W . d e l l . c o m s u p p o r t . d e l l . c o m
January DR715
Contents
Entering the BMC Setup Module BMC Setup Module Options
Memory Information Screen
Hard Drive Installation Guidelines
Installing an Expansion Card
Installing a SAS Controller Card
Installing a RAID Battery
Configuring the Boot Device
Installing Memory Modules 130 Removing Memory Modules 132
Replacing the System Battery 138
Installing the Power Supply Distribution
128
Troubleshooting a Wet System 168
Troubleshooting the System Battery 170
Troubleshooting System Memory 174
159
193
197
Glossary Index
Other Information You May Need
About Your System
Accessing System Features During Startup
Front-Panel Features and Indicators
Front-Panel Features and Indicators About Your System
System, the power is turned off
Device driver errors when using
System, the system performs a
Is turned off. If the system is not
Back-Panel Features and Indicators
Connecting External Devices
Power Indicator Codes
Redundant Power Supply Indicators Function
Green indicates that the power supply is operational
Providing DC power to the system
NIC Indicator Codes
LCD Status Messages
E1000
Call Support
E1114 Temp Ambient
E1118 CPU Temp
E1211 Romb Batt
E1214 ## PwrGd
E1216
E1217 E121A 8V PwrGd
E122E
E122F 5V PwrGd
E1231
E1232
E123C Planar LOM
E1310 RPM Fan ##
E1313 Fan
Redundancy
E1414
Thermtrip
E1418
Presence
E141F CPU Protocol
E1421 CPU Init
E1422 CPU Machine
Chk
E1620 PS # Input
Range
E1624
E1625
Err B## D##
E1712
E171F Pcie Fatal
E1811 HDD ## Rbld
Abrt
E1812 HDD ##
Removed
Fault
E2011 Mem Config
E1A15 SAS Cable D
E1A18 PDB Ctrl
E2013 Shadow Bios
Controller E2017 Timer Fail
E2018 Prog Timer
E2019 Parity Error
E201F Drac Config
E2020 CPU Config
Disable Dimm
E2021 Memory
Solving Problems Described by LCD Status Messages
System Messages
Removing LCD Status Messages
Memory disabled
Configuration
Update Remote
Bios Update
Error Remote
Access
Failure Error
Keyboard are Securely Attached to Correct Connectors
Mode detected
Keyboard data
Line failure
Keyboard stuck
No boot device
No timer tick
Interrupt PCI Bios failed
To install
PCIe Fatal Error
Reset Slot
Caused a system
Embedded
Seek error
Enabled
ROM bad checksum
Sector not found
Setup program
Timer chip
Configuration Operation Honored TPM failure
Modify to allow This change Reset the system Unexpected
Installed memory
Unsupported CPU
Combination
Stepping Detected Utility
Diagnostics Messages
Write fault
Write fault on
Alert Messages
About Your System
Entering the System Setup Program
Responding to Error Messages
System Setup Options
Using the System Setup Program
Main Screen
System if any changes were made
Main System Setup Program Screen
Or DVD drive. See Sata Configuration Screen on
Boot Sequence
On the hard drives installed in your system
Cache size, and so on. See Table
Memory Information Screen
CPU Information Screen
Specified processor
Enabling AMD PowerNow! Technology
Displays the family, model, and stepping
Sata Configuration Screen
Mode sets the Sata subsystem to native Sata mode
Port is enabled if devices are attached to the port
Port
All Ports On default
Integrated Devices Screen
All Ports Off
System board
Serial Communication Screen
System Security Screen
When set to Off default, presence of the TPM is not
When set to On with Pre-boot Measurements,
Stores the pre-boot measurements compliant with
When set to On without Pre-boot Measurements,
Button is enabled in the System Setup program
When disabled, the button can only turn on system
Power
NMI Button Disabled default
Exit Screen
System and Setup Password Features
Using the System Password
Using the System Setup Program
Using the System Setup Program
Using the Setup Password
See Disabling a Forgotten Password on
Disabling a Forgotten Password
Baseboard Management Controller Configuration
Entering the BMC Setup Module
BMC Setup Module Options
Using the System Setup Program
Installing System Components
Installing System Components
Recommended Tools
Inside the System
Drive release latch
Power supplies
System fan
Installing the Front Drive Bezel
Front Drive Bezel
Removing the Front Drive Bezel
Hard drives System board System memory
Bezel tabs
Installing an Insert on the Front Drive Bezel
Removing an Insert on the Front Drive Bezel
Opening the System
Tab notch Insert tab
Hook slot Cover latch Foot Installing System Components
Opening and Closing the System Latch release lock
Reinstall the system cover a Lift up the cover latch
Closing the System
Removing and Installing Blank Drive EMI Fillers
Removing and Installing a Blank Drive EMI Filler Filler tabs
Removing the Processor Shroud
Cooling Shrouds
Removing the Expansion Card Shroud
Rear shroud alignment tabs
Gripping points
Installing the Processor Shroud
Shroud touch point
Power Supplies
Installing the Expansion Card Shroud
Removing a Redundant Power Supply
Pull the power supply straight out to clear the chassis
Installing a Redundant Power Supply
Cable retention bracket
Removing a Non-redundant Power Supply
Page
Shroud
Power supply release tab
Screws Installing System Components
Installing a Non-redundant Power Supply
Removing a Hard Drive
Hard Drive Installation Guidelines
Hard Drives
Carrier release tab
Installing a Hard Drive
10. Installing a Hard Drive in a Drive Bracket Hard drive
Drive
Satab cable to system board
Connector to SAS controller card
Removing a Hot-plug Hard Drive
Installing a Hot-plug Hard Drive
Drive bracket
Removing a Hot-plug Hard Drive Blank
Installing a Hot-plug Hard Drive Blank
Diskette Drive
Removing the Diskette Drive
15. Removing or Installing a Diskette Drive Diskette drive
Drive bay screw slots Drive release latch
Installing a Diskette Drive
Connect the power cable to the drive
16. Installing Diskette Drive Shoulder Screws
Diskette drive connectors
Optical and Tape Drives
Removing an Optical or Tape Drive
Drive bay screw slots
Drive bay screw slots
Drive alignment screws SAS tape drive SAS cable
Installing an Optical or Tape Drive
101
21. Installing Optical or Tape Drive Shoulder Screws
103
104
Ribbon cable notch
105
Pata optical drives Pata data cable
106
107
Expansion Cards
Removing an Expansion Card
Installing System Components
109
Expansion card
Installing an Expansion Card
111
Installing a SAS Controller Card
SAS Controller Card
Installing System Components
SAS/SATA backplane power
Connector Top of processor shroud
113
SAS/SATA backplane
RAID Battery
Removing a SAS Controller Card
Installing a RAID Battery
115
Removing a RAID Battery
Configuring the Boot Device
RAC Card
Removing the RAC Card
117
118
Installing a RAC Card
119
Internal USB Memory Key Connector
Installing the Optional Internal USB Memory Key
121
TOE key
Removing the Expansion Card Fan
Integrated TOE
Cooling Fans
Securing slots Installing System Components
123
Installing the Expansion Card Fan
Removing the System Fan
Fan release tab Installing System Components
125
Installing the System Fan
127
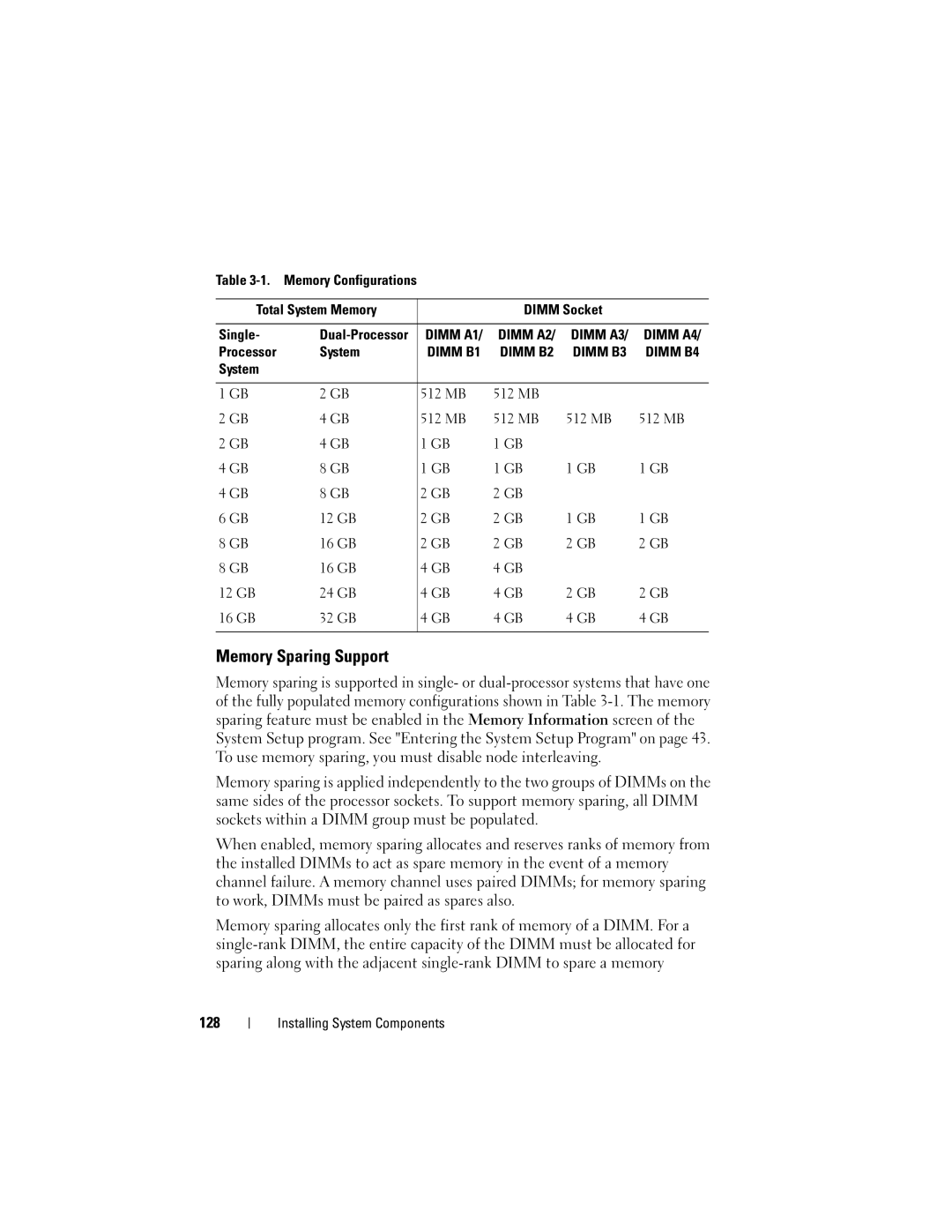
General Memory Module Installation Guidelines
System Memory
System 512 MB 12 GB 16 GB 24 GB 32 GB
Memory Sparing Support
Processor System
129
CPU CPUs 512 16 GB
Installing Memory Modules
130
33. Installing and Removing a Memory Module Memory module
131
Removing Memory Modules
133
Processors
Removing a Processor
134
Release levers Thermal grease
Rotate the processor shield upward and out of the way
135
Installing a Processor
Unpack the new processor
137
System battery is a 3.0-volt V, coin-cell battery
System Battery
Replacing the System Battery
36. Replacing the System Battery
139
Installing System Components
141
Chassis Intrusion Switch
Removing the Chassis Intrusion Switch
Installing the Chassis Intrusion Switch
Intrusion connector on system board
143
Power Supply Distribution Board
Removing the Power Supply Distribution Board
Shroud release latch Shroud alignment guides
145
Power supply cage
Installing the Power Supply Distribution Board
147
SAS/SATA Backplane
Removing the SAS/SATA Backplane
149
Installing the SAS/SATA Backplane
SAS cable connector Power cable
151
Control Panel Service-only Procedure
Removing the Control Panel
Screws Control panel
System Board Service Only Procedure
Installing the Control Panel
Removing the System Board
153
Installing System Components
155
Installing the System Board
157
158
Safety First-For You and Your System
Management software Documentation Monitors power indicator
Start-Up Routine
159
Troubleshooting External Connections
Troubleshooting the Video Subsystem
Monitor is not working properly Video memory is faulty
Checking the Equipment
Troubleshooting the Keyboard
161
Troubleshooting Your System
Troubleshooting the Mouse
163
Troubleshooting Serial I/O Problems
165
Troubleshooting a Serial I/O Device
Troubleshooting a USB Device
Troubleshooting Your System
167
Troubleshooting a NIC
NIC cannot communicate with network
Troubleshooting a Wet System
Liquid spilled on the system Excessive humidity 168
169
Troubleshooting a Damaged System
System was dropped or damaged
Troubleshooting the System Battery
Troubleshooting Redundant Power Supplies
171
Troubleshooting System Cooling Problems
Troubleshooting a Fan
173
Troubleshooting System Memory
175
Troubleshooting an Internal USB Key
System cannot read data from a USB memory key
177
Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive
Error message indicates a diskette drive problem
Troubleshooting Your System
Troubleshooting an Optical Drive
179
Troubleshooting a Scsi Tape Drive
Troubleshooting a Hard Drive
181
Troubleshooting Your System
Troubleshooting a Hot-plug Hard Drive
183
Troubleshooting Your System
Troubleshooting a SAS or SAS RAID Controller
185
Troubleshooting Your System
Troubleshooting Expansion Cards
187
Troubleshooting Your System
Troubleshooting the Microprocessors
189
Troubleshooting Your System
191
192
Using Dell PowerEdge Diagnostics
System Diagnostics Features
System Diagnostics Testing Options
When to Use the System Diagnostics
Running the System Diagnostics
Using the Custom Test Options
Selecting Devices for Testing
Selecting Diagnostics Options
195
Viewing Information and Results
System Board Jumpers and Connectors
Jumpers and Connectors
System Board Jumpers and Connectors 33 32
198
Serial connector
199
200
SAS/SATA Backplane Board Connectors
201
202
203
204
Getting Help
Contacting Dell
205
206
207
Amperes AC Alternating current
208
Celsius
209
210
211
212
Hz Hertz
213
214
215
216
217
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
System diskette See bootable diskette System memory See RAM
218
219
220
221
222
223
Index
Index
225
Post
227
Upgrades processor
USB
Warranty Wet system troubleshooting
229
230