Accessories, and Tools
Simatic Customer Support Online Services
Further Support
Simatic Premium Hotline
Glossary
Ground
GAP factor
Lightning protection equipotential bonding
Lightning arresters
Master
Master-slave technique
Optical power loss FO
Optical power budget FO
MaxTSDR
MinTSDR
Reaction time
Signal propagation time
Redundancy
Reference potential
Slave
Simatic NET PC modules
Softnet for Profibus
Standard rail
Token rotation time
Token ring
Page
Index
Index