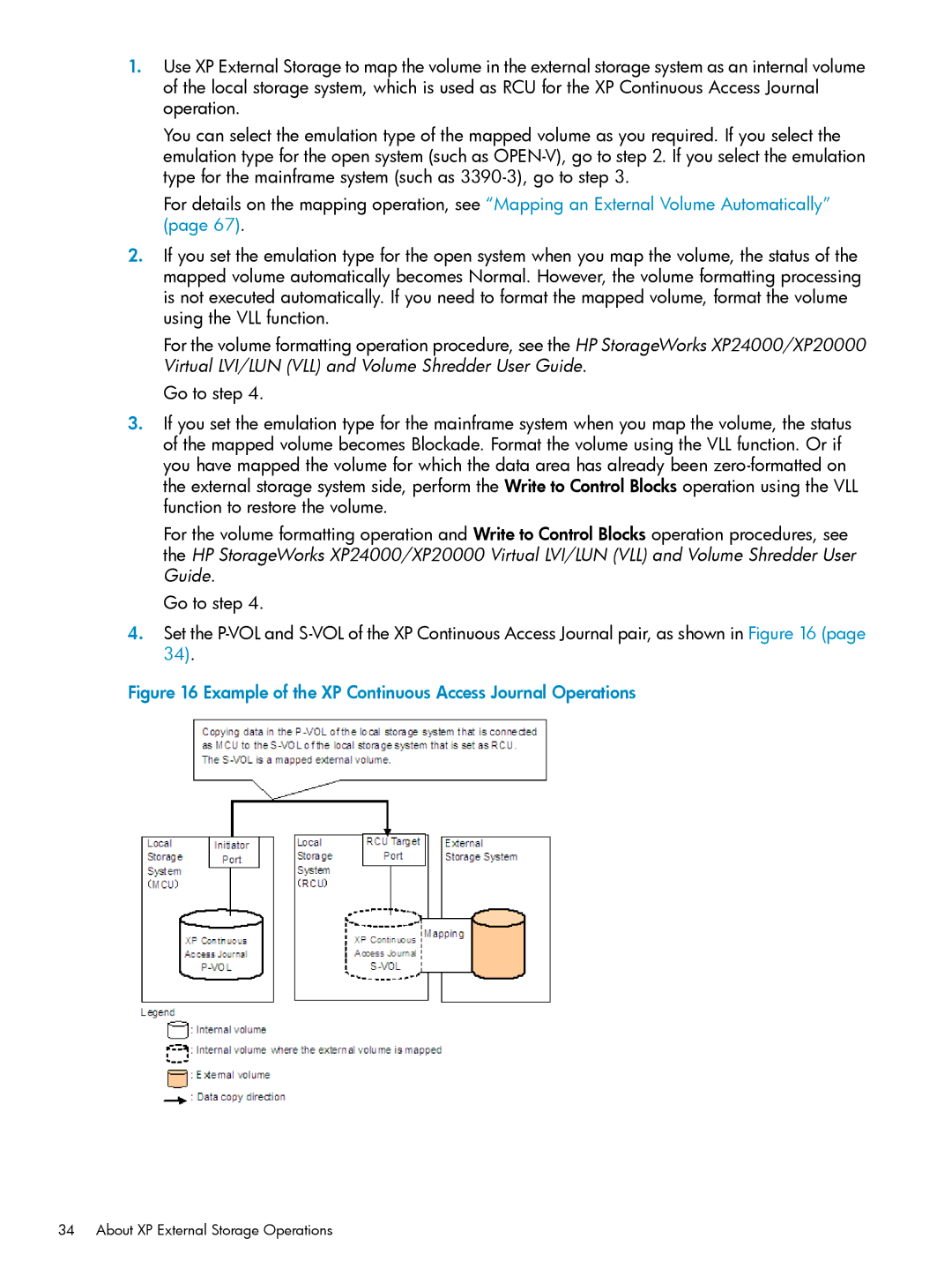
1.Use XP External Storage to map the volume in the external storage system as an internal volume of the local storage system, which is used as RCU for the XP Continuous Access Journal operation.
You can select the emulation type of the mapped volume as you required. If you select the emulation type for the open system (such as
For details on the mapping operation, see “Mapping an External Volume Automatically” (page 67).
2.If you set the emulation type for the open system when you map the volume, the status of the mapped volume automatically becomes Normal. However, the volume formatting processing is not executed automatically. If you need to format the mapped volume, format the volume using the VLL function.
For the volume formatting operation procedure, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) and Volume Shredder User Guide.
Go to step 4.
3.If you set the emulation type for the mainframe system when you map the volume, the status of the mapped volume becomes Blockade. Format the volume using the VLL function. Or if you have mapped the volume for which the data area has already been
For the volume formatting operation and Write to Control Blocks operation procedures, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) and Volume Shredder User Guide.
Go to step 4.
4.Set the