USER’S Guide
Certification
Warranty Information
General
Safety Summary
Safety Symbols
EMC
Declaration
Declaration of Conformity
Printing History
Acoustic Noise Information
Table of Contents
DVM Connections
Checkout Procedure Case of Trouble
VXIplug&play Power Products Instrument Drivers
Types of Scpi Commands
Triggering Output Changes
Types of Scpi Messages
Scpi Data Formats
Introduction Programming the Output
Measurement Commands 104
Inhibit/Fault Indicator
Calibration Commands 100
Display Commands 103
Trigger Commands 126
Output Commands 114
Status Commands 121
System Commands 125
Performing the Calibration Procedure 154
Common Commands
Additional Commands
Specifications 143 Supplemental Characteristics 144
Introduction 177
Error Number List 161
Introduction 165
Basic
Front Panel At a Glance
Quick Reference
Use the front panel Address key to configure the interface
Instrument Configuration
Rear Panel At a Glance
Use the Function keys and Entry keys to enter a new value
Front Panel Number Entry
Immediate Action Keys
Front Panel Annunciators
Front Panel Menus At a Glance
ABORt CALibrate
Scpi Programming Commands At a Glance
Installing the VXIplug&play instrument driver
Using the front panel
Using the programming interface
Programming the unit using Scpi COMPatibility commands
Description
Safety Considerations
Options and Accessories
Option
Agilent 66309D
Description and Model Differences
Agilent
Agilent 66309B
Front Panel Controls
Common Capabilities
Remote Programming
Dc Source Output 1 Characteristic
Output 1 Characteristic
Output 2 Characteristic
Output 2 Characteristic
Option 521 Description Agilent 66309B/D only
Option 521 Factory Settings
Option 521 Relay Modes
Page
Check the Phone Connections
Installation and Operation Checklist
Check the Operating Settings and Conditions
Additional Agilent 66311/66309 Operating Settings Checks
Damage Packaging Material
Cleaning
Inspection
Location
Rack Mounting
Connect the Power Cord
Input Connections
Bench Operation
Current Ratings
Turn the unit off before connecting any wires
Output Connections
Output
Remote Sense Connections
Remote Sense Connections
Remote Sense Connections with External Relays
Maintaining Stability while Remote Sensing
Load Regulation and Voltage Drop in the Remote Sense Leads
Open Sense Lead Protection
Message Description
Local Sensing
Output Compensation
OVP Considerations
DVM Connections
Measuring Circuits Not Powered by the Main Output
Measuring Circuits that are Not Powered by the Main Output
Measuring Circuits Floating with Respect to the Main Output
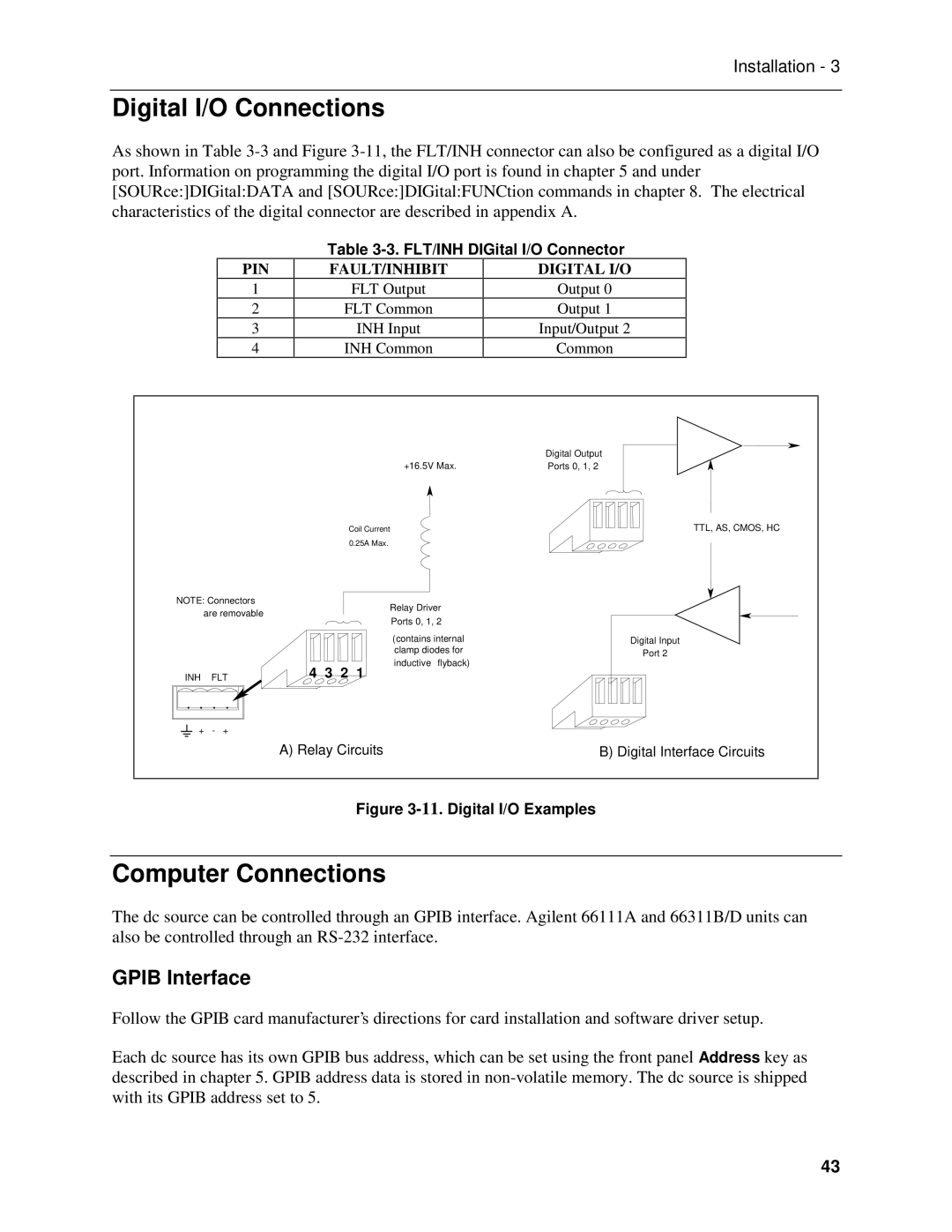
10. FLT/INH Examples
External Protection Connections
Gpib Interface
FLT/INH DIGital I/O Connector
Digital I/O Connections
Computer Connections
Pin Input/Output Description
RS-232 Interface
Press Protect
Checkout Procedure
Procedure Display Explanation
Press Output On/Off
Procedure Display Explanation
Enter Number 12, Enter Press Output On/Off
Selftest Error Messages
Case of Trouble
Press Shift, Channel
Line Fuse
Runtime Error Messages
Power-On Selftest Errors
Runtime Error Messages
Front Panel Description
Introduction
Front Panel Operation
System Keys
Display Command Function
OFF
Immediate Action Keys
Function Keys
Scrolling Keysq
Display Measurement
Metering Keys
Over Current
Output Control Keys
Entry Keys
Entry Keys
Selecting the DVM on Agilent 66311D/66309D units
Using the Front Panel Display
Examples of Front Panel Programming
Selecting an output on Agilent 66309B/D units
Typecap High
Set the output voltage
Set the output current limit
Set the output compensation
Keypad, press Enter Number, 7, Enter
Enable the output
Set the output 2 voltage
Set the output 2 current limit
Overcurrent
Querying and Clearing Output Protection and Errors
Disable Overvoltage Protection as follows
Query and Clear Errors as follows
Use the Meter menu for making front panel measurements
Making Basic Front Panel Measurements
Making Enhanced Front Panel Measurements
Default Front Panel Measurement Parameters
Currdet Acdc
Making DVM Measurements Agilent 66311D/66309D only
Use the Meter menu for making DVM measurements
Currrang Auto
Set the Gpib address as follows
Setting the Gpib Address and Programming Language
To configure the Ridfi mode of the port, proceed as follows
To configure the Digio mode of the port, proceed as follows
Storing and Recalling Instrument States
Gpib References
External References
Scpi References
System Requirements
VXIplug&play Power Products Instrument Drivers
Downloading and Installing the Driver
Supported Applications
Gpib Address
Accessing Online Help
Gpib Capabilities of the DC Source
RS-232 Capabilities of the DC Source
RS-232 Flow Control
Introduction to Scpi
Baud Rate
Conventions Used in This Guide
Types of Scpi Commands
Boldface font
Including Common Commands
Multiple Commands in a Message
Moving Among Subsystems
Headers
Using Queries
Types of Scpi Messages
Message Unit
Scpi Data Formats
Class Suffix Unit Unit with Multiplier
Scpi Command Completion
Suffixes and Multipliers
Response Data Types
Scpi Conformance Information
Using Device Clear
Scpi Conformed Commands
Non-SCPI Commands
Programming the Output
Power-on Initialization
Enabling the Output
Output Current
Output Voltage
Output Trigger Model
Setting the Voltage or Current Transient Levels
Triggering Output Changes
Scpi Triggering Nomenclature
Single Trigger
Enabling the Output Trigger System
Selecting the Output Trigger Source
Generating Triggers
Average Measurements
Making Basic Measurements
Controlling Measurement Samples
Window Functions
Making Enhanced Measurements
RMS Measurements
Current Ranges and Measurement Detector
Minimum and Maximum Measurements
Pulse Measurements
High/Low Measurements
Returning All Measurement Data From the Data Buffer
Making DVM Measurements
Measurement Trigger Model
Triggered Measurements
Sequence Form Alias SEQuence2 ACQuire
INTernal
Enabling the Measurement Trigger System
Selecting the Measurement Trigger Source
Selecting the Sensing Function
Single Triggers
Generating Measurement Triggers
Trigacqcouncurr number or Trigacqcounvolt number
Pre-trigger and Post-trigger Data Acquisition
Programming the Status Registers
DC Source Status Model
Power-On Conditions
Operation Status Group
Bit Configurations of Status Registers
Status Byte Register
PON Power On Bit
Questionable Status Group
Standard Event Status Group
RQS Bit
Determining the Cause of a Service Interrupt
Servicing Operation Status and Questionable Status Events
MSS Bit
Monitoring Both Phases of a Status Transition
Inhibit/Fault Indicator
Remote Inhibit RI
Pin
Discrete Fault Indicator DFI
Using the Inhibit/Fault Port as a Digital I/O
Bit Weight
Subsystem Commands
Subsystem Commands Syntax
Language Dictionary
Language Dictionary
Programming Parameters
Common Commands
CALibrateCURRentMEASureLOWRange
Calibration Commands
CALibrateCURRent
CALibrateCURRent2
CALibrateDVM
CALibratePASSword
CALibrateDATA
CALibrateDATE
CALibrateVOLTage2
CALibrateSAVE
CALibrateSTATe
CALibrateVOLTage
DISPlayMODE
Display Commands
DISPlay
DISPlayCHANnel
FORMat
Measurement Commands
104
Query Syntax
FORMatBORDer
MEASureARRayCURRent? FETChARRayCURRent?
MEASureARRayVOLTage? FETChARRayVOLTage?
NR3
MEASureCURRent? FETChCURRent?
MEASureCURRent2?
MEASureCURRentACDC? FETChCURRentACDC?
107
MEASureCURRentHIGH? FETChCURRentHIGH?
MEASureCURRentLOW? FETChCURRentLOW?
MEASureCURRentMAXimum? FETChCURRent MAXimum?
MEASureVOLTage? FETChVOLTage?
MEASureCURRentMINimum? FETChCURRentMINimum?
MEASureDVM? FETChDVM?
MEASureDVMACDC? FETChDVMACDC?
109
MEASureVOLTage2
MEASureVOLTageACDC? FETChVOLTageACDC?
MEASureVOLTageHIGH? FETChVOLTageHIGH?
110
MEASureVOLTageLOW? FETChVOLTageLOW?
MEASureVOLTageMAXimum? FETChVOLTageMAXimum?
MEASureVOLTageMINimum? FETChVOLTageMINimum?
111
SENSeCURRentDETector
SENSeCURRentRANGe
Query Syntax SENSeCURRentDETector?
SENSeSWEepPOINts
SENSeFUNCtion
SENSePROTectionSTATe
SENSeSWEepOFFSetPOINts
Query Syntax SENSeWINDowTYPE?
SENSeSWEepTINTerval
SENSeWINDow
Query Syntax SENSeSWEepTINTerval?
OUTPut1 2RELayMODE
Output Commands
INSTrumentCOUPleOUTPutSTATe
OUTPut1
115
OUTPutDFI
OUTPutDFISOURce
OUTPutPONSTATe
OUTPutTYPE
OUTPutPROTectionDELay
OUTPutPROTectionCLEar
OUTPutRIMODE
SOURceCURRent2
SOURceCURRent
117
SOURceCURRent2TRIGger
Command Syntax Parameters RST Value Examples
SOURceCURRentPROTectionSTATe
SOURceCURRentTRIGger
119
SOURceDIGitalDATA
SOURceDIGitalFUNCtion
SOURceVOLTage
120
SOURceVOLTage2
SOURceVOLTagePROTection
SOURceVOLTagePROTectionSTATe
SOURceVOLTage2TRIGger
Status Commands
STATusPRESet
SOURceVOLTageTRIGger
STATusOPERationCONDition?
STATusOPERationENABle
Bit Configuration of Operation Status Registers
STATusOPERation?
STATusQUEStionable?
Parameters Preset Value
Bit Configuration of Questionable Status Registers
STATusOPERationNTR STATusOPERationPTR
124
STATusQUEStionableENABle
STATusQUEStionableCONDition?
STATusQUEStionableNTR STATusQUEStionablePTR
SYSTemVERSion?
System Commands
SYSTemERRor?
SYSTemLANGuage
INITiateSEQuence INITiateNAME
Trigger Commands
Related Commands
ABORt
TRIGgerSOURce
TRIGger
127
128
TRIGgerSEQuence2 TRIGgerACQuire
TRIGgerSEQuence2COUNtCURRent TRIGgerACQuireCOUNtCURRent
TRIGgerSEQuence2COUNtDVM TRIGgerACQuireCOUNtDVM
Unit
TRIGgerSEQuence2COUNtVOLTage TRIGgerACQuireCOUNtVOLTage
129
130
TRIGgerSEQuence2HYSTeresisDVM TRIGgerACQuireHYSTeresisDVM
TRIGgerSEQuence2LEVelDVM TRIGgerACQuireLEVelDVM
TRIGgerSEQuence2LEVelCURRent TRIGgerACQuireLEVelCURRent
131
132
TRIGgerSEQuence2LEVelVOLTage TRIGgerACQuireLEVelVOLTage
TRIGgerSEQuence2SLOPeCURRent TRIGgerACQuireSLOPeCURRent
Returned Parameters
TRIGgerSEQuence2SLOPeVOLTage TRIGgerACQuireSLOPeVOLTage
TRIGgerSEQuence2SLOPeDVM TRIGgerACQuireSLOPeDVM
133
TRIGgerSEQuence1DEFine TRIGgerSEQuence2DEFine
TRIGgerSEQuence2SOURce TRIGgerACQuireSOURce
134
135
Common Commands
Command Syntax *CLS Parameters None
Bit Configuration of Standard Event Status Enable Register
Example
Field Information
136
137
Query Syntax *OPT? Returned Parameters Aard
RCL NRf
Parameters Example
Example *SAV Related Commands *RCL *RST 138
Command Syntax *SAV NRf
RST Settings
139
Power-on Value
Bit Configuration of Status Byte Register
Query Syntax *STB?
Query Syntax TST? Returned Parameters NR1
TRG
Additional Commands
VOLTagePROTectionTRIPped?
CURRentPROTectionTRIPped?
VOLTageLIMitHIGH?
VOLTageLIMitLOW?
Table A-1. Performance Specifications
Specifications
143
Agilent 66309B/D
Supplemental Characteristics
Table A-2. Supplemental Characteristics
144
145
146
Table A-4. Agilent 66309B/D Option 521 Characteristics
Table B-1. Equipment Required
Test Setup
Equipment Required
147
Turn-On Checkout
Performing the Verification Tests
148
Steps 6-10 apply to Agilent 66309B/D output 2 only
Voltage Programming and Measurement Accuracy
Current Programming and Measurement Accuracy
Output terminals on both outputs 1
Current Sink Measurement
Steps 7-11 apply to Agilent 66309B/D output 2 only
150
151
DVM Measurement Accuracy
152
DVM Voltage Measurement Agilent 66309D only
153
Front Panel Calibration Menu
Performing the Calibration Procedure
154
Voltage Programming and Measurement Calibration
Front Panel Calibration Procedure
Check the Language Setting
Enable Calibration Mode
156
Steps 11-16 apply to Agilent 66309B/D output 2 only
Overvoltage Protection Calibration
Current Programming and High-Range Measurement Calibration
157
Steps 27-32 apply to Agilent 66309B/D output 2 only
Calcurrmeas AC
158
Restore the Language Setting
DVM Calibration applies to Agilent 66311D, 66309D only
Saving the Calibration Constants
Calibration Over the Gpib
Calibration Error Messages
Changing the Calibration Password
Table B-3. Gpib Calibration Error Messages
Page
Table C-1. Error Numbers
Error Number List
161
162
Error Messages
163
Error Messages C
Page
National Instruments Gpib Driver
Assigning the Gpib Address in Programs
165
Example 1. National Instruments Interface Example
Error Handling
166
Example Programs D
167
168
Example 2. Controller Using Basic
169
Example 3. Current Pulse Measurement Using Basic
170
171
172
DFI Programming Example
Example 5. DFI Example Using Basic
173
Page
Close the Unit
Configure the Power Transformer
Install the Correct Line Fuse
Open the Unit
176
Figure E-1, Power Transformer AC Input Connections
Table F-1. COMPatibility Power-on Settings
Command Setting
177
178
Compatibility Command
Similar Scpi Command
Table F-2. COMPatibility Commands
179
180
Error
NumberError String Description/Explanation/Examples
Table F-3. COMPatibility Errors
181
Table F-5. Bit Configuration of Serial Poll Register
Page
183
Index
184
Index
185
186
OVERTEMPERATURE, 47 OVERVOLTAGE, 47 OVLD, 47, 60, 61
187
Subsystem commands syntax, 96 suffixes
Type CAP
188
Japan
United States Latin America
Canada Australia/New Zealand
Europe Asia Pacific
Manual Updates