KS152JB Universal Communications Controller Technical Specifications
If the DMA is in alternate cycles mode, then each time DMA cycle is completed DMXRQ goes to 0, thus
A channel 1 DMA in progress will always be overridden by a DMA request of any kind from channel 0. If a channel 1 DMA to XRAM is in progress and is
4.4 DMA Arbitration
The DMA Arbitration described in this section is not arbitration between two devices wanting to access a shared RAM, but
The 8XC152 provides two DMA channels, either of which may be called into operation at any time in response to real time conditions in the application circuit. Since a DMA cycle always uses the 8XC152’s internal bus, and there’s only one internal bus, only one DMA channel can be ser- viced during a single DMA cycle. Executing program instructions also requires the internal bus, so program execution will also be suspended in order for a DMA to take place.
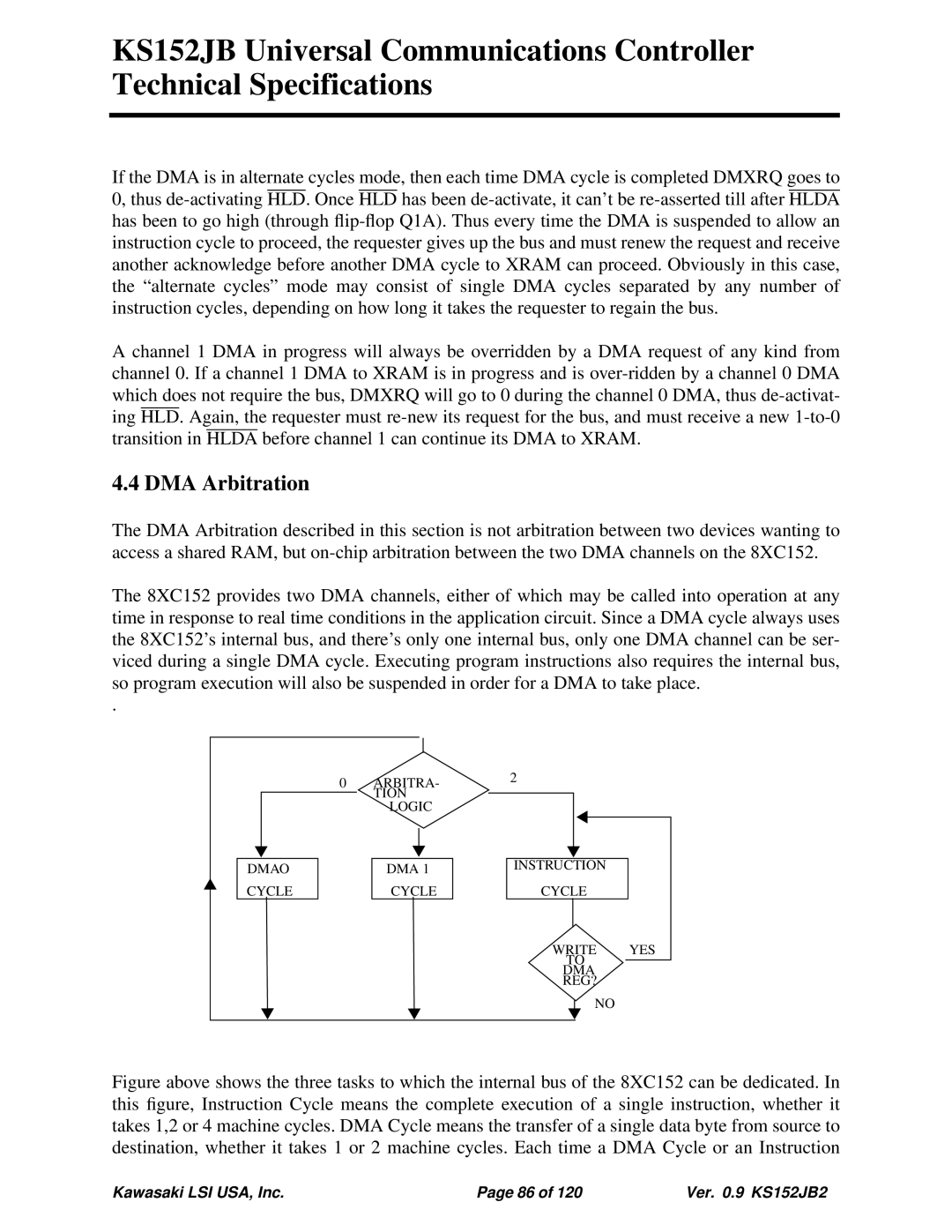
.
0 | ARBITRA- | 2 |
|
| TION |
|
|
| LOGIC |
|
|
DMAO | DMA 1 | INSTRUCTION |
|
|
| ||
CYCLE | CYCLE | CYCLE |
|
|
| WRITE | YES |
|
| TO |
|
|
| DMA |
|
|
| REG? |
|
|
| NO |
|
Figure above shows the three tasks to which the internal bus of the 8XC152 can be dedicated. In this figure, Instruction Cycle means the complete execution of a single instruction, whether it takes 1,2 or 4 machine cycles. DMA Cycle means the transfer of a single data byte from source to destination, whether it takes 1 or 2 machine cycles. Each time a DMA Cycle or an Instruction
Kawasaki LSI USA, Inc. | Page 86 of 120 | Ver. 0.9 KS152JB2 |