KS152JB Universal Communications Controller Technical Specifications
The functions of the ARB and REQ bits in PCON, then, are
ARB | REQ | Hold/Hold Acknowledge Logic |
|
|
|
0 | 0 | Disabled |
0 | 1 | C152 generates HLD, detects HLDA |
1 | 0 | C152 detects HLD, generates HLDA |
1 | 1 | Invalid |
|
|
|
4.3.3 USING THE HOLD/HLDA ACKNOWLEDGE
The HOLD/HOLDA logic only affects DMA operation with external RAM and don’t affect other operations with external RAM, such as MOVX instruction.
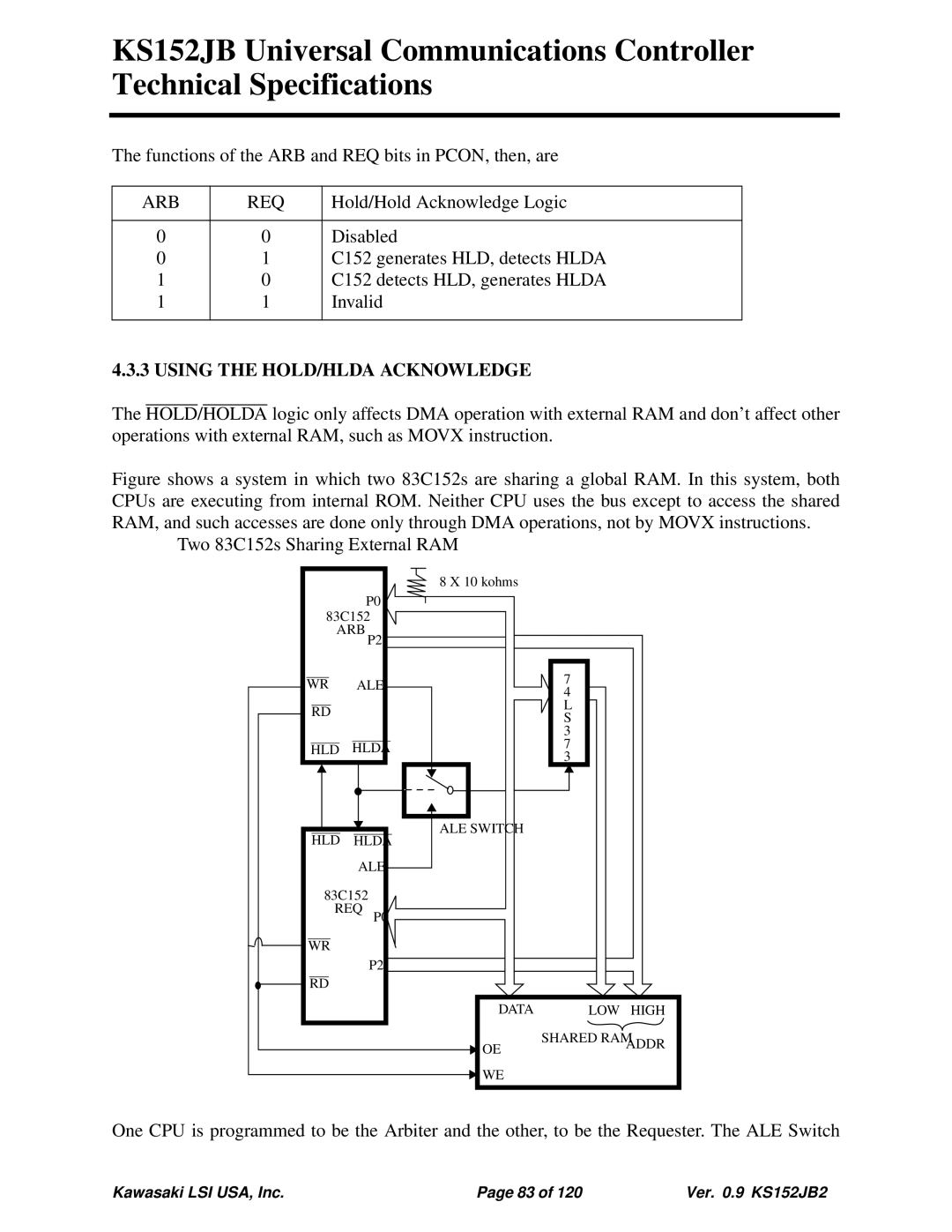
Figure shows a system in which two 83C152s are sharing a global RAM. In this system, both CPUs are executing from internal ROM. Neither CPU uses the bus except to access the shared RAM, and such accesses are done only through DMA operations, not by MOVX instructions.
Two 83C152s Sharing External RAM
| 8 X 10 kohms |
|
|
| P0 |
|
|
83C152 |
|
| |
ARB |
|
| |
| P2 |
|
|
WR | ALE | 7 |
|
4 |
| ||
|
|
| |
RD |
| L |
|
| S |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| 3 |
|
HLD | HLDA | 7 |
|
3 |
| ||
|
|
| |
HLD | ALE SWITCH |
|
|
HLDA |
|
| |
| ALE |
|
|
83C152 |
|
| |
REQ P0 |
|
| |
WR |
|
|
|
| P2 |
|
|
RD |
|
|
|
| DATA | LOW | HIGH |
|
| SHARED RAM | |
| OE |
| ADDR |
|
|
| |
| WE |
|
|
One CPU is programmed to be the Arbiter and the other, to be the Requester. The ALE Switch
Kawasaki LSI USA, Inc. | Page 83 of 120 | Ver. 0.9 KS152JB2 |