Teledyne Advanced Pollution Instrumentation T-API
MODEL CARBON MONOXIDE ANALYZER
9480 Carroll Park Drive San Diego, CA
Toll Free 800 Telephone 858 Fax
SAFETY MESSAGES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Viewing and modifying variables
FIGURES
TABLES
FIGURE B.1 RS-232PIN ASSIGNMENTS
FIGURE 10.1 OPTO PICKUP WAVEFORM
FIGURE 10.2 DETECTOR WAVEFORM
1.1Preface
1.0INTRODUCTION
WARRANTY POLICY
1.2 Warranty
COVERAGE
NON-TELEDYNEAPI MANUFACTURED EQUIPMENT
1.3 Principle of operation
1.4 Specifications
STEEL. LEAK CHECK ALL FITTINGS WITH SOAP SOLUTION
1.5 Installation and overview
SEE FIGURE 1.4 FOR REAR PANEL PNEUMATIC
CONNECTIONS. SAMPLE GAS SHOULD ONLY COME
VOLTAGE AND FREQUENCY
CHECK THAT ANALYZER IS SET UP FOR PROPER
POWER PLUG MUST HAVE GROUND LUG
REPEATEDLY PRESSING ENTR TO GET THE
CARBON MONOXIDE ANALYZER FIGURE
REAR PANEL ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS FIGURE
1.6.1 Electrical connections
1.6 Electrical and pneumatic connections
1.6.3 Status Outputs
ZERO OR SPAN CHECKS CAN BE PERFORMED IN ANY ORDER
STATUS OUTPUTS
1.6.4 RS-232
1.6.5 Pneumatic system
1.6.6 Sample gas connection see Figure
USE VENT LINE WHEN SAMPLING FROM
1.6.7 Zero/span valve connections see Figure
USE PTFE, GLASS, STAINLESS STEEL OR
1.6.8 Exhaust connections see Figure
FLOW DIAGRAM FIGURE
REAR PANEL PNEUMATIC CONNECTIONS FIGURE
REAR PANEL FIGURE
MODEL 300 ASSEMBLY LAYOUT FIGURE
1.7 Operation verification
SETUP VALUES
INSTALLED OPTIONS
CONFIGURATION DATA
FINAL TEST AND CALIBRATION VALUES
1.8.1 Rack mount with slides
1.8 Options
1.8.2 Zero/span valves
A 1¾ MINIMUM SEPARATION BETWEEN EACH
1.8.3 Internal zero/span
Page
2.1.3 E2 ROM backup of software configuration
2.1Key features
2.0OPERATION
2.1.1 CO readout
PASSWORD LEVELS
2.1.7 Password protection
Password
2.1.6 RS-232interface
2.2.1 Front panel display
2.2 Front panel
Meaning
SYSTEM MODES
TEST MEASUREMENTS
Meaning
WARNING MESSAGES
2.2.2 Programmable push buttons
Warning Message
Meaning
2.2.3 Status LED’s
Meaning
STATUS LED’s
State
Page
3.1 Manual zero/span check
3.0 PERFORMANCE TESTING
3.1.1 Zero Check
3.1.2 Span Check
3.1.3 Dual Range Calibration
3.2 IZS zero/span check Option
Step
Action
Mode
3.3 Zero/span valves Option
3.4 Automatic zero/span check
THE PROGRAMMED START TIME MUST BE A MINIMUM OF 5 MINUTES LATER THAN THE REAL TIME CLOCK See Section 4.3 and 4.4 for setting real time clock
ALTERS THE FORMULAS USED TO COMPUTE THE
THE CALIBRATE FEATURE OF AUTO SEQUENCES
CARBON MONOXIDE READING. THIS METHOD OF
CALIBRATION IS NOT APPROVED BY USEPA AND IS
CALIBRATION CONTROLS
Default
Button Sequence
Function
→0 is detected, the CPU will go into hold-off
3.9 Hold off
3.7Remote zero/span check or adjustment RS-232
3.8 Power-onhold off
4.1 Setup mode operation
4.0 SETUP MODE
4.4 Setting the date
4.3Setting the time-of-day
4.5 Adjusting the clock speed
CORRECTED CONCENTRATION =
4.7 Setting the analog output offset
4.6 Setting the CO concentration range
4.6.1 Single range mode SNGL
4.6.2 Dual range modeDUAL
4.9 Setting the analyzer I.D
4.8 Setting the RS-232baud rate
4.10 Disabling the calibration password
4.11 Data acquisition system DAS
4.11.1 Data Channels
Data Channel Edit Menu
4.11.2 Setting-upData Channels
Button
Description
for RS-232access and
Setting
ATIMER
sample or issue a
Name
Triggering Events
Description
be deleted because memory must be re-initialized
Setting
Setting Range
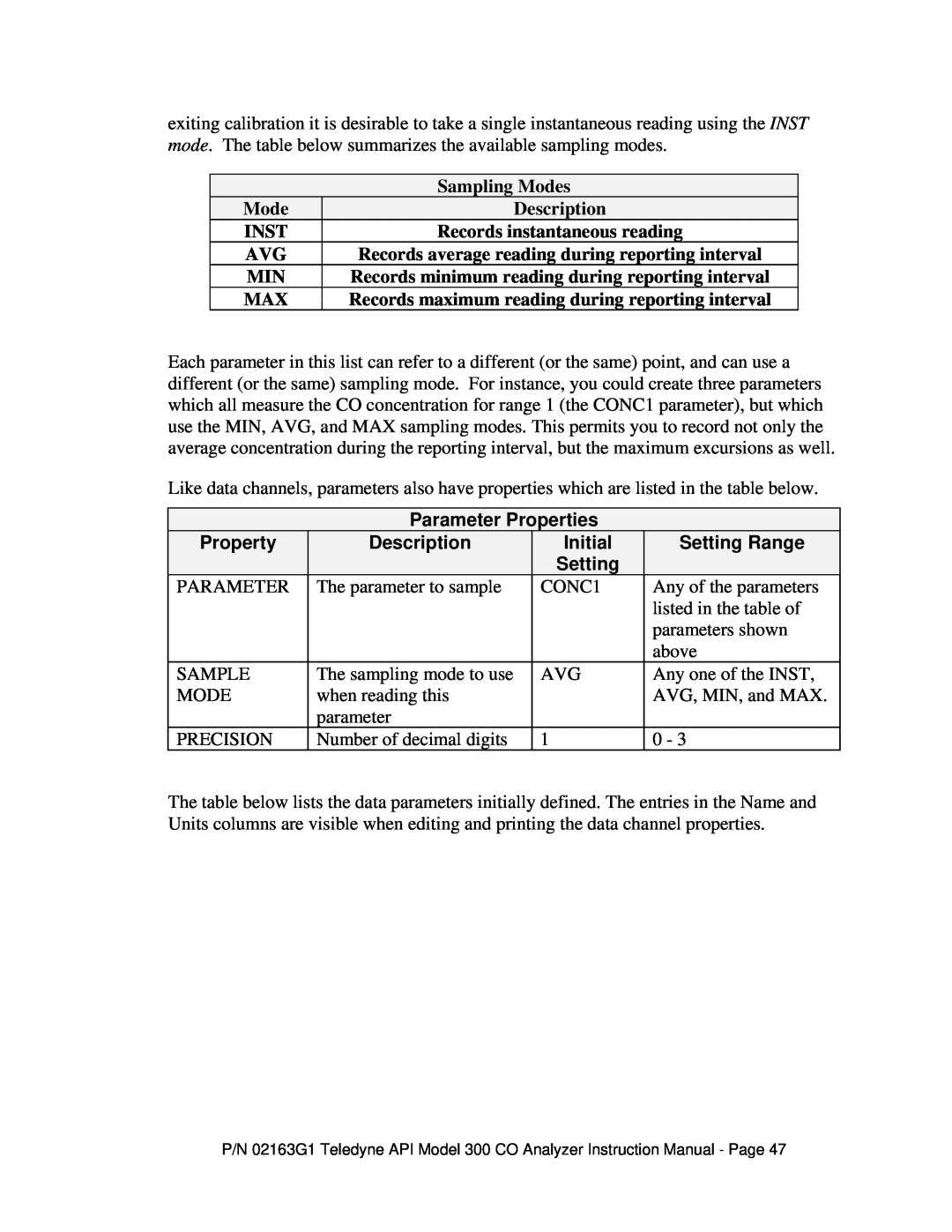
Sampling Modes
Mode
CO Reference signal
CO Measure signal
DC power supply composite voltage
Data Parameters
DESCRIPTION
4.11.3 RS-232reporting
Setting
Property
4.13 Summary of setup functions
4.12 Software configuration
Press SETUP-DAS
Scroll through setup properties until
SETUP-RNGE-UNIT
Page
5.2 Diagnostic tests
5.0 DIAGNOSTICS
SETUP-DIAG
5.1 Test measurements
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
5.2.1 Signal I/O
Signal
Test #
Description
Contro
Signal
ST FLOW ALARM
5.2.3 D/A output
TABLE 5.2 I/O SIGNALS
5.2.4 Electric Test
0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 100%, 0%
Page
6.0 HANDLING WARNINGS
Page
RS-232MESSAGE TYPES
7.0 RS-232COMMUNICATIONS
Character
Message Type
D id REPORT “name” RECORDS=number COMPACT VERBOSE
7.1 DAS reporting
D REPORT “PNUMTC” COMPACT
7.2 Warnings
D REPORT “CONC” RECORDS=100 VERBOSE
Command
WARNING MESSAGE CLEAR COMMANDS
7.3 Status/control
Warning Message Cleared
CONTROL COMMANDS
7.4 Diagnostics
Command Message
Meaning
DIAGNOSTIC REPORTS Report
DIAGNOSTIC COMMANDS
Command
Function
7.5 Test measurements
TEST MEASUREMENT REQUEST COMMANDS
7.6 Viewing and modifying variables
Var. Name
RS-232VARIABLE NAMES
Legal Values
Button Sequence
Page
8.0 CALIBRATION
BE CAREFUL WHEN PULLING IN OUTSIDE AIR
8.1REQUIRED EQUIPMENT AND GAS STANDARDS
PARTICULARLY IF OUTSIDE HUMIDITY AND
INLET VENTING RECOMMENDATIONS FIGURE
GAS GENERATION SYSTEM FIGURE
8.2 MULTI-POINTCALIBRATION
TRACEABLE VOLUME STANDARD
THE TEST GAS MUST BE INTRODUCED INTO THE
ANALYZER THROUGH THE SAMPLE INLET PORT
8.2.1PROCEDURE
14.Push “CAL” 15.Enter password. If enabled
Range DCPS Box Temp Wheel Temp Bench Temp
8.3 ZERO/SPAN CHECKING
Sample Temp Sample Flow Pressure
MR ratio Measure/reference ratio CO Reference
9.1.1 Box temperature limits
9.0 ADJUSTMENTS
9.1 Power supply board adjustment
M300 ELECTRICAL BLOCK DIAGRAM FIGURE
1.Press SETUP-MORE-DIAG
9.2 A/D - D/A Calibration procedure
9.3 Dark current signal adjust procedure
TO ADJUST ANALOG RECORDER OFFSET SEE SECTION
Switch
9.4 Output voltage range changes
100 mV
9.6 DC power supply
9.5 Flow readout adjustment
FLOW AND PRESSURE READOUT ADJUSTMENT FIGURE
9.7 CPU
Page
CARDS WHILE UNDER POWER
10.0 TROUBLESHOOTING
10.1 Overview
DO NOT DISCONNECT CPU OR OTHER DIGITAL
10.2.2 Checking the CPU and display
10.2.1 Checking the power sub-systems
10.2.3Checking the keyboard
10.3 Troubleshooting using warning messages
Corrective Action
WARNING MESSAGES
BENCH HEAT
IF THE VALUE OF ANY TEST FUNCTION IS DISPLAYED
10.4 Troubleshooting using test function values
AS “XXXX”, THIS INDICATES THAT THE READING IS
OFF SCALE OR OTHERWISE NON-VALID
10.5 Troubleshooting dynamic problems
10.5.2Noisy, unstable, or non-linearspan readings
10.5.1Noisy or unstable readings at zero
10.5.3Slow response to changes in concentration
10.5.5Cannot zero or cannot dynamic zero
Flow is zero
10.6.1 Troubleshooting flow problems
Low Flow
10.6.2Troubleshooting temperature problems
High Flow
Sample Temperature
10.6.3.1 Analog Inputs
10.6.3 Checking the V/F card
10.6.3.2 Digital to Analog Converters
10.6.3.3 Digital I/O lines
V/F BOARD JUMPERS - FACTORY SETTINGS
10.6.3.4
Factory Set Jumpers
User Set Switches
10.6.4Checking the DC power supply board
Switch
100 mV
10.6.6 Checking the Synchronous Demodulator Board
10.6.5 Checking the pneumatic sensor board
10.6.8 Checking Optical Alignment
10.6.7 Checking the Opto Interrupter
10.Adjust R7 for a CO MEAS reading of 4200 ±200 mV
10.7 Warranty/repair questionnaire
Page
11.1 Model 300 maintenance schedule
11.0 ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
11.2Replacement of sample filter
Examine and clean as
DO NOT EXCEED 15 PSI OF PRESSURE
11.3.1 Using a leak checker
11.3 Leak checking
SOLUTION. IF THERE IS NO INTERNAL
BE CAREFUL USING THE BUBBLE
PRESSURE, THE SOLUTION MAY ENTER
DO NOT ATTEMPT TO USE THE BUBBLE SOLUTION
the front panel. It should read the same as the version number that was located on the top right corner of the label on the PROM
12.1SPARE PARTS FOR CE MARK UNITS
12.0SPARE PARTS LISTS
00969-01
12.2 SPARE PARTS FOR NON-CEMARK UNITS
00960-02
RS-232& Status Outputs
APPENDIX A - LIST OF AVAILABLE MODEL 300 OPTIONS
Internal Zero/Span IZS with valves
Rack Mount and Slides
Page
Cables & Adapters come
Connectors
in 4 general types
Signal
Wiring
Data Communications Software for a PC
Troubleshooting the modem connection
enable modem transmission
Page
Title
APPENDIX C - ELECTRICAL DRAWING INDEX
Drawing Number