Data Manual
Important Notice
Contents
−10
PC Card Controller Programming Model −1
ExCA Compatibility Registers Functions 0 and 1 −1
Ohci Controller Programming Model −1
Ohci Registers −1
Vii
PHY Register Configuration 10−1
TI Extension Registers −1
Viii
SD Host Controller Programming Model −1
Flash Media Controller Programming Model −1
Smart Card Controller Programming Model −1
Mechanical Information 15−1
Electrical Characteristics −1
Xii
List of Illustrations
Xiii
List of Tables
Xiv
Functions 0 and 1 PCI Configuration Register Map
Title −13
Xvi
Xvii
Xviii
1 PCI7621 Controller
Controller Functional Description
3 PCI7611 Controller
2 PCI7421 Controller
Power Switch Interface
PCI Bus Power Management
4 PCI7411 Controller
Multifunctional Terminals
PCI Bus Interface Specification for PCI-to-CardBus Bridges
Features
Related Documents
PCI Local Bus Specification Revision
Trademarks
Ordering Information
Terms and Definitions
−1. Terms and Definitions
Term Definitions
Page
Terminal Descriptions
−2. PCI7421 GHK/ZHK-Package Terminal Diagram
−3. PCI7611 GHK/ZHK-Package Terminal Diagram
−4. PCI7411 GHK/ZHK-Package Terminal Diagram
Terminal Signal Name Number
−1. Signal Names by GHK Terminal Number
ACC/BE2
Breset
VCC
VCC Acperr
BCC/BE0 BCE1
Scclk
SCVCC5V
Latch
GNT Perr
Grst Frame
RIOUT/PME
Vsspll
Signal Name Terminal Number
−2. CardBus PC Card Signal Names Sorted Alphabetically
PC2TEST3
Sdcmd
Perr Trdy GND
Prst GND
Signal Terminal Signal Name Number
−3 -Bit PC Card Signal Names Sorted Alphabetically
−12
−13
Detailed Terminal Descriptions
−14
−4. Power Supply Terminals
−5. PC Card Power Switch Terminals
−6. PCI System Terminals
−15
−16
−7. PCI Address and Data Terminals
−17
−8. PCI Interface Control Terminals
−18
−9. Multifunction and Miscellaneous Terminals
−10 -Bit PC Card Address and Data Terminals
Stschg
−11 -Bit PC Card Interface Control Terminals
AOE
PCIO3 Vccb
−12. CardBus PC Card Interface System Terminals
BCAD0
−13. CardBus PC Card Address and Data Terminals
BCCD2
−14. CardBus PC Card Interface Control Terminals
Cstop
−26
−15. Ieee 1394 Physical Layer Terminals
−16. SD/MMC Terminals
−17. Memory Stick/PRO Terminals
−27
−28
−18. Smart Media/XD Terminals
−19. Smart Card Terminals †
−30
Eeprom
Power Supply Sequencing
SD/MMC MS/MSPRO
SD/MMC
Clamping Voltages
I/O Characteristics
Peripheral Component Interconnect PCI Interface
1 1394 PCI Bus Master
Device Resets
Serial Eeprom I2C Bus
VCC Grst Prst Pclk
ROM A1 SCL A2 SDA VCC
Functions 0 and 1 CardBus Subsystem Identification
Function 2 Ohci 1394 Subsystem Identification
PC Card Applications
Function 3 Flash Media Subsystem Identification
Function 4 SD Host Subsystem Identification
PC Card Insertion/Removal and Recognition
Low Voltage CardBus Card Detection
UltraMedia Card Detection
−2. PC Card-Card Detect and Voltage Sense Connections
Flash Media Card Detection
CD2//CCD2 CD1//CCD1 VS2//CVS2 VS1//CVS1
VCC VPP/VCORE
−3. TPS2228 Control Logic-xVPP/VCORE
Internal Ring Oscillator
−4. TPS2228 Control Logic-xVCC
−5. TPS2226 Control Logic-xVPP
Integrated Pullup Resistors for PC Card Interface
LED Socket Activity Indicators
Spkrout and Caudpwm Usage
Spkrout Binaryspkr
11 48-MHz Clock Requirements
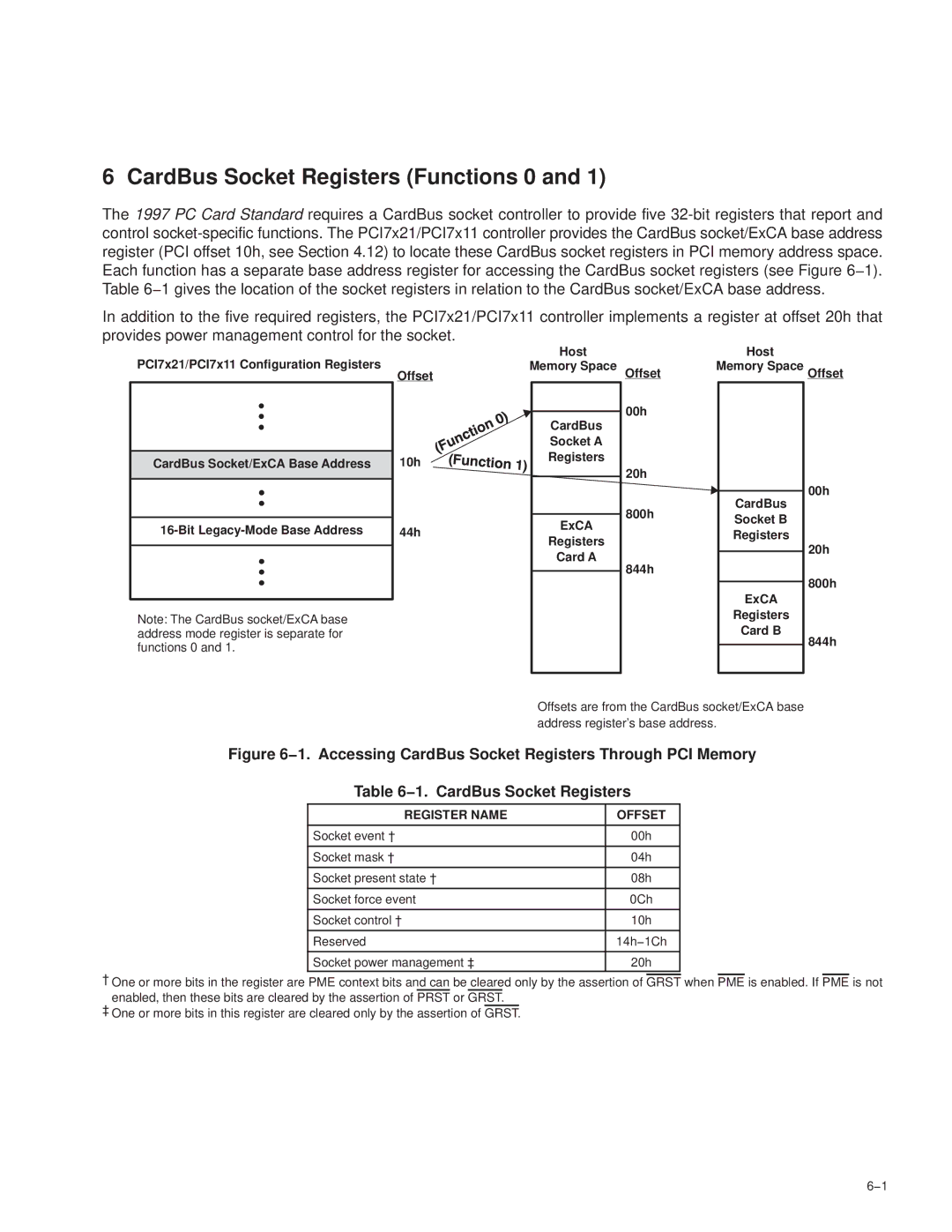
CardBus Socket Registers
−7. CardBus Socket Registers
LED
Serial Eeprom Interface
Accessing Serial-Bus Devices Through Software
Serial-Bus Interface Implementation
Serial-Bus Interface Protocol
−8. Serial-Bus Protocol Acknowledge
−7. Serial-Bus Start/Stop Conditions and Bit Transfers
−10. Serial-Bus Protocol-Byte Read
Serial-Bus Eeprom Application
−9. Eeprom Loading Map
Serial ROM Byte Description Offset
GPE
PCI 2Ch, subsystem vendor ID, byte
LinkEnh HCControl.Program Phy Enable
PCI 2Dh, subsystem vendor ID, byte
PCI 2Eh, subsystem ID, byte
Programmable Interrupt Subsystem
PC Card Functional and Card Status Change Interrupts
−10. Interrupt Mask and Flag Registers
Card Type Event Mask Flag
Card Type Event Signal Description
Interrupt Masks and Flags
−11. PC Card Interrupt Events and Description
Using Parallel PCI Interrupts
Using Parallel IRQ Interrupts
Using Serialized Irqser Interrupts
Power Management Overview
SMI Support in the PCI7x21/PCI7x11 Controller
−12. Interrupt Pin Register Cross Reference
1 1394 Power Management Function
Integrated Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator LDO-VR
CardBus PC Card Power Management
CardBus Functions 0 and 1 Clock Run Protocol
Supply VCC Vren Vrport
Suspend Mode
5 16-Bit PC Card Power Management
Requirements for Suspend Mode
Reset GNT Suspend Pclk
Ring Indicate
Cstsmask CSC Ringen RI Cdresume
Rienb Riout
PCI Power Management
−15. Power-Management Registers
Power-management control/status CSR
−16. Function 2 Power-Management Registers
CardBus Bridge Power Management
−17. Function 3 Power-Management Registers
−18. Function 4 Power-Management Registers
Acpi Support
Master List of PME Context Bits and Global Reset-Only Bits
−28
−29
PHY Port Cable Connection
Ieee 1394 Application Information
−31
Crystal Selection
Bus Reset
Cphy + CBD
−32
−33
−34
−1. Bit Field Access Tag Descriptions
PCI Configuration Register Map Functions 0
−2. Functions 0 and 1 PCI Configuration Register Map
Access TAG Name Meaning
Vendor ID
Vendor ID Register
Device ID-Smart Card enabled
Device ID Register Functions 0
Device ID
Command
Command Register
−3. Command Register Description
BIT Signal Type Function
Status Register
Status
−4. Status Register Description
Revision ID Register
Class Code Register
Cache Line Size Register
Register Latency timer
Latency Timer Register
Header Type Register
Bist Register
Capability Pointer Register
CardBus Socket Registers/ExCA Base Address Register
CardBus socket registers/ExCA base address
Register Capability pointer
Secondary Status Register
Secondary status
−5. Secondary Status Register Description
PCI Bus Number Register
CardBus Bus Number Register
Subordinate Bus Number Register
Register CardBus latency timer
CardBus Latency Timer Register
CardBus Memory Base Registers 0
Memory base registers 0
CardBus I/O Base Registers 0
CardBus Memory Limit Registers 0
Memory limit registers 0
Base registers 0
Interrupt Line Register
CardBus I/O Limit Registers 0
Limit registers 0
Register Interrupt line
Interrupt pin − PCI function
Interrupt Pin Register
Interrupt pin
Bridge Control Register
−6. Interrupt Pin Register Cross Reference
Bridge control
Subsystem vendor ID
Subsystem Vendor ID Register
PC Card 16-Bit I/F Legacy-Mode Base-Address Register
Subsystem ID Register
Subsystem ID
PC Card 16-bit I/F legacy-mode base-address
System Control Register
System control
−8. System Control Register Description
−8 . System Control Register Description
Register Mccd debounce
Mccd Debounce Register
General Control Register
General control
General control
−9. General Control Register Description
General-Purpose Event Status Register
General-purpose event status
−10. General-Purpose Event Status Register Description
General-Purpose Input Register
General-Purpose Event Enable Register
General-Purpose Output Register
General-purpose output
−13. General-Purpose Output Register Description
Multifunction Routing Status Register
Multifunction routing status
−14. Multifunction Routing Status Register Description
Retry Status Register
Retry status
−15. Retry Status Register Description
Card Control Register
Card control
−16. Card Control Register Description
Device Control Register
Device control
−17. Device Control Register Description
Diagnostic Register
Diagnostic
−18. Diagnostic Register Description
Next Item Pointer Register
Capability ID Register
Register Capability ID
Register Next item pointer
Power Management Capabilities Register
Power management capabilities
−19. Power Management Capabilities Register Description
Power Management Control/Status Register
Power management control/status
−20. Power Management Control/Status Register Description
Power management control/status bridge support extensions
Power-Management Data Register
Power-management data
Bpccen
Serial Bus Index Register
Serial Bus Data Register
Serial bus data
−22. Serial Bus Data Register Description
Register Serial bus slave address
Serial Bus Slave Address Register
−24. Serial Bus Slave Address Register Description
Rwcmd
Serial Bus Control/Status Register
Serial bus control/status
−25. Serial Bus Control/Status Register Description
−38
ExCA Compatibility Registers Functions 0
−1. ExCA Register Access Through I/O
−1. ExCA Registers and Offsets
Exca Register Name PCI Memory Address Exca Offset Offset HEX
ExCA identification and revision
ExCA Identification and Revision Register
−2. ExCA Identification and Revision Register Description
Iftype
ExCA Interface Status Register
ExCA interface status
−3. ExCA Interface Status Register Description
ExCA Power Control Register
ExCA power control
−4. ExCA Power Control Register Description-82365SL Support
ExCA Interrupt and General Control Register
Register ExCA interrupt and general control
−6. ExCA Interrupt and General Control Register Description
ExCA Card Status-Change Register
ExCA card status-change
−7. ExCA Card Status-Change Register Description
Register ExCA card status-change interrupt configuration
ExCA Card Status-Change Interrupt Configuration Register
ExCA Address Window Enable Register
ExCA address window enable
−9. ExCA Address Window Enable Register Description
ExCA I/O Window Control Register
ExCA I/O window control
−10. ExCA I/O Window Control Register Description
ExCA I/O Windows 0 and 1 Start-Address High-Byte Registers
ExCA I/O Windows 0 and 1 Start-Address Low-Byte Registers
ExCA I/O Windows 0 and 1 End-Address High-Byte Registers
ExCA I/O Windows 0 and 1 End-Address Low-Byte Registers
ExCA Memory Windows 0−4 Start-Address Low-Byte Registers
ExCA Memory Windows 0−4 Start-Address High-Byte Registers
ExCA Memory Windows 0−4 End-Address Low-Byte Registers
ExCA Memory Windows 0−4 End-Address High-Byte Registers
ExCA Memory Windows 0−4 Offset-Address Low-Byte Registers
ExCA Memory Windows 0−4 Offset-Address High-Byte Registers
ExCA card detect and general control
ExCA Card Detect and General Control Register
ExCA Global Control Register
ExCA global control
−15. ExCA Global Control Register Description
ExCA I/O Windows 0 and 1 Offset-Address High-Byte Registers
ExCA I/O Windows 0 and 1 Offset-Address Low-Byte Registers
Register ExCA memory windows 0−4
ExCA Memory Windows 0−4 Page Registers
CardBus Socket Registers Functions 0
Socket Event Register
Socket event
−2. Socket Event Register Description
Socket Mask Register
Socket mask
−3. Socket Mask Register Description
Socket Present State Register
Socket present state
−4. Socket Present State Register Description
Socket force event
Socket Force Event Register
−5. Socket Force Event Register Description
Socket Control Register
Socket control
−6. Socket Control Register Description
Socket Power Management Register
Socket power management
−7. Socket Power Management Register Description
Pmcsrbse
−1. Function 2 Configuration Register Map
Device ID Register
BIT Field Name Type Description
−2. Command Register Description
−3. Status Register Description
Latency timer and class cache line size
Latency Timer and Class Cache Line Size Register
Class Code and Revision ID Register
Class code and revision ID
Ohci Base Address Register
Header Type and Bist Register
TI Extension Base Address Register
TI extension base address
−8. TI Base Address Register Description
CardBus CIS Pointer Register
CardBus CIS Base Address Register
CardBus CIS base address
−9. CardBus CIS Base Address Register Description
Power management capabilities pointer
Power Management Capabilities Pointer Register
Subsystem Identification Register
Subsystem identification
Register Interrupt pin
−11. Interrupt Line Register Description
BIT Field Name Type Description Intrline
01h Inta 02h Intb 03h Intc Bits Intsel
Ohci Control Register
Minimum Grant and Maximum Latency Register
Capability ID and next item pointer
Capability ID and Next Item Pointer Registers
Nextitem
Capabilityid
−16. Power Management Capabilities Register Description
Power Management Extension Registers
Power Management Control and Status Register
Power management control and status
Power management extension
PCI PHY control
PCI PHY Control Register
−19. PCI PHY Control Register Description
Cnaout
PCI Miscellaneous Configuration Register
PCI miscellaneous configuration
−20. PCI Miscellaneous Configuration Register Description
Link Enhancement Control Register
Link enhancement control
−21. Link Enhancement Control Register Description
Subsystem access
Subsystem Access Register
−22. Subsystem Access Register Description
Subdevid
Gpio Control Register
Gpio control
−23. Gpio Control Register Description
GPIOENB1 GPIO1
Disablebmc GPIO0
GPIODATA1
= GPIO0
−1. Ohci Register Map
DMA Context Register Name Abbreviation Offset
Guid ROM Guidrom
Isochronous receive interrupt mask IsoRecvIntMaskSet
IsoRecvIntEventClear
PhysicalRequestFilterHiClear
Physical request filter low PhysicalRequestFilterLoSet
Asynchronous context control ContextControlSet
Isochronous receive context command
ContextControlClear
Request Transmit Reserved
Ohci Version Register
Ohci version
−2. Ohci Version Register Description
−3. Guid ROM Register Description
Guid ROM Register
Guid ROM
RSU
CSR Data Register
Asynchronous Transmit Retries Register
Asynchronous transmit retries
−4. Asynchronous Transmit Retries Register Description
CSR Control Register
CSR Compare Register
CSR compare
CSR control
Configuration ROM header
Configuration ROM Header Register
−6. Configuration ROM Header Register Description
Bus Identification Register
Bus Options Register
Bus options
−7. Bus Options Register Description
Guid Low Register
Guid High Register
Guid high
Guid low
Posted Write Address Low Register
Configuration ROM Mapping Register
Posted Write Address High Register
Posted write address high
−10. Posted Write Address High Register Description
Host controller control
Host Controller Control Register
−11. Host Controller Control Register Description
RSU RSC Rscu
Self-ID Buffer Pointer Register
Self-ID buffer pointer
LPS RSC
Self-ID Count Register
Self-ID count
−12. Self-ID Count Register Description
Isochronous receive channel mask high
Isochronous Receive Channel Mask High Register
Isochronous receive channel mask low
Isochronous Receive Channel Mask Low Register
Interrupt event
Interrupt Event Register
−15. Interrupt Event Register Description
RSC Rscu
Arrq Rscu
Arrs Rscu
Interrupt Mask Register
MasterIntEnable
Interrupt mask
−16. Interrupt Mask Register Description
Arrs RSC
Arrq RSC
Generation
Isochronous transmit interrupt event
Isochronous Transmit Interrupt Event Register
Isochronous transmit interrupt mask
Isochronous Transmit Interrupt Mask Register
Reserved. Bits 31−4 return 0s when read
Isochronous Receive Interrupt Event Register
Isochronous receive interrupt event
Initial Bandwidth Available Register
Isochronous Receive Interrupt Mask Register
Isochronous receive interrupt mask
Initial bandwidth available
Initial Channels Available Low Register
Initial Channels Available High Register
Fairness control
Fairness Control Register
−22. Fairness Control Register Description
Value for this field is 00h
Link Control Register
Link control
−23. Link Control Register Description
Node Identification Register
Node identification
−24. Node Identification Register Description
PHY Layer Control Register
PHY layer control
−25. PHY Control Register Description
Isochronous Cycle Timer Register
Isochronous cycle timer
−26. Isochronous Cycle Timer Register Description
Asynchronous Request Filter High Register
Asynchronous request filter high
−27. Asynchronous Request Filter High Register Description
From that node are accepted
Asynchronous Request Filter Low Register
Asynchronous request filter low
−28. Asynchronous Request Filter Low Register Description
Physical request filter high
Physical Request Filter High Register
−29. Physical Request Filter High Register Description
PhysReqAllBusses
That node are handled through the physical request context
Physical Upper Bound Register Optional Register
Physical Request Filter Low Register
Physical request filter low
−30. Physical Request Filter Low Register Description
Asynchronous context control
Asynchronous Context Control Register
−31. Asynchronous Context Control Register Description
Rscu RSU
Asynchronous Context Command Pointer Register
Asynchronous context command pointer
DescriptorAddress
Isochronous Transmit Context Control Register
Isochronous transmit context control
RSC RSU
Isochronous transmit context command pointer
Isochronous Transmit Context Command Pointer Register
Isochronous Receive Context Control Register
Isochronous receive context control
Not be changed while bit 10 active or bit 15 run is set to
When software clears bit 15 run
MultiChanMode
Context match register see .46 is ignored
Isochronous receive context command pointer
Isochronous Receive Context Command Pointer Register
Isochronous receive context command pointer
−43
Isochronous Receive Context Match Register
Isochronous receive context match
−35. Isochronous Receive Context Match Register Description
−1. TI Extension Register Map
DV and MPEG2 Timestamp Enhancements
Link Enhancement Control Set
Link Enhancement Control Clear A8Ch
Isochronous Receive Digital Video Enhancements
Isochronous Receive Digital Video Enhancements Register
Isochronous receive digital video enhancements
420h/424h see .44 is cleared to
Reserved. Bits 7 and 6 return 0s when read
CIPStrip1
Ohci offset 420h/424h see .44 is cleared to
Link Enhancement Register
Reserved. Bit 11 returns 0 when read 10 ‡
Link enhancement
−3. Link Enhancement Register Description
Timestamp Offset Register
Timestamp offset
−4. Timestamp Offset Register Description
Page
Base Registers
−1. Base Register Configuration
Address BIT Position
RHB IBR
−2. Base Register Field Descriptions
Field Size Type Description
RHB
LLC to service the interrupt
Long bus reset being performed
Timeout
Is unaffected by bus reset
Port Status Register
−3. Page 0 Port Status Register Configuration
−4. Page 0 Port Status Register Field Descriptions
BIT Position Address
Hardware reset and is unaffected by bus reset
−5. Page 1 Vendor ID Register Configuration
Vendor Identification Register
−6. Page 1 Vendor ID Register Field Descriptions
Vendor-Dependent Register
−7. Page 7 Vendor-Dependent Register Configuration
−8. Page 7 Vendor-Dependent Register Field Descriptions
NPA
−9. Power Class Descriptions
Power-Class Programming
Node does not need power and does not repeat power
PC0-PC2 Description
10−8
Flash Media Controller Programming Model
−1. Function 3 Configuration Register Map
11−2
Stepenb
Pcispeed Devsel
Programming interface. This field returns 00h when read
Storage controller
Is deasserted
Flash Media Base Address Register
Flash media base address
−7. Flash Media Base Address Register Description
Capabilities Pointer Register
Subsystem Vendor Identification Register
Subsystem vendor identification
Capabilities pointer
−8. PCI Interrupt Pin Register
Intsel Bits Useinta Intpin
11−8
Maximum Latency Register
Minimum Grant Register
This field returns 00h when read
−12. Power Management Capabilities Register Description
Pmestat RCU
Power Management Bridge Support Extension Register
Pmeen
PME Rsvd
Power Management Data Register
Power management data
−14. General Control Register
−15. Subsystem Access Register Description
SubsystemVendorID
Register at PCI offset 2Ch 11−14
Diagnostic
−16. Diagnostic Register Description
Tbdctrl
Plln
11−16
−1. Function 4 Configuration Register Map
Slot information
Maximum current
12−2
Bit 5 returns 0 when read
Therefore, bit 9 returns 0 when read
Transactions therefore, bit 4 returns 0 when read
Bit 3 returns 0 when read
Syserr RCU
Peripheral
DMA capabilities
12−5
Memory-read line, and memory-read multiple transactions
Read
12−6
SD host base address
SD Host Base Address Register
−7. SD host Base Address Register Description
Type
12−8
12.12 Interrupt Line Register
Space see Section 12−9
Register Maximum latency
Slot Information Register
−11. Maximum Latency Register Description
Numberslots
12−11
Driver is able to use it
−13. Power Management Capabilities Register Description
Controller to generate PME
Revision 12−12
Enable. Enables Signaling
Power management bridge support extension
Register
12−13
01 = Intb 10 = Intc 11 = Intd
−15. General Control Register
Dmaen
Dmasupport bit of each SD host socket is
−17. Diagnostic Register Description
−16. Subsystem Access Register Description
Reserved. Bits 31−17 return 0s when read
Register at PCI offset 2Ch
Slot 0 3.3-V Maximum Current Register
Slot 1 3.3-V Maximum Current Register
Slot 2 3.3-V Maximum Current Register
Slot 3 3.3-V Maximum Current Register
Slot 4 3.3-V Maximum Current Register
Slot 5 3.3-V Maximum Current Register
12−18
−1. Function 5 Configuration Register Map
1Ch−28h
60h−FCh
13−2
Seren
Intdis
Tabtsig RCU
Is enabled and the Smart Card controller has
Intstat
13−4
Offset 08h Type Read-only Default 0780 0000h
Smart Card base address register
Smart Card Base Address Register
Card is a multifunction device
Smart Card base address register
Smart Card Base Address Register 1−4
Smart Card base address register 1−4
13−7
13−8
13.13 Interrupt Line Register
−7. PCI Interrupt Pin Register
−8. Minimum Grant Register Description
Space see Section 13−9
13−10
−9. Maximum Latency Register Description
PMED3HOT
−11. Power Management Capabilities Register Description
PMED2
PMED1 PMED0 D2SUPPORT
PME Grst Rsvd
Dstate
13−12
Gated to reduce power consumption
−13. General Control Register
Pin = 01 = Intb pin = 10 = Intc pin = 11 = Intd pin =
Class Code Alias Register
Subsystem ID Alias Register
Subsystem ID alias
−14. Subsystem ID Alias Register Description
Smart Card configuration
Smart Card Configuration 1 Register
Smart Card configuration
13−15
−15. Smart Card Configuration 1 Register Description
−16. Smart Card Configuration 2 Register Description
Smart Card Configuration 2 Register
Pwrupdelay
Reserved. Bits 7−0 return 0s when read 13−17
13−18
Recommended Operating Conditions see Note
Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Temperature Ranges†
Operation MIN NOM MAX Unit
Avdd VCC VDPLL15 VDPLL33 Vccp
Recommended Operating Conditions
TJ#
Parameter Terminals Operation Test Conditions MIN MAX Unit
14.4.2 Driver
14.4.1 Device
14.4.3 Receiver
Parameter Test Condition MIN MAX Unit
Operating, Timing, and Switching Characteristics
Switching Characteristics for PHY Port Interface
Parameter Alternate Test Conditions MIN MAX Unit
Parameter Test Conditions MIN TYP MAX Unit
Mechanical Information
15−2
Package Option Addendum