NBG-460N
Page
Related Documentation
About This Users Guide
Intended Audience
User Guide Feedback
About This Users Guide
Document Conventions
Syntax Conventions
NBG-460N Computer Server
Telephone Switch Router Modem
Icons Used in Figures
Dslam
Safety Warnings
Safety Warnings NBG-460N User’s Guide
Contents Overview
Contents Overview NBG-460N User’s Guide
Table of Contents
Chapter Connection Wizard
Part II Network
WAN
177
Part IV Management
235
Part V Maintenance and Troubleshooting 261
Part VI Appendices and Index
Table of Contents NBG-460N User’s Guide
Part
Page
Applications
Getting to Know Your NBG-460N
Overview
LAN
Wireless Applications
Router Mode
NBG460N
AP Mode
3 AP + Bridge
Bridge
AP + Bridge Application
Bridge Application
Bridge Loop Two Bridges Connected to Hub
Ways to Manage the NBG-460N
Features Available in Router Mode vs. AP Mode
Feature Router AP Mode Bridge
Router vs. AP vs. Bridge
LEDs
Power
Good Habits for Managing the NBG-460N
Front Panel LEDs
WAN
Wireless LAN Off Wireless LAN is not ready or has failed
This feature Off Device is in normal power mode
Wlan
Getting to Know Your NBG-460N NBG-460N User’s Guide
WPS Button
WPS Button NBG-460N User’s Guide
Accessing the Web Configurator
Introducing the Web Configurator
Web Configurator Overview
Change Password Screen
Procedure to Use the Reset Button
Resetting the NBG-460N
Navigating the Web Configurator
Icon Description
Status Screen in Router Mode
Status Screen Icon Key
Scheduler
Label Description
Dhcp
Is enabled and N/A when the Wlan is disabled
Wlan is disabled
When the line is disconnected
Memory Usage
Link TAB Function
Navigation Panel
Screens Summary
LAN
VPN
NAT
Ddns
Mgmt
Summary Bandwidth Management Monitor
Mode As a Router or a Access Point Language
Summary Any IP Table
Logs View Log
Summary Dhcp Table
Summary BW Mgmt Monitor
Summary Packet Statistics
Host Name field
Stop Click Stop to stop refreshing statistics
Summary VPN Monitor
Intervals field
This is the security association index number
Association Time
Summary Wireless Station Status
This is the index number of an associated wireless station
NBG-460N’s Wlan network
Introducing the Web Configurator NBG-460N User’s Guide
Wizard Setup
Connection Wizard
Connection Wizard System Information
System Name
Domain Name
Underscores are accepted
This option is only available if WPS is not enabled
Connection Wizard Wireless LAN
Use the same Ssid in order to access the network
Ssid
Basic WEP Security
Wizard Basic WEP Security
Ascii
Extend WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK Security
WEP
HEX
Key
Connection Wizard Internet Configuration
Pre-Shared
Do this
Connection Description Type
Ethernet Connection
PPPoE Connection
Pptp
ISP Parameter for Internet Access
Pptp Connection
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Wizard Pptp Connection
Use fixed IP address
Your IP Address
WAN IP Address Assignment
Provided by your ISP
10.0.0.0 172.16.0.0 192.168.0.0
IP Address and Subnet Mask
Private IP Address Ranges
DNS Server Address Assignment
WAN IP and DNS Server Address Assignment
Choose an IP address
WAN MAC Address
WAN IP Address Assignment
Connection Wizard Bandwidth management
Wizard WAN MAC Address
Connection Wizard Complete
Wizard Bandwidth Management
Connection Wizard Complete
Connection Wizard NBG-460N User’s Guide
Internet
How to Connect to the Internet from an AP
Tutorials
Push Button Configuration
NBG460N
Example WPS Process PIN Method
WPA-PSK
SSIDExample3
Channel Security
Pre-Shared Key ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey
Configure Your Notebook
Tutorial Status AP Mode
Connecting a Wireless Client to a Wireless Network
Using AP + Bridge Mode and WDS
Link Status
Configuring Your Bridge Mode Settings
WPA2-PSK
Pre-Shared Key ThisismyWPA2-PSKpre-sharedkey
Site-To-Site VPN Tunnel Tutorial
Site-To-Site VPN Tunnel Settings
Setting BOB’S NBG-460N JACK’S NBG-460N
Configuring Bob’s NBG-460N VPN Settings
Tutorial Property
Configuring Jack’s NBG-460N VPN Settings
Tutorial Authentication Method
Tutorial Property
Tutorial Authentication Method
Checking the VPN Connection
Pinging Jack’s Local IP Address
Configuring Bandwidth Management by Application
Bandwidth Management for your Network
Configuring Bandwidth Management by Custom Application
Configuring Bandwidth Allocation by IP or IP Range
Fields Services Real Audio Rtsp VDO Live FTP
Refer to Appedix F on the Bandwidth Mgnt
AP Mode
Setting your NBG-460N to AP Mode
Status AP Mode
Status Screen
This shows the LAN port’s Dhcp role Client or None
Display Network Wireless LAN WPS screen
System Setting Configuration Mode
Schedules
Menu AP Mode
Or connected
Reset the factory defaults to your NBG-460N
Maintenance System General
Setting Logs View Log
Mask or to get the LAN IP address from a Dhcp server
Sys OP General
Configuring Your Settings
LAN Settings
Wlan and Maintenance Settings
Table below describes the labels in the screen
Logging in to the Web Configurator in AP Mode
Network
Page
Wireless LAN
Example of a Wireless Network
What You Should Know
Wireless Security Overview
What You Can Do
Ssid
100
Types of Encryption for Each Type of Authentication
No Authentication Radius Server
Weakest Stronges t
101
General Wireless LAN Screen
Printable 7-bit Ascii characters for the wireless LAN
WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK are available in this field
No Security
102
Select Static WEP , WPA-PSK , WPA , WPA2-PSK or WPA2 to add
WEP Encryption
103
WEP keys and displays them in the Key fields below
Select 64-bit WEP or 128-bit WEP to enable data encryption
104
Correct WEP key
105
AP or peer computer
Hex
106
Server, the reauthentication timer on the Radius server has
Security Mode field
Priority
4 WPA/WPA2
107
Has priority
Server, the reauthentication timer on the Radius server
108
MAC Filter Screen
109
110
MAC
111
Wireless LAN Advanced Screen
Quality of Service QoS Screen
RTS/CTS
WMM QoS Policy
112
On page 123 for more information
You want to apply WMM QoS
113
Application Priority Configuration
Configuration screen
User-Defined
114
Mail
WPS Screen
115
116
WPS Station Screen
Scheduling Screen
Push Button
Following times fields
117
Whole day
Day
WDS Screen
118
119
Security Mode Static WEP
Between the NBG-460N and any wireless clients
120
ASCII/HEX
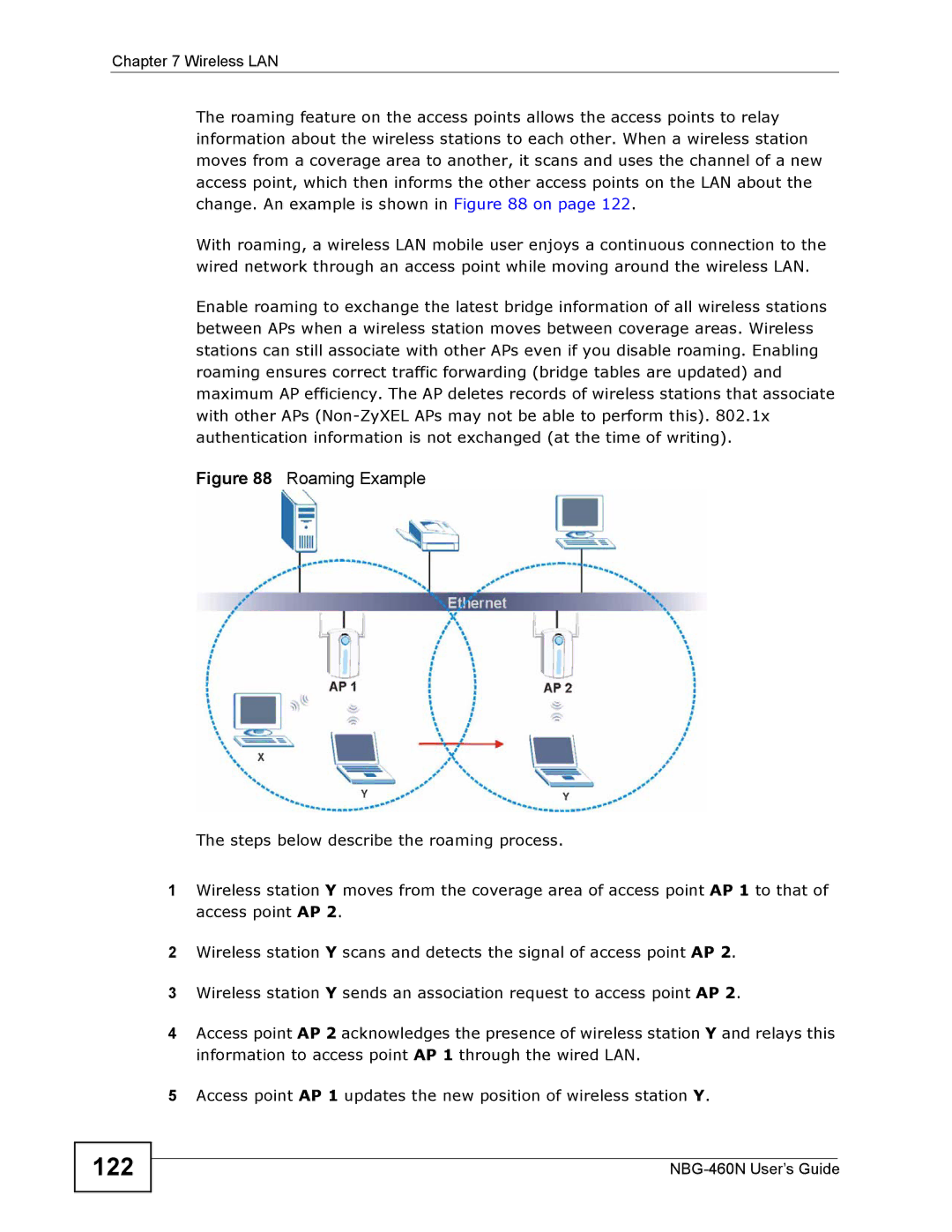
Roaming
Security Mode WPA2-PSK
Technical Reference
121
122
Roaming Example
Quality of Service
123
124
WiFi Protected Setup
IPod Touch Web Configurator
WMM QoS Priorities
Login Screen
125
System Status
126
127
WAN connection is not working
128
MBM
129
WPS in Progress
Port Forwarding
Turn the rule OFF
130
Rule is turned on
131
Accessing the iPod Touch Web Configurator
Accessing the iPod Touch Web Configurator
132
133
LAN and WAN
134
Configuring Your Internet Connection
What You Need To Know
WAN MAC Address
Multicast
135
Iptv STB Port
136
You have two STBs
137
You have one STB
192.168.1.20
138
NetBIOS over TCP/IP
Auto-Bridge
139
Internet Connection
Ethernet Encapsulation
Defined changes to None after you click Apply
140
Address
WAN MAC
141
Setting or upload a different ROM file
PPPoE Encapsulation
Select Clone the computers MAC address IP Address and enter
All of the LANs computers will have access
142
Computer’s
143
DNS Servers First DNS
Different ROM file
Pptp Encapsulation
144
145
Pptp connection
Select Clone the computers MAC address IP Address
Advanced WAN Screen
146
147
Select Igmp V-1,IGMP V-2 or None
Igmp
When the NBG-460N gets a WAN IP address that is not
To be in Router Mode for the Iptv STB port to work
148
LAN
149
LAN TCP/IP
IP Pool Setup
LAN IP Screen
150
LAN TCP/IP
LAN IP Alias
151
152
Any IP Setup
Advanced LAN Screen
IP address that you assign. Unless you are implementing
LANs, WANs and the ZyXEL Device
153
Any IP
154
155
156
Dhcp
157
158
Dhcp General Screen
Dhcp Advanced Screen
159
Select the Enable Dhcp Server check box. When you clear
Must have their DNS server addresses manually configured
160
NBG-460Ns system DNS server configured in the WAN Internet
Client List Screen
Select DNS Relay to have the NBG-460N act as a DNS proxy.
Host names. After you click Apply, the MAC address and IP
161
This is the index number of the host computer
Them
162
Network Address Translation NAT
163
Default Server Setup
Enable Network
Select the check box to enable NAT
General NAT Screen
NAT Application Screen
165
166
Fields under Add Application Rule
Wake On LAN is enabled
167
168
Configuring Servers Behind Port Forwarding Example
Game List Example
NAT Advanced Screen
169
Can establish through the NBG-460N
Users may not be able to access the Internet
170
171
LAN that requested the service
Trigger Port Forwarding Example
Traffic to a server on the WAN
Two Points To Remember About Trigger Ports
172
173
Dynamic DNS
DynDNS Wildcard
174
Enable Dynamic Select this check box to use dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS Screen
175
WAN IP address
176
Part
177
178
Firewall
179
180
About the NBG-460N Firewall
Triangle Routes
Triangle Routes and IP Alias
181
182
Services Screen
General Firewall Screen
183
Icmp
184
Add Firewall Rule screen
Pool
Add Firewall Rule Screen
185
Single IP is selected as the Address Type
Address Type
Click Clear All to empty the Blocked Services
186
187
188
189
Content Filtering
Content Filtering Profiles
Keyword Blocking URL Checking
Restrict Web Features
190
Days and Times
Filter Screen
191
Web Proxy
192
Cookies
Allowed
193
Which content filtering will be enforced
Schedule Screen
Not affected
Domain Name or IP Address URL Checking
Customizing Keyword Blocking URL Checking
194
Full Path URL Checking
IPSec VPN
195
IKE SA IKE Phase 1 Overview
196
IP Addresses of the NBG-460N and Remote IPSec Router
IPSec SA IKE Phase 2 Overview
197
Local Network and Remote Network
General Screen
198
VPN Rule Setup Basic
199
Feature to work
200
Secure Gateway Address field set to
Enabled
201
202
With dynamic WAN IP addresses
Your computer in the Local Content field. The NBG-460N
203
204
Address field refer to the Secure Gateway Address field
VPN Rule Setup Advanced
205
Security VPN General Rule Setup IKE Advanced
206
Select No to disable it
207
208
209
210
211
212
Each IPSec SA. It is more secure but takes more time
VPN Rule Setup Manual
213
Security VPN General Rule Setup Manual
214
215
216
SPI
217
Secure
Trailing spaces are truncated
SA Monitor Screen
218
219
VPN and Remote Management
IKE SA Proposal
Diffie-Hellman DH Key Exchange
220
221
Authentication
VPN Example Matching ID Type and Content
Remote Ipsec Router
222
Negotiation Mode
VPN Example Mismatching ID Type and Content
15.6.6 VPN, NAT, and NAT Traversal
223
224
IPSec Protocol
Encapsulation
225
IPSec SA Proposal and Perfect Forward Secrecy
Additional IPSec VPN Topics
SA Life Time
Private DNS Server
Encryption and Authentication Algorithms
226
227
Private DNS Server Example
228
Management
229
230
Lanwan
Static Route
231
IP Static Route Screen
232
Static Route Setup Screen
233
234
FTP
Bandwidth Management
235
Chat, Email
General Configuration Screen
236
Mbps
237
Management check box
Connected to the WAN port has an upstream speed of 10 Mbps
Advanced Configuration
238
Wlan Bandwidth
239
Low
Wlan to WAN
Rule Configuration with the Pre-defined Service
240
To Wlan
Rule Configuration User Defined Service Rule Configuration
241
Monitor Screen
242
Service Description
Predefined Bandwidth Management Services
Media Bandwidth Management Setup Services
Technical References
244
Default Bandwidth Management Classes and Priorities
Bandwidth Management Priority with Default Classes
Class Type Priority
Bandwidth Management Priorities
Bandwidth Management Priorities
245
246
Remote Management
247
Remote Management and NAT
System Timeout
Remote Management Limitations
248
249
Specify to access the NBG-460N using this service
WWW Screen
Remote management
250
Telnet Screen
FTP Screen
DNS Screen
251
252
You specify to send DNS queries to the NBG-460N
253
Universal Plug-and-Play UPnP
NAT Traversal
UPnP Screen
254
Using UPnP in Windows XP Example
255
256
Network Connections
Internet Connection Properties Advanced Settings
257
Web Configurator Easy Access
258
259
Network Connections My Network Places
260
Network Connections My Network Places Properties Example
Maintenance Troubleshooting
261
262
263
System
System General Screen
264
Time Setting Screen
265
266
Select User Defined Time Server Address and enter the IP
267
268
Logs
269
270
Log categories that you selected in the Log Settings
View Log Screen
Display
Time and date
Log Settings
271
Messages will not be sent via e-mail
Mail Log Settings Mail Server
272
Smtp
273
Sent via e-mail
274
System Maintenance Logs
Log Descriptions
LOG Message Description
System Error Logs
275
276
Access Control Logs
TCP Reset Logs
Firewall Attack Alerts screen
277
Packet Filter Logs
278
Icmp Logs
UPnP packets can pass through the firewall
Content Filtering Logs
279
280
Attack Logs
281
IPSec Logs
282
IKE Logs
283
284
802.1X Logs
285
PKI Logs
Packet Direction Description
ACL Setting Notes
286
Type Code Description
Syslog Logs
287
Icmp Notes
LOG Display Payload Type
288
RFC-2408 Isakmp Payload Types
289
Tools
Firmware Upload Screen
Maintenance Tools Firmware
290
Upload Error Message
Network Temporarily Disconnected
Restore Configuration
Configuration Screen
Backup Configuration
Maintenance Restore Configuration
Configuration Restore Successful
293
294
Back to Factory Defaults
Restart Screen
Green
Indicate either Ready or MAC Address error
Wake On LAN
295
Maintenance Tools Green
296
Configuration Mode
297
Category Link TAB
Advanced Configuration Options
298
Sys Op Mode
299
300
Router
Maintenance Sys OP Mode General
301
302
Firewall or bandwidth management
303
Language
Language Screen
304
305
Troubleshooting
Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
NBG-460N Access and Login
306
307
Advanced Suggestions
Internet Access
308
309
Internet connection is slow or intermittent
Resetting the NBG-460N to Its Factory Defaults
310
Wireless Router/AP Troubleshooting
311
Advanced Features
312
313
Product Specifications and Wall- Mounting Instructions
Hardware Features
PWR, LAN1-4, WAN, WLAN, WPS
Bluetooth enabled devices, and other wireless LANs
Firmware Features
Such as microwave ovens, wireless phones
314
315
316
Feature Specifications
Feature Specification
Standards Supported
Protocol MBM Media Bandwidth Management
Wall-mounting Instructions
317
318
Masonry Plug and M4 Tap Screw
Appendices Index
319
320
321
Disable pop-up Blockers
Internet Explorer Pop-up Blockers
Enable pop-up Blockers with Exceptions
322
Select Settings…to open the Pop-up Blocker Settings screen
323
JavaScripts
324
325
Internet Options Security
Java Permissions
326
327
Java Sun
328
Java Sun
329
Introduction to IP Addresses
Structure
Subnet Mask Identifying Network Number
Subnet Masks
330
1ST 2ND 3RD 4TH Octet
Subnet Masks
331
Network Size
Binary 1ST 2ND 3RD 4TH Decimal Octet
Maximum Host Numbers
Notation
332
Alternative Subnet Mask Notation
Subnetting
333
Example Four Subnets
334
335
IP/SUBNET Mask Network Number Last Octet BIT Value
336
Example Eight Subnets
Subnet Planning
16-bit Network Number Subnet Planning
Configuring IP Addresses
337
NO. Borrowed Subnet Mask NO. Hosts PER Host Bits Subnets
338
Private IP Addresses
Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
339
340
Installing Components
Windows 95/98/Me
Configuring
341
Verifying Settings
342
Windows 2000/NT/XP
343
344
Windows XP Control Panel
345
Windows XP Local Area Connection Properties
346
Windows XP Internet Protocol TCP/IP Properties
347
Windows XP Advanced TCP/IP Properties
348
Macintosh OS 8/9
349
350
Macintosh OS 8/9 TCP/IP
Macintosh OS
351
352
Using the K Desktop Environment KDE
Linux
353
Red Hat 9.0 KDE Ethernet Device General
Using Configuration Files
354
Red Hat 9.0 Static IP Address Setting in ifconfig-eth0
Red Hat 9.0 DNS Settings in resolv.conf
Verifying Settings
356
357
Wireless LAN Topologies
Ad-hoc Wireless LAN Configuration
Basic Service Set
358
Channel
359
360
RTS/CTS
Preamble Type
Ieee 802.11g Wireless LAN
Fragmentation Threshold
361
Ieee 802.11g
Ieee
362
Data Rate Modulation Mbps
Types of Radius Messages
Types of Authentication
363
EAP-MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm
EAP-TLS Transport Layer Security
EAP-TTLS Tunneled Transport Layer Service
364
Peap Protected EAP
365
Comparison of EAP Authentication Types
WPA2
Encryption
User Authentication
366
367
27.0.2 WPA2-PSK Application Example
27.0.3 WPA2 with Radius Application Example
Security Parameters Summary
Wireless Security Relational Matrix
Authentication Encryptio Enter METHOD/ KEY
368
Services
369
Name Protocol Ports Description
Examples of Services
370
371
372
373
Copyright
Certifications
Disclaimer
374
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
Viewing Certifications
ZyXEL Limited Warranty
375
376
Registration
Classes and priorities
Index
377
CTS Clear to Send
Encapsulating Security Payload. See ESP
378
Essid
Ethernet PPPoE. see also PPP over Ethernet
379
IKE SA
Language Link type 40
Mbssid
380
MAC
Radius
QoS QoS priorities Quality of Service QoS
381
Wireless security 98 overview
382
383
Xbox Live ZyNOS 39
384