MES-2110
Page
About This Users Guide
Intended Audience
Customer Support
Document Conventions
Syntax Conventions
Firewall
MES-2110 Computer Server
Dslam
Telephone Router
Safety Warnings
Safety Warnings MES-2110 User’s Guide
Contents Overview
Contents Overview MES-2110 User’s Guide
Table of Contents
Chapter System Details
10.1
Igmp
137
Chapter Command Line Interface 179
Index 229
Table of Contents MES-2110 User’s Guide
Introduction
Overview
Backbone Application
Bridging Example
Backbone Application
High Performance Switching Example
Ieee 802.1Q Vlan Application Examples
Shared Server Using Vlan Example
Metro Ethernet
Ways to Manage the MES-2110
Metro Ethernet
Good Habits for Managing the MES-2110
Hardware Installation and Connection
Installation Scenarios
Desktop Installation Procedure
Rack-mounted Installation Requirements
Mounting the MES-2110 on a Rack
Attaching the Mounting Brackets to the MES-2110
Attaching the Mounting Brackets
Mounting the MES-2110 on a Rack
Mounting the MES-2110 on a Rack
Hardware Overview
Front Panel
Front Panel Connections
Console Port
Gigabit Ethernet Ports
Label Description
Default Ethernet Negotiation Settings
Mini-GBIC Slots
Transceiver Installation
Power Connections Overview
Removing the Fiber Optic Cables
AC Power Connection
DC Power Connection
LED Descriptions
Powering on the MES-2110
LEDs
LED Color Statu Description
Green Blinking
Mbps Ethernet network
Tutorials
Igmp Snooping
Radius Configuration
Set Igmp Query Mode to Auto
Tutorials
Tutorials
MVR Tutorial Values
MVR Configuration
Setting Value
Based802.1q before proceeding
Open the Configuration Igmp Menu MVR screen
Tutorials
For Pri-Overide, select Enable
Vlan ID Priority
Untrusted ARP Inspection
Set Action to Enable and Dhcp Snooping Vlan Mode to All-VLAN
Outgoing Traffic Bandwidth
Frame Tagging
Frame Tagging Example
To configure frame tagging
Tutorials MES-2110 User’s Guide
Web Configurator
System Login
Introduction
Web Configurator Login
Web Configurator Main Screen
Main Screen
System Details Configuration Mgmt Config System Restart Menu
Navigation Panel Sub-links Overview
Snmp
Web Configurator Screen Sub-links Details
System Details Configuration Mgmt Config Restart Menu
Sntp
Navigation Panel Links
Link Description
Dhcp
ARP
Saving Your Configuration
Set Up the Administrative Password
Made on the MES-2110 and restart the MES-2110
Switch Lockout
Resetting the MES-2110
Reload the Configuration File
Resetting the MES-2110 Via the Console Port
System Details
System Information Screen
Board Information Screen
IP address from a Dhcp server if Dhcp client is enabled
Dhcp Configuration Screen
Address, subnet mask and a default gateway IP address
Undo Click this to restore your last saved settings Apply
System Details Dhcp Config Apply
Configuration
Port Configuration Screen
Truncated in some Web Configurator screens
Auto
Port Status Screen
Duplex This indicates the port’s duplex mode Half or Full
Disabled
Manage the MES-2110 via that port
Rmon Status Screen
This shows whether auto-negotiation is On or Off
RX+TX
Configuration Rmon Status
Switch in Loop State
Loop Detection
Loop Detection Screen
Loop detection Probe Frame
Enabled, the MES-2110 sends probe frames from this port to
Snmp traps when it shuts down a port via the loop detection
Feature
Down this port
Loop Detection MES-2110 User’s Guide
Jumbo Frame Configuration Screen
Jumbo Frame
Frame Size
Jumbo Frame MES-2110 User’s Guide
Ieee 802.1x Authentication
802.1x
Ieee 802.1x Authentication Process
Guest Vlan
10.2 802.1x Global Configuration Screen
Server UDP
10.3 802.1x Radius Server Configuration Screen
MES-2110. The key is not sent over the network
Port Number 1812 Server
10.4 802.1x Port Configuration Screen
Before configuring it on each port
Reauthenticat
Guest Vlan
10.5 802.1x Radius Server Configuration Screen
Clients for port access
Supported Radius Attributes
Technical Reference
Radius and TACACS+
Radius vs. TACACS+
Attributes Used for Authentication
Attributes Used for Authenticating Privilege Access
Radius Attributes Exec Events via Console
Attribute Start INTERIM-UPDATE Stop
Attributes Used for Accounting
Radius Attributes Exec Events via Telnet/SSH
Attributes Used for Accounting Ieee 802.1x Events
Radius Attributes-Exec Events via
802.1x MES-2110 User’s Guide
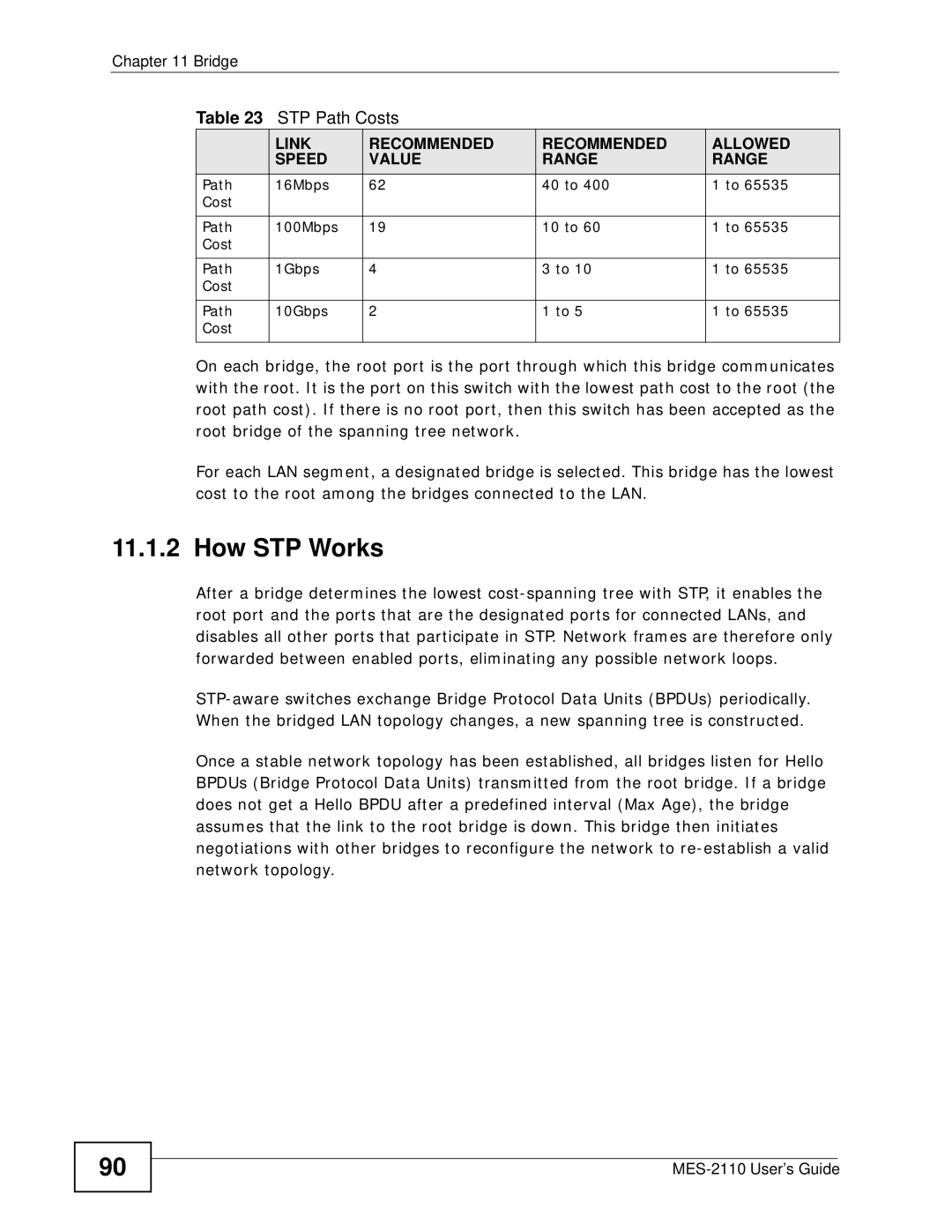
STP Path Costs
Bridge
STP Terminology
Link Recommended Allowed Speed Value Range
How STP Works
Path 16Mbps 40 to Cost 100Mbps 10 to 1Gbps 10Gbps
STP Port States
Bridge Configuration Screen
STP Port States
Port Description State
You select Rstp 802.1W in the Ring Protocol field
Rstp System Configuration Screen
Are done configuring
Tunnel port receives Bridge Protocol Data Units Bpdu
Root Bridge Information
Same priority, the switch with the lowest MAC address will
Determines Hello Time, Max Age and Forwarding Delay
List box
Selected from among the MES-2110 ports attached to
Allowed range is 4 to 30 seconds
As a general rule
Network. The allowed range is 6 to 40 seconds
Spanning Tree Port Configuration
255 and the default value is
Cost 1~65535 Enter the port’s path cost
P2P
User Priority
Introduction to Ieee 802.1Q Tagged VLANs
Tpid
CFI Vlan ID
Vlan Term Description Parameter
Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames
Ieee 802.1Q Vlan Terminology
Vlan
Vlan Type Screen
Port-Based Vlan Screen
Vlan Type Use this to set the MES-2110 to Port-Based or Tag
100
Port-Based Vlan Configuration
Then you cannot access the web configurator from a computer
Connected to this port
Vlan Stacking Example
Tag-Based Vlan Screens
Vlan Stacking
101
Vlan Stacking Port Roles
102
Vlan Tag Format
Vlan Tag Format
103
Type Priority
Single and Double Tagged 802.11Q Frame Format
Frame Format
104
802.1Q Frame
Vlan Stacking Configuration Screen
105
SP Tpid
106
Spvid
Tag-Based Port Information Screen
107
Pvid
108
Tag-Based Port Configuration Screen
Enter the Vlan ID from 1-4094 that you want to configure
Select whether you want to Add or Modify a Vlan ID
Management Vlan Screen
109
Unless your current access belongs to the new Vlan
110
Management Vlan This is the current management Vlan
Bandwidth Control Setup
Bandwidth Control
111
112
Broadcast Storm Control Setup
Broadcast Storm Control
113
Storm Control Configuration
114
Storm Control Status
Port Mirroring Setup
Port Mirroring
115
Volatile memory when you are done configuring
116
Select the monitor port number from the list
Link Aggregation
Dynamic Link Aggregation
117
Static Trunking Example
Link Aggregation ID Local Switch
Link Aggregation ID Peer Switch
Link Aggregation ID
Link Aggregation Setting
119
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
120
Lacp
Lacp Link Status
121
MAC
122
IP Multicast Addresses
Igmp Snooping
123
Igmp Configuration
Igmp Snooping and VLANs
124
125
Igmp Vlan
Igmp Vlan Query Mode
126
Igmp Status
MVR Overview
127
Types of MVR Ports
MVR Modes
How MVR Works 128
General MVR Configuration
129
Disable to turn this feature off
130
Select Dynamic to send Igmp reports to all MVR source ports
MVR Group Configuration
131
Drop-down list box
Group Configuration
132
MVR Group Status
MVR Configuration Example
133
134
MVR Group Configuration Example
135
136
137
Dhcp Relay Configuration
Dhcp Relay Agent Information
Relay Agent Information
Bytes This is the Vlan that the port belongs to
Dhcp Relay Configuration
138
To a Dhcp server
139
Option82 Information
140
IP Source Guard
141
Dhcp Snooping Overview
142
Dhcp Snooping Configuration
143
144
Dhcp requests will not succeed
Mode VLANs or specific VLANs to Dhcp servers Dhcp Snooping
Dhcp Binding Table
145
146
Ddhhmm
Configuring ARP Inspection
ARP Inspection Screen
147
148
Addresses permanently
149
150
MAC
151
MAC Table Status Screen
152
Lock MAC Address Learning Screen
Undo Click this to load your last saved settings Apply
MES-2110 or static manually configured
153
Port This is the port number Lock
MAC Filter Configuration Screen
154
To activate MAC address learning on the port
155
156
MAC Limit Configuration Screen
Addresses may access port 2 at any one time. a sixth device
Aged out. MAC address aging out time can be set in the MAC
QoS Base Configuration Screen
QoS
157
Configuring the Base Configuration Screen
158
159
802.1p Priority Table
160
161
Tag Priority Table
IP Dscp Priority Table
Number This is the Ieee 802.1p priority level Priority
Configuration QoS Menu IP Dscp Priority
162
Priority Override Configuration Screen
163
164
Mgmt Config and System Restart Menu
Serial Port Configuration Screen
165
Snmp Configuration Screens
166
Snmp Communities Screen
Snmp Commands
Command Description
IP Trap Manager Screen
Sntp Screen
168
Traps to
169
Alarms and Logs
170
171
Syslog
User Password
User Configuration Screen
Characters using characters found on a standard keyboard
172
Cable Test Screen
173
PHY RX/TX
Host DoS Protection
174
Test
Port Abnormal Traffic Detection Screen
175
Fields below
Upgrading the Firmware
176
Managing the Configuration File
177
Restarting the System
178
Console Port Management
Command Line Interface
Setting Default Value
Logging
Saving Changes
Using Shortcuts and Getting Help
Command / Keys Description
180
Basic Commands
Command Modes
Exit Command
Logging Out
Basic Commands
182
Privileged Command Mode
Privileged Commands
183
184
185
Make while using the MES-2110
Command line interface
Permanently save any changes you
186
Configuration Mode
Configuration Mode Commands
Ancillary Trigger Description
187
188
189
190
191
Address over Telnet
192
Igmp Snooping Example
193
Radius Configuration Example
194
This command to work
MVR Mode
MVR-Configuration Mode Commands
195
MVR Command Example
196
Vlan Mode
Vlan Mode Commands
197
Interface Mode
Vlan ID Priority Example
198
Interface Mode Commands
199
200
201
Bytes 1522 bytes + 4 bytes for
202
Port, the port must allow frames
Second tag to pass through it
Outgoing Traffic Bandwidth Limit Example
Sets the service provider Vlan ID of the current Ports
Untrusted ARP Inspection Example
203
Frame Tagging Examples
204
205
206
Troubleshooting
Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
207
MES-2110 Access and Login
208
209
Advanced Suggestions
210
Pop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions
MES-2110 Configuration and Console
211
My changes in the Web Configurator keep getting overwritten
212
213
214
Specification Description
Product Specifications
Hardware Specifications
215
Firmware Specifications
Feature Description
216
217
218
Standards Supported
Standard Description
Installing a Fuse
Removing a Fuse
219
220
Common Services
221
Commonly Used Services
222
Name Protocol Ports Description
223
224
Copyright
Certifications
225
226
FCC Warning CE Mark Warning
ZyXEL Limited Warranty
227
228
Index
229
230
231
MVR 127 configuration
Password 58 path cost 89, 93 port authentication
TACACS+
Weighted round robin scheduling
232