Teledyne Electronic Technologies
Model GFC 7001E Family Carbon Monoxide Analyzers
Model GFC7001E Carbon Dioxide Analyzer
Safety Messages
This page intentionally left blank
Coverage
Warranty
Warranty Policy 02024D
Warranty Model GFC7001E Carbon Dioxide Analyzer
Rev Name/Description
About this Manual
Manual Information Model GFC7001E Carbon Dioxide Analyzer
Table of Contents
Part II Operating Instructions Basic Operation
149
107
185
Calibration Procedures
229
217
227
Maintenance Schedule & Procedures
305
Primer on ELECTRO-STATIC Discharge
List of Figures
List of Appendices
110
List of Tables
Teledyne’s Serial I/O Command Types 157
This page intentionally left blank
Part General Information
Teledyne Analytical Instruments
GFC 7001E Family Overview
Introduction
Additional Documentation
Table of Contents
Using this Manual
Maintenance Schedule and Procedures
Advanced Features of the GFC 7001E/EM Analyzer
Basic Operation of the GFC 7001E/EM Analyzer
GFC 7001E/EM Validation and Verification
M 300E/300EM Basic Unit Specifications
Specifications and Approvals
Specifications
EPA Equivalency Designation
TUV Designation
Safety Compliance
CE Mark Compliance
Emissions Compliance
This page intentionally left blank
GFC 7001E/EM Analyzer Layout
Getting Started
Exhaust
Sample
Rear Panel Label Function
IZS
Internal Layout GFC 7001E
Internal Layout GFC 7001EM with CO2 and O2 Sensor Option
Optical Bench Layout
Electrical Shock Hazard
General Safety Hazard
Unpacking the GFC 7001E/EM Analyzer
Area Minimum Required Clearance
Ventilation Clearance
Ventilation Clearance
Electrical Connections
Power Connection
Analog Output Connector
Connecting the Status Outputs
PIN Analog Output Voltage Signal Current Signal
Analog Output Connections
Condition
Status Output Signals
Rear Panel Status Label Definition
Control Input Connector Control Input Signals
Connecting the Control Inputs
Connecting to a LAN or the Internet
Connecting the Serial Ports
Connecting to a Multidrop Network
Pneumatic Connections
NIST-SRM Type Nominal Concentration
Span Gas
Pneumatic Connections to GFC 7001E/EM Basic Configuration
Calibration Gas Sources
Sample Gas Source
Exhaust Outlet
Initial Operation
Input Gas Venting
Startup
Name Color Behavior Significance
Front Panel Display during System Warm-Up
Possible Warning Messages at Start-Up
Functional Check
Interferents for CO2 Measurements
Initial Calibration of the GFC 7001E/EM
Singl Entr
Verifying the GFC 7001E/EM Reporting Range Settings
Dilution Ratio Set Up
Set CO Span Gas Concentration
Zero/Span Calibration
To perform the zero/span calibration procedure, press
4. CO2 Sensor Calibration Procedure
3. O2 Sensor Calibration Procedure
GFC 7001E/EM Analyzer is now ready for operation
Thank YOU
FAQ’S
Frequently Asked Questions
Term Description/Definition
Glossary
Data Acquisition System
As Teflon
Rack Mount Kits OPT 20 to OPT
Optional Hardware and Software
Model GFC7001E Carbon Dioxide Analyzer
Option Description Number
Current Loop Analog Outputs Option
Carrying STRAP/HANDLE OPT
Current Loop Option Installed on the Motherboard
Calibration Valves Options 50A, 50B, 50E, 50H
Expendables and Spares Kits Options 42A
General Information Related to ALL Valve Options
ZERO/SPAN Valve Option 50A
Internal Pneumatics OPT 50A
Mode Valve Condition Sample
Zero/Span Valve Operating States for Option
Zero CAL
Sample GAS Source
Pneumatic Set Up OPT 50A
Calibration GAS Sources
Span GAS
Zero/Span Valve Operating States for Option 50B
ZERO/SPAN/SHUTOFF Valve Option 50B
Internal Pneumatics OPT 50B
Calibration GAS Sources Span GAS
Pneumatic Set Up OPT 50B
Input GAS Venting
Exhaust Outlet
Internal Pneumatics OPT 50H
ZERO/SPAN Valve with Internal CO Scrubber Option 50H
Exhaust Ouitlet
Pneumatic Set Up OPT 50H
Internal Pneumatics OPT 50E
ZERO/SPAN/SHUTOFF with Internal Zero AIR Scrubber Option 50E
Pneumatic Set Up OPT 50E
60A
Communication Options
60B
60C
12 GFC 7001E/EM Ethernet Card
Ethernet Option 63A
Ethernet + Multidrop OPT 63C
Second GAS Sensors
Oxygen Sensor Option 65A
Theory of Operation Paramagnetic measurement of O2
Pneumatic Operation of the O2 Sensor
Operation within the GFC 7001E/EM Analyzer
Carbon Dioxide Sensor Option 67A
1. CO2 Sensor Ranges and Specifications
Theory of Operation
Ndir measurement of CO2
16 CO2 sensor Theory of Operation
Pneumatic Operation of the CO2 Sensor
17 GFC 7001E/EM Internal Pneumatics with CO2 Sensor Option
Electronic Operation of the CO2 Sensor
19 Concentration Alarm Relay
Concentration Alarm Relay Option
Optional Hardware and Software
Maintenance Mode Switch
Special Features
Second Language Switch
Dilution Ratio Option
Part Operating Instructions
This page intentionally left blank
Analyzer Operating Modes
Basic Operation
Overview of Operating Modes
Sample Mode
Test Functions Defined
List of Warning Messages
IR source may be faulty
Examples
Calibration Mode
Setup Mode
Setup Acal Automatic Calibration
Setup CFG Configuration Information
Password Level Menu Access Allowed
Setup Pass Password Feature
Password Levels
Basic Operation Model GFC7001E Carbon Dioxide Analyzer
Basic Operation Model GFC7001E Carbon Dioxide Analyzer
Setting the internal Clock’s Time and Day
Adjusting the Internal Clock’s Speed
Physical Range Versus Analog Output Reporting Ranges
Setup Rnge Analog Output Reporting Range Configuration
GFC 7001E Family Physical range by Model
Model Range
Analog Output Ranges for CO Concentration
Analog Output Connector Pin Out
Range Range1 Low Range Range2 High Range
Reporting Range Modes
Sngl Dual Auto
This is the default reporting range mode for the analyzer
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 101
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 102
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 103
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 104
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 105
Setup RNGE DIL Using the Optional Dilution Ratio Feature
Setup Idas Using the Data Acquisition System Idas
Advanced Features
Front Panel LED Status Indicators for iDAS
Idas Status
IDAS Data Channel Properties
Idas Structure
IDAS Channels
Default Idas Channels
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 110
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 111
Conc ATIMER, 1
Setup DAS EDIT Accessing the Idas Edit Mode
Name Conc Trigger Event Atimer
Channel No
Editing iDAS Data Channel Names
Editing iDAS Triggering Events
IDAS Data Parameter Functions
Editing iDAS Parameters
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 116
Editing Sample Period and Report Period
Report Periods in Progress When Instrument Is Powered Off
Editing the Number of Records
RS-232 Report Function
Enabling/Disabling the Holdoff Feature
DISABLING/ENABLING Data Channels
Compact Report Feature
Starting Date Feature
IDAS Configuration Using Apicom
Remote Idas Configuration
IDAS Configuration Through a Terminal Emulation Program
IDAS Configuration Using Terminal Emulation Programs
OFF
Setup More Vars Internal Variables Vars
Allowed Vars Variable Description Default Values
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 126
Setup More Diag Using the Diagnostics Functions
Accessing the Diagnostic Features
Accessing the Analog Output Signal Configuration Submenu
Using the GFC 7001E/EM ANALYZER’S Analog Outputs
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 130
Analog Output Voltage Range Min/Max
Analog Output Voltage / Current Range Selection
Range Name Range Span Minimum Output Maximum Output
Curr
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 132
Calibration of the Analog Outputs
Automatic Calibration of the Analog Outputs
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 135
Individual Calibration of the Analog Outputs
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 137
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 138
Manual Adjustment of Current Loop Output Span and Offset
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 140
MVDC
Voltage across Resistor for 2-20 mA Resistor for 4-20 mA
100 MVDC
Current Loop Output Check
Turning AN Analog Output OVER-RANGE Feature ON/OFF
Adding a Recorder Offset to AN Analog Output
Test Channel Description Zero Full Scale None
Selecting a Test Channel Function for Output A4
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 145
AIN Calibration
11 CO Concentration Alarm Default Settings
Setup MORE Alrm Using the GAS Concentration Alarms
Setting the GFC 7001E Concentration Alarm Limits
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 148
Comm Port Default Settings
Setup MORE Comm Using the ANALYSER’S Communication Ports
Remote Operation
RS-232 DTE and DCE Communication
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 150
Comm Port Baud Rate
Comm Port Communication Modes
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 153
Comm Port Testing
Machine ID
Terminal Mode Software Commands
Help Commands in Terminal Mode
Terminal Operating Modes
ESC
ID Command CR
Command Syntax
Teledyne’s Serial I/O Command Types
Command Command Type
Dddhhmm Id Messagecrlf
Status Reporting
RS-232PASS=NNNNNN
Comm Port Password Security
Logon Is the default password
Location of JP2 on RS-232-Multidrop PCA Option
Multidrop RS-232 SET UP
Host
Make Sure Jumper between JP2 pins 21 Is installed
Tapi Analyzer
Last
CPU RS-485 Setup
RS-485 Configuration of COM2
RX/TX RX/TX+ GND
Back Panel Connector Pin-Outs for COM2 in RS-485 Mode
Ethernet Status Indicators
Remote Access VIA the Ethernet
Ethernet Card COM2 Communication Modes and Baud Rate
LED Function
Configuring the Ethernet Interface Option Using Dhcp
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 166
Manually Configuring the Network IP Addresses
ON/OFF
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 169
Changing the ANALYZER’S Hostname
Actions
Modbus Setup
Minimum Requirements
Remote Access by Modem
AT Y0 &D0 &H0 &I0 S0=2 &B0 &N6 &M0 E0 Q1 &W0
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 174
Hessen Comm Port Configuration
Using the GFC 7001E/EM with a Hessen Protocol Network
General Overview of Hessen Protocol
RS-232 Communication Parameters for Hessen Protocol
Activating Hessen Protocol
Selecting a Hessen Protocol Type
Mode ID Mode Description CMD
Setting the Hessen Protocol Response Mode
Teledyne’s Hessen Protocol Response Modes
BCC
Gas List Entry Format and Definitions
Hessen Protocol GAS List Entries
Editing or Adding Hessen Gas List Entries
Deleting Hessen Gas List Entries
Status Flag Name Default BIT Assignment
Setting Hessen Protocol Status Flags
Operational FLAGS1
SPARE/UNUSED Bits
Instrument ID Code
To assign or reset the status flag bit assignments, press
Apicom Remote Control Program
Before Calibration
Calibration Procedures
Automatic ZERO/SPAN CAL/CHECK Autocal
CO Calibration Quality Analysis
Required EQUIPMENT, SUPPLIES, and Expendables
Before Calibration
Traceability
Data Recording Devices
ZERO/SPAN Calibration Checks VS. ZERO/SPAN Calibration
Setup for Basic Calibration Checks and Calibration
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 189
Performing a Basic Manual Calibration Check
Performing a Basic Manual Calibration
Setting the Expected Span Gas Concentration
Zero/Span Point Calibration Procedure
Manual Calibration with ZERO/SPAN Valves
Setup for Calibration Using Valve Options
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 194
Manual Calibration Checks with Valve Options Installed
Manual Calibration Using Valve Options
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 197
Automatic ZERO/SPAN CAL/CHECK Autocal
Mode Name Action
Use of Zero/Span Valve with Remote Contact Closure
Autocal Modes
Attribute Action
AutoCal Attribute Setup Parameters
Example AutoCal Sequence
1415
0030
To program the example sequence shown in -4, press
Setup Acal Programming and Auto CAL Sequence
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 202
DURATION30.0 Minutes
AutoCal with Auto or Dual Reporting Ranges Modes Selected
Calibration Data Quality Evaluation
CO Calibration Quality
Function Minimum Value Optimum Value
Maximum Value
Dark Calibration Test
Calibration of the GFC 7001E/EM’S Electronic Subsystems
Pressure Calibration
Flow Calibration
Electrical Test Calibration
Calibration of Optional Sensors
1. O2 Sensor Calibration Procedure
1.1. O2 Calibration Setup
Set O2 Span Gas Concentration
Activate O2 Sensor Stability Function
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 212
Set CO2 Span Gas Concentration
2. CO2 Sensor Calibration Procedure
2.1. CO2 Calibration Setup
Activate CO2 Sensor Stability Function
2.4. CO2 Zero/Span Calibration
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 216
Calibration of Equipment General Guidelines
EPA Calibration Protocol
Calibration Requirements
Spare Parts and Expendable Supplies
Calibration EQUIPMENT, SUPPLIES, and Expendables
Data Recording Device
Matrix for Calibration Equipment & Supplies
Recommended Standards for Establishing Traceability
Activity Matrix for Quality Assurance Checks
Calibration Frequency
Level 1 Calibrations Versus Level 2 Checks
Level 2 Zero and Span Check
Zero and Span Checks
Level 1 Zero and Span Calibration
Precision Check
ZERO/SPAN Check Procedures
Precisions Calibration
Precision Calibration Procedures
Auditing Procedure
Calibration Audit
Data Reduction Audit
Linearity Test
Dynamic Multipoint Calibration Procedure
System AUDIT/VALIDATION
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 225
References
Part Technical Information
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 228
Measurement Fundamentals
Theory of Operation
Measurement Method
Absorption Path Lengths for GFC 7001E and GFC 7001EM
GAS Filter Correlation
Measurement Fundamentals with GFC Wheel
GFC Wheel
Effect of CO in the Sample on CO Meas & CO REF
Measure Reference Ratio
Effects of Interfering Gas on CO Meas & CO REF
Summary Interference Rejection
Pneumatic Operation
Internal Pneumatic Flow Basic Configuration
Critical Flow Orifice
Flow Rate Control
Critical Flow Orifice Area High LOW Pressure
Spring Rings Filter
Pneumatic Sensors
Particulate Filter
Sample Pressure Sensor
Sample Flow Sensor
Overview
Electronic Operation
Mother
PC 104 Bus
Board
Sync Demod
Flash Chip
Central Processing Unit CPU
DISK-ON-MODULE DOM
IR Source
Temperature Control
Optical Bench & GFC Wheel
Schmidt Triggers
Sensor
Segment Sensor
Overview
Synchronous Demodulator SYNC/DEMOD Assembly
IR Photo-Detector
GFC 7001E/EM Sync/Demod Block Diagram
Signal Synchronization and Demodulation
Sync Demod Sample and Hold Circuits
IR Beam Passing Through
Dark Calibration Switch
Photo-Detector Temperature Control
Sync/Demod Status LED’s
Sync/Demod Status LED Activity
Relay Board
Electric Test Switch
Heater Control
GFC Wheel Motor Control
Status LED’s
LED Color Function Status When LIT Status When Unlit
11.5.5.6. I2C Watch Dog Circuitry
Relay Board Status LED’s
To D Conversion
Motherboard
Sensor Inputs
Thermistor Interface
External Digital I/O
Analog Outputs
Internal Digital I/O
Power UP Circuit
Power SUPPLY/ Circuit Breaker
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 250
Mother
Communication Interface
Keyboard
Relay Board
Analyzer Status LED’s
Front Panel Interface
Keyboard
Front Panel Status LED’s
Keyboard/Display Interface Electronics
Display
Keypad Decoder
Front Panel
KEY-DEPRESS-DETECT Circuit
Keypad Decoder
I2C Interface Chip
Display Power Watch DOG
Display Data Decoder
Display Controller
Adaptive Filter
Software Operation
Calibration Slope and Offset
Temperature and Pressure Compensation
Measurement Algorithm
Internal Data Acquisition System Idas
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 258
Qualified Personnel
Maintenance Schedule & Procedures
Maintenance Schedule
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 260
Action
GFC 7001E/EM Maintenance Schedule
CO Meas
Date Recorded Function Operating Mode Stability
MR Ratio
Pres
Predictive uses for Test Functions
Predicting Failures Using the Test Functions
Function Condition Behavior
Interpretation
Rebuilding the Sample Pump
Maintenance Procedures
Replacing the Sample Particulate Filter
Pressure Leak Check
Performing Leak Checks
Vacuum Leak Check and Pump Check
Performing a Sample Flow Check
Cleaning the Optical Bench
Cleaning Exterior Surfaces of the GFC 7001E/EM
Suspect a Leak First
Troubleshooting & Repair
General Troubleshooting
Viewing and Clearing Warning Messages
Fault Diagnosis with Warning Messages
Config
Fault Condition Possible Causes Message
Cannot DYN
Initialized
Fault Diagnosis with Test Functions
Test Functions Indicated Failures
Pres Sample FL Samp Temp Bench Wheel BOX Temp
Test Functions
Time Range Stabil CO Meas CO REF
PHT Drive Slope Offset
Diag Signal I/O Using the Diagnostic Signal I/O Function
CPU Status LED
CPU Status Indicator
Internal Electronic Status LED’S
Sync/Demod Board Status Failure Indications
LED Function Fault Status Indicated Failures
Sync Demodulator Status LED’s
I2C Status LED Failure Indications
Relay PCA
Relay Board Status LED’s
Relay Board Status LED Failure Indications
GFC 7001E/EM Internal GAS Flow Diagrams
GAS Flow Problems
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 279
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 280
Troubleshooting & Repair
Flow is Zero
Typical Sample GAS Flow Problems
Low Flow
High Flow
Miscalibrated
Calibration Problems
Displayed Flow = Warnings
Actual Flow Does Not Match Displayed Flow
Inability to Zero no Zero KEY
NON-REPEATABLE Zero and Span
Inability to Span no Span KEY
Temperature Problems
Other Performance Problems
Box or Sample Temperature
Bench Temperature
IR Photo-Detector TEC Temperature
GFC Wheel Temperature
Excessive Noise
DC Power Supply
AC Mains Configuration
DC Power Test Point and Wiring Color Codes
Name Test POINT# TP and Wire Color
KEYBOARD/DISPLAY Interface
DC Power Supply Acceptable Levels
Socket
Relay Board Control Devices
Function Control Device
Electrical Test
Sensor Assembly
Sync/Demodulator Assembly
GFC Wheel Drive
Opto Pickup Assembly
Opto Pickup Board Nominal Output Frequencies
TP2 TP4
Pressure/Flow Sensor Assembly
Test Channel / Analog Outputs Voltage
13.5.7.1. A/D Functions
Full Scale Output of Voltage Range
Step Nominal Output Voltage
Output Range Nominal Output Values Step Current
Analog Outputs Current Loop
PIN Left to Right Status
Status Outputs
12 Status Outputs Check
Control Inputs Remote Zero, Span
General RS-232 Troubleshooting
RS-232 Communications
Optional CO2 Sensor
Troubleshooting Analyzer/Modem or Terminal Operation
Repairing Sample Flow Control Assembly
Repair Procedures
REMOVING/REPLACING the GFC Wheel
15 Opening the GFC Wheel Housing
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 301
18 Removing the GFC Wheel
Checking the Sync/Demodulator Circuit Gain
Adjustment Made Here
Adjusting the Sync/Demodulator, Circuit Gain
Technical Assistance
DISK-ON-MODULE Replacement Procedure
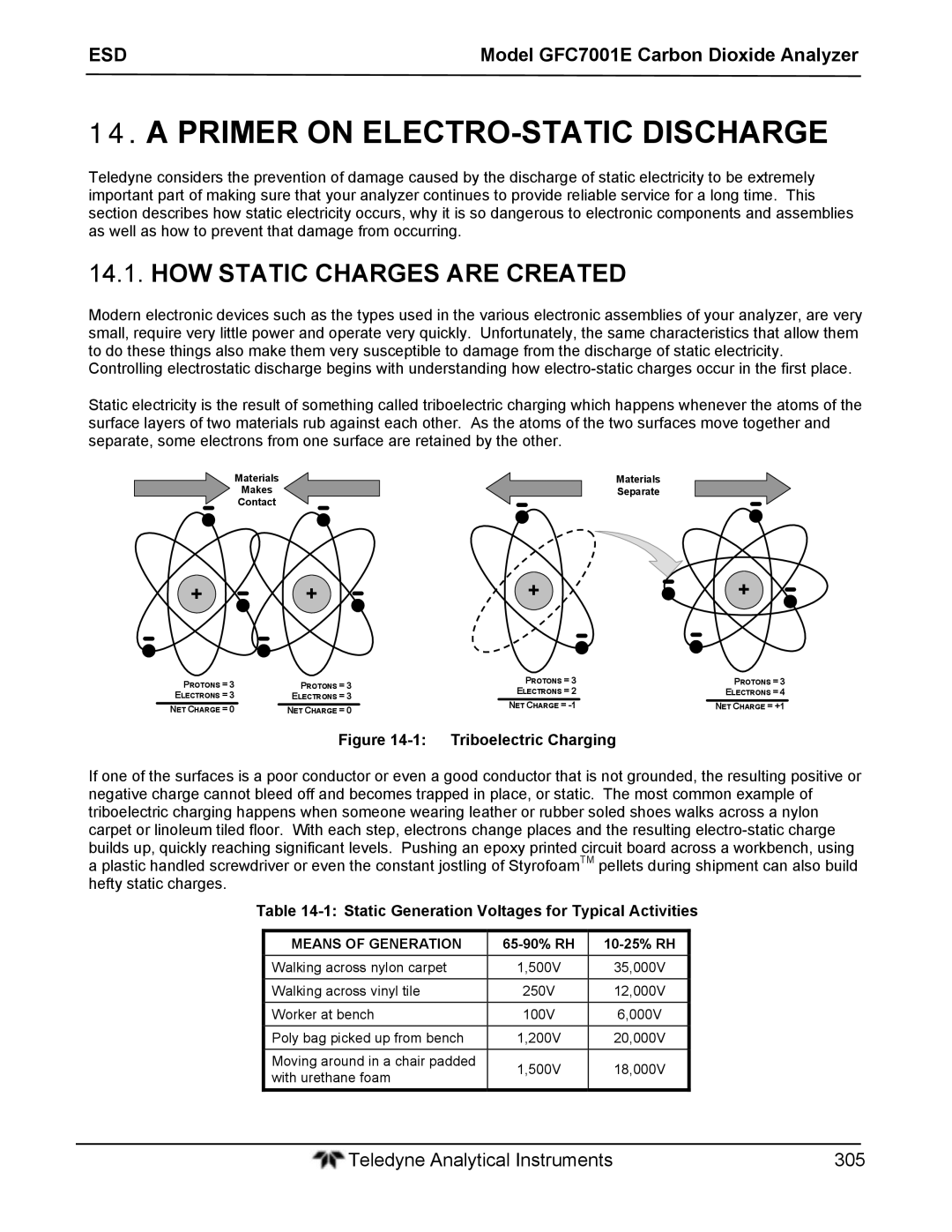
HOW Static Charges are Created
Primer on ELECTRO-STATIC Discharge
Static Generation Voltages for Typical Activities
Means of Generation
Sensitivity of Electronic Devices to Damage by ESD
HOW ELECTRO-STATIC Charges Cause Damage
Damage Susceptibility Voltage
Device Range
General Rules
Common Myths about ESD Damage
Basic Principles of Static Control
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 308
Working at an Anti-ESD Work Bench
Working at the Instrument Rack
Transferring Components from Rack to Bench and Back
Opening Shipments from Teledyne’ Customer Service
ESD Hazard
Packing Components for Return to Teledyne’s Customer Service
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 312
Analog CAL WARNING, 49, 88 Analog Inputs
Bench Temp WARNING, 49, 88, 182, 269 Bench Temperature
Index
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 315
Pnuntc
Internal Span Gas Generator
Rear Board not DET, 49, 88, 182
Pressure Span Inlet
Relay Board WARN, 49, 88, 269 relay PCA
Calibration
Source WARNING, 49, 88
Span2 Inlet, 32 Specifications, 25
Interactive Mode
Vent Outlet
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 320
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 321