F2MC-8L
Page
Fujitsu Limited
Page
Fujitsu Limited
Purpose of This Manual and Intended Reader
Trademark
Structure of This Manual
This appendix shows the I/O map and instructions list
This chapter describes the functions and operation of Uart
Copyright 2005-2008 Fujitsu Limited All rights reserved Iii
Reading this Manual
Example notation of multi-use pins P33/EC pin
Contents
127
115
161
135
205
243
225
259
279
339
313
347
375
357
403
Appendix a
RST
Changes For details, refer to main body
Xii
Chapter Overview
Overview
Features of MB89202/F202RA Series
Uart
Up to 26 pins of I/O ports
Low-power consumption modes standby modes
Wild registers
KB Flash with read protection
1 MB89202/F202RA Series Models
MB89202/F202RA Series Product Lineup
MB89201 MB89F202/F202RA MB89V201
Cmos
2 CPU and Peripheral Functions of MB89202/F202RA Series
Specification
PWM
Uart
1 Differences between Models
Differences between Models
Package MB89201 MB89F202/F202RA MB89V202
Current consumption
1 Block Diagram of MB89202/F202RA Series
Block Diagram of MB89202/F202RA Series
1 Pin Assignment of DIP-32P-M06
Pin Assignment
2 Pin Assignment of FPT-34P-M03
Pin Assignment of FPT-34P-M03
Package Dimension of DIP-32P-M06
Package Dimensions
Package Dimension of FPT-34P-M03
Pin Functions Description 1/2
Pin Functions Description
Pin No Circuit Function Name Type
Pin Functions Description 2/2
Circuit Types 1/2 Remarks
I/O Circuit Types
Types Circuit Remarks
Circuit Types 2/2
Overview
Chapter Handling Devices
Precautions on Handling Devices
Handling Devices
Precautions on Handling Devices
Product name Operating voltage Step-down circuit
Step-down circuit stabilization time
Oscillation stabilization wait time 218/FCH
Chapter CPU
CPU
Memory Space
Area address 0000H to 007FH
RAM area
Memory Map
Vector Table Area Address FFC0H to Ffffh
Specific-purpose Areas
1 Vector /2
Address in the vector table
Fffd H
Fffb H
Fffe H Ffff H
Bit Operand Storage State
Location of 16-bit Data on Memory
Bit Data Storage State in Stack
Functions of the Dedicated Register
Dedicated Register
Program counter PC
Accumulator a
Index register
Temporary Accumulator T
Extra-pointer EP
Stack pointer SP
Bits for Indicating Arithmetic Operation Results
Condition Code Register CCR
1 Interrupt Levels
Bits for Controlling Acceptance of Interrupts
IL1 IL0
Register Bank Pointer RP
4 Configuration of Register Bank Pointer
General-Purpose Registers
1 Configuration of Register Bank
Features of the General-purpose Registers
1 Interrupt Requests and Interrupt Vectors 1/2
Interrupts
1 Interrupt Requests and Interrupt Vectors 2/2
L01 to LF1 L00 to LF0 Requested interrupt level Priority
Interrupt Level Setting Registers ILR1 to ILR4
2 Steps in the Interrupt Operation
Steps in the Interrupt Operation
CPU
Example of multiple interrupts
Multiple Interrupts
Interrupt request sample wait time
Interrupt Processing Time
Interrupt handling time
Stack Operation at the End of Interrupt Processing
Stack Operation at Interrupt Processing
XXH
E0H
0000H 0080H 0280H
Stack Area for Interrupt Processing
RAM
ROM Ffffh
1 Reset Sources
Reset
Power-on reset
Reset Sources and Oscillation Stabilization Wait Time
1 Configuration of Reset Flag Register Rsfr
Reset Flag Register Rsfr
Ponr
Bit name Description
Erst
Wdog
Function of the External Reset Pin
External Reset Pin
3 Reset Operation Flow
Reset Operation
State of Reset Waiting for Stabilization of Oscillation
Mode Fetch
Influence from a Reset of Contents in RAM
States of Pins after the CPU Reads the Mode Data
State of Each Pin at Reset
1shows the clock supply map
Clock
1 Clock Supply Map
For a crystal resonator or ceramic resonator
Clock Generator
For an external clock
Clock Controller
4 Block Diagram of Clock Controller
System clock selector
Oscillator
Clock controller
Oscillation stabilization wait time selector
System Clock Control Register Sycc
5 Configuration of System Clock Control Register Sycc
Instruction Cycle tINST
Gears Clock Speed Switching Function
Clock Mode
2 Operations in Each Clock Mode
Sycc CS1 CPU
Operations in Active Mode
Oscillation stabilization wait time during operation
Oscillation Stabilization Wait Time
Sycc WT1, WT0
Oscillation stabilization wait time at a reset
Sleep mode
Standby Mode Low-Power Consumption Mode
Stop mode
State of pins in standby mode
Operations in Standby Mode
RUN
Sleep Stop SPL=0 SPL=1
Transition to sleep mode
Sleep Mode
Cancellation of sleep mode
Transition to stop mode
Stop Mode
1 Standby Control Register Stbc
Standby Control Register Stbc
SLP
STP
SPL
Resv
2 State Transition Diagram
Diagram for State Transition in Standby Mode
Transition to and cancellation of standby mode
3 Transition to and Cancellation of Clock Mode
4 Transition to and Cancellation of Standby Mode
State transition Transition conditions
Stbc register Mode STPbit7 SLPbit6
Cancellation of Standby Mode by an Interrupt
Oscillation Stabilization Wait Time
Mode Data
Memory Access Mode
Operations for Selecting Memory Access Mode
1 Settings for Mode Data
2 Operations for Selecting Memory Access
CPU
Overview of I/O Ports Programming Example of I/O Port
Chapter Ports
O Ports
Overview of I/O Ports
Functions of Ports
Register name Read/Write Address Initial value
2 Registers of Ports
Xxxxxxxxb
Xxxxb
Port
Pins of Port
Registers PDR0, DDR0, and PUL0 of Port
Block Diagram of Port
PDR0, DDR0, PUL0
Registers of Port 0 PDR0, DDR0, and PUL0
2 Pull-up Resistor Settings PUL0
Port 0 pull-up setting register PUL0
Operations of Port 0 Functions
Operation in stop mode
Input and output form Circuit Name Output Type
1 Pins of Port
PDR3, DDR3, PUL3
Registers PDR3, DDR3, and PUL3 of Port
Setting the output from a peripheral enable
Setting a port pin to serve external interrupts
Registers of Port 3 PDR3, DDR3, PUL3
Port 3 data register PDR3
Name Read Write
Port 3 pull-up setting register PUL3
Operation in mode enabling the input to a peripheral
Operation in mode enabling the output from a peripheral
Operations of Port 3 Functions
P30/UCK/SCK
Input Output
PDR4, DDR4, OUT4
Registers of Port
Registers of Port 4 PDR4
When being written Read Address
This section describes the registers associated with port
Functions of Port 4 Registers
Operations of Port 4 Functions
Analog input mode setting
Input and output Circuit Pin name Function Form
Pin of Port
Pin may serve Type Input Output
PDR5, DDR5, PUL5
Port 5 data register PDR5
Registers of Port 5 PDR5, DDR5, PUL5
Port 5 data direction register DDR5
2 Pull-up Setting Register PUL5
Port 5 pull-up setting register PUL5
Operations of Port 5 Functions
P50/PWM
Pin name Function
Pins of Port Peripherals for Input and output form Circuit
Input Output Type Serve
101
1 Block Diagram of Port6
PDR6, DDR6, PUL6
Registers PDR6, DDR6, and PUL6 of Port
102
Port 6 data register
Registers of Port 6 PDR6, DDR6, PUL6
Port 6 data direction register DDR6 for P60, P61
104
Port 6 pull-up setting register PUL6
Operations of Port 6 Functions
106
Pin name Function Input and output form Circuit Output Type
Pins of Port
PDR7, DDR7, PUL7
Registers PDR7, DDR7, and PUL7 of Port
108
Port 7 data register PDR7
Registers of Port 7 PDR7, DDR7, PUL7
Port 7 data direction register DDR7
110
Port 7 pull-up setting register PUL7
Operations of Port 7 Functions
112
Programming Example of I/O Port
Processing specification
114
Coding example
Chapter TIME-BASE Timer
TIME-BASE Timer
Overview of Time-base Timer
1 Time Intervals for Time-base Timer
2 Clock Cycles Supplied by Time-base Timer 1/2
117
2 Clock Cycles Supplied by Time-base Timer 2/2
Time-base timer counter
Configuration of Time-base Timer
Interval timer selector
Counter clear circuit
1 Time-base Timer Control Register Tbtc
Time-base Timer Control Register Tbtc
Tbie
Tbof
TBC1, TBC0
TBR
Ffec H Ffed H
Interrupt of Time-base Timer
Operations of Time-base Timer
Operations of Time-base Timer Functions
Operations of Clock Supply Function
123
2 Operations of Time-base Timer
Clearing time-base timer
Coding examples
Program Example for Time-base Timer
126
Popw a Reti Ends END
Chapter Watchdog Timer
Watchdog Timer
Overview of Watchdog Timer
1 Watchdog Timer Time Intervals
Time-base timer output Oscillation frequency 12.5 MHz
Watchdog timer counter 1-bit counter
Configuration of Watchdog Timer
Reset control circuit
Counter clear control circuit
WTE3, WTE2
Watchdog Control Register Wdtc
WTE1, WTE0
Activating watchdog timer
Operations of Watchdog Timer Functions
Clearing watchdog timer
Time intervals of watchdog timer
Stopping watchdog timer
Program Example for Watchdog Timer
134
Chapter BIT PWM Timer
BIT PWM Timer
Overview of 8-bit PWM Timer
1 Range of Intervals and Square Wave Output
Count clock cycle Interval Square wave output Hz
Internal clock Output of an 8/16-bit capture timer/counter
PWM Timer Functions
137
138
1 Block Diagram of an 8-bit PWM Timer
Configuration of 8-bit PWM Timer
Bit counter
Count clock selector
Comparator
PWM generation circuit and PWM output control circuit
Block Diagram of the Pin Related to the 8-bit PWM Timer
Pin of 8-bit PWM Timer
P50/PWM pin
1 Registers Related to the 8-bit PWM Timer
Registers of 8-bit PWM Timer
2 PWM Control Register Cntr
PWM Control Register Cntr
TPE
Bit name Function
TIR
TIE
PWM Compare Register Comr
While the interval timer is operating
Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 0023H
Xxxxxxxxb
146
While the PWM timer is operating
Interrupt of 8-bit PWM Timer
1 Setting Interval Timer Functions
Operations of the Interval Timer Functions
149
2 Operations of an 8-bit PWM Timer
1 Setting 8-bit PWM Timer Functions
Operations of the 8-bit PWM Timer Functions
151
States in Each Mode During Operation
153
While interval timer functions are enabled
154
While PWM timer functions are enabled
Error
This section provides notes on using 8-bit PWM timer
00 H 01 H 02 H 03 H 04 H
156
Processing specifications
Program Example for PWM Timer
158
Popw Reti Ends
159
Program Example of PWM Timer Functions
160
Chapter BIT Capture TIMER/ Counter
16-BIT Capture TIMER/COUNTER
Overview of 8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter
163
Count clock cycle Interval time Square wave output range Hz
164
3 Interval Time and Square Wave Output Range in 16-bit Mode
165
Counter Function
1 Block Diagram of 8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter
Configuration of 8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter
Timer 0/1 control registers TCR0, TCR1
Timer 0/1 data registers TDR0, TDR1
Bit capture timer/counter interrupt
Count clock selectors 0/1
P33/EC pin
Pins of 8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter
P34/TO/INT10 pin
169
Block Diagram for 8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter Pins
1 Registers of 8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter
Registers of 8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter
2 Capture Control Register Tccr
Capture Control Register Tccr
172
3 Timer 0 Control Register TCR0
Timer 0 Control Register TCR0
174
TSTR1
Timer 1 Control Register TCR1
TFCR1
TIF1
T1IEN
TSTR1
PEN
Timer Output Control Register TCR2
Tsel
Bit mode timer
Timer 0 Data Register TDR0
179
Bit mode
7 Timer 1 Data Register TDR1
Timer 1 Data Register TDR1
181
Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1
Capture Data Registers H and L Tcph and Tcpl
Tcph
Tcpl
Bit mode Capture mode Timer Timer 0 + timer
8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter of Interrupts
Timer 0 interrupt operation in the 8-bit mode
FFF2 H FFF3 H
FFF4 H FFF5 H
184
1 Setting of Interval Timer Function Timer
Explanation of Operations of Interval Timer Functions
186
2 Setting of Interval Timer Function Timer
187
3 Interval Timer Function Operation in 8-bit Mode Timer
188
4 Setting of Interval Timer Function in 16-bit Mode
Operation of Counter Functions
1 Setting of Counter Function in 8-bit Mode
190
Detection of the number of events
191
3 Setting of Counter Function in 16-bit Mode
192
4 Counter Function Operation in 16-bit Mode
Functions of Operations of Capture Functions
1 Setting of Capture Function in 8-bit Mode
Ccmsk Tcmsk
195
2 Capture Mode Operation
196
3 Setting of Capture Function in 16-bit Mode
1 Counter Operation in Standby Mode and at Halfway Stop
8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter Operation in Each Mode
Using only timer 0 in 8-bit mode
10-1 Error Occurring until the Count Operation is Started
199
Program Example for 8/16-bit Capture Timer/Counter
Popw Xchw Reti Ends END
Wari Clrb TIF0
201
202
Program Example of Counter Function
Cmpw BNE READ16
Xchw Incw
203
204
Chapter BIT PPG Timer
12-BIT PPG Timer
Overview of 12-bit PPG Timer
207
Bit PPG Function
208
1 Block Diagram of 12-bit PPG Timer
Configuration of 12-bit PPG Timer Circuit
Bit PPG control registers 3 RCR23 and 4 RCR24
Bit PPG control registers 1 RCR21 and 2 RCR22
210
P37/BZ/PPG pin
Pin of 12-bit PPG Timer
212
PUL write
Readable and Writable Unused 213
Registers of 12-bit PPG Timer
RCK1, RCK0
1 12-bit PPG Control Register 1 RCR21
Bit PPG Control Register 2 RCR22
2 12-bit PPG Control Register 2 RCR22
Bit PPG Control Register 3 RCR23
3 12-bit PPG Control Register 3 RCR23
217
Rcen
Bit PPG Control Register 4 RCR24
4 12-bit PPG Control Register 4 RCR24
1 Setting 12-bit PPG Timer
Operations of 12-bit PPG Timer Functions
220
2 Operation of 12-bit PPG Timer
Limitation of H width setting
This section provides notes on using the 12-bit PPG timer
Resolution
Setting change during operation
2 Error before Count Operation Start
1 Setting Change during 12-bit PPG Timer Operation
Program Example for 12-bit PPG Timer
224
Chapter External Interrupt Circuit 1 Edge
External Interrupt Circuit 1 Edge
Overview of External Interrupt Circuit
1 Block Diagram of External Interrupt Circuit 1 EIC1, EIC2
Configuration of External Interrupt Circuit
External interrupt 1 control registers EIC1, EIC2
Edge detecting circuits
228
P35/INT11 and P36/INT12 pins
Pins of External Interrupt Circuit
1 Pins Associated with External Interrupt Circuit
TCR2PEN=0
PDR
230
1 Registers Associated with External Interrupt Circuit
Registers of External Interrupt Circuit
2 External Interrupt Control Register 1 EIC1
External Interrupt Control Register 1 EIC1
EIE1
EIR1
EIR0
233
234
EIE0
3 External Interrupt Control Register 2 EIC2
External Interrupt Control Register 2 EIC2
EIE2
EIR2
236
Interrupt of External Interrupt Circuit
FFF8H FFF9H IRQ2
Exercise Caution when Changing Edge Polarity Selection
238
Operations of External Interrupt Circuit
1 Setting External Interrupt Circuit
240
2 Operation of External Interrupt 1 INT10
Program Example for External Interrupt Circuit
242
Chapter External Interrupt Circuit 2 Level
External Interrupt Circuit 2 Level
External interrupt 2 control register EIE2
Interrupt request generating circuit
P04/INT24 to P07/INT27
P00/INT20/AN4 to P03/INT23/AN7
INT25
INT26
247
248
Register Bit name External interrupt pin
EIE2 External interrupt 2 control register Address
2 External Interrupt Circuit 2 Control Register EIE2
External Interrupt 2 Control Register EIE2
251
3 External Interrupt 2 Flag Register EIF2
External Interrupt 2 Flag Register EIF2
ILR3 007DH LA1 bit5 LA0 bit4
EIE2
255
2 Operation of External Interrupt 2 INT20
EIE2 EQU
Aden EQU
EIF2 EQU
Intv Dseg ABS Data Segment ORG 0FFE6H Irqa Wari
Popw a Xchw A,T Reti Ends END
Pushw a Xchw A,T
257
258
Chapter Converter
D Converter
Overview of A/D Converter
1 Block Diagram of the A/D Converter
Configuration of A/D Converter
Analog channel selector
Clock selector
Sample hold circuit
Converter
P03/INT23/AN7 to P00/INT20/AN4 and P43/AN3 to P40/AN0
Pins of A/D Converter
264
Block Diagram of the Pins Related to the A/D Converter
1 Registers Related to the A/D Converter
Registers of A/D Converter
2 A/D Control Register 1 ADC1
12.4.1 A/D Control Register 1 ADC1
ADI
ANS2, ANS1, ANS0
Admv
RESV0
3 A/D Control Register 2 ADC2
12.4.2 A/D Control Register 2 ADC2
269
12.4.3 A/D Data Register Addh and Addl
When A/D conversion functions are enabled
5 A/D Enable Register Aden
12.4.4 A/D Enable Register Aden
Interrupt of A/D Converter
Software activation
Operations of A/D Converter Functions
Continuous activation
274
Operations of A/D Conversion Functions
Input impedance of the analog input
This section describes notes on using the A/D converter
Input clock of continuous activation
Conversion time
276
Program Example for A/D Converter
MOV Addh
MOV Addl
278
This chapter describes the functions and operations of Uart
Chapter Uart
1 Uart Operating Modes
Overview of Uart
Choice of the Transfer Clock Rate
Serial Switch
281
282
Asynchronous transfer mode Synchronous transfer mode
283
Divider for clock Transfer rate bps
1 Block Diagram of Uart
Configuration of Uart
Clock generator
Serial mode control register SMC
Reception control circuit
Transmission control circuit
286
Uart interrupt sources
P30/UCK/SCK
Pins of Uart
P31/UO/SO
P32/UI/SI
288
Block Diagram of the UART-relating Pins
1shows the UART-relating registers UART-relating Registers
Registers of Uart
2 Serial Mode Control Register SMC
Serial Mode Control Register SMC
Smde
SBL
Scke
SOE
3 Serial Rate Control Register SRC
Serial Rate Control Register SRC
293
4 Serial Status and Data Register SSD
Serial Status and Data Register SSD
295
296
Receiving Status
When operating mode is
When operating mode is 0, 1, or
Serial Input Data Register Sidr
Serial Input Data Register Sidr
7 Serial Output Data Register Sodr
Serial Output Data Register Sodr
8 Clock Divider Selection Register UPC
Clock Divider Selection Register UPC
300
Pren
5 Description of the Serial Switch Register Ssel Bits
Serial Switch Register Ssel
Ssel
302
10 Block Diagram of Serial Switch Register
Reception Interrupt
Interrupt of Uart
Uart Interrupt Related Registers and Vector Table Addresses
FFF0H FFF1H IRQ6
1 Transferred Data Format
Operations of Uart Functions
305
Theory of Operation for Operating Mode 0, 1, 2,
3 Transmission Operations in Operating Mode 0, 1, 2, or
Transmission Operations Operating Mode 0, 1, 2,
4 Reception Operations in Operating Mode 0, 1, or
Reception Operations Operating Mode 0, 1, or
308
7 Reception Operations in Operating Mode
Reception Operations Operating Mode 2 Only
310
Program Example for Uart
Program specifications
312
Chapter BIT Serial I/O
Overview of 8-Bit Serial I/O
Serial Function Switching
BIT Serial I/O
1 Shift Clock Cycle and Transfer Rate
1 Block Diagram of 8-bit Serial I/O
Configuration of 8-Bit Serial I/O
Shift clock control circuit
Serial mode register SMR
Shift clock counter
Bit serial I/O interrupt
P32/UI/SI pin
Pins of 8-Bit Serial I/O
P31/UO/SO pin
P30/UCK/SCK pin
318
Block Diagram for 8-bit Serial I/O Pins
Bit Serial I/O Registers
Registers of 8-Bit Serial I/O
2 Serial Mode Register SMR
Serial Mode Register SMR
Sioe
Siof
CKS1, CKS0
321
SST
BDS
322
Serial Data Register SDR
When the serial I/O is in transfer operation
Serial Data Register SDR
At serial output operation
Bit Serial I/O Interrupt Register and Vector Table
Interrupt of 8-Bit Serial I/O
1 8-bit Serial I/O Interrupt Register and Vector Table
Serial output operation via internal shift clock
Operations of Serial Output Functions
Operation at Serial Output Completion
Serial output operation using external shift clock
326
Operations of Serial Input Functions
Serial input operation using internal shift clock
Operation at Serial Input Completion
Serial input operation using external shift clock
328
Bit serial I/O operation in sleep mode
14.8 8-Bit Serial I/O Operation in Each Mode
Bit serial I/O operation in stop mode
330
331
When the External Shift Clock is Used
332
Error at serial transfer start
This section provides notes on using the 8-bit serial I/O
Malfunction due to noise
Shift clock idle state
Example of 8-Bit Serial I/O Connection
335
Bidirectional Serial I/O Operation
Program Example for 8-Bit Serial I/O
Wari Clrb Siof
Program Example for 8-bit Serial Input
Pushw MOV
Popw Reti Ends END
338
Pushw Xchw MOV SDR
Chapter Buzzer Output
Buzzer Output
Overview of the Buzzer Output
1 Output Frequencies
Clock supplier Buzzer output Square wave output at 12.5 MHz
Buzzer output selector
Configuration of the Buzzer Output
Pin of the Buzzer Output
Block Diagram of the Pin Related to the Buzzer Output
BZ pin
1 Buzzer Register Bzcr
Buzzer Register Bzcr
344
1 Functions of Each Bit in Buzzer Register Bzcr
Bzcr EQU
Program Example for Buzzer Output
346
Chapter Wild Register Function
Wild Register Applicable Addresses
Overview of the Wild Register Function
Wild Register Function
1 Wild Register Applicable Addresses
Memory area part
Configuration of the Wild Register Function
Control circuit part
1 Registers Related to Wild Register Function
Registers of the Wild Register Function
1 Functions of Data Setting Register Wrdr
Data Setting Registers WRDR0 and WRDR1
Wild register number Register name Function
WRDR0
2 Functions of Higher Address Set Register Wrarh
Higher Address Set Registers WRARH0 and WRARH1
WRARH0
WRARH1
3 Functions of Lower Address Set Register Wrarl
Lower Address Set Registers WRARL0 and WRARL1
WRARL0
WRARL1
5 Address Comparison EN Register Wren
Address Comparison EN Register Wren
Data Test Set Register Wror
Test register. Do not access this register
Wild Register Addresses List
Operations of the Wild Register Functions
1 Operation Order of Wild Register
2 Wild Register Addresses List
Chapter Flash Memory
Writing to/Erasing Flash Memory
Overview of Flash Memory
Flash Memory Register
Flash Memory
1 Flash Memory Control Status Register Fmcs
Flash Memory Control Status Register Fmcs
360
Inte
Starting the Flash Memory Automatic Algorithm
1 Command Sequence Table
1 Bit Assignments of Hardware Sequence Flags
Confirming the Automatic Algorithm Execution State
2 Hardware Sequence Flag Functions
State
Automatic Erasing
Data Polling Flag DQ7
Toggle Bit Flag DQ6
Timing Limit Exceeded Flag DQ5
Toggle Bit-2 Flag DQ2
Detailed Explanation of Writing to Erasing Flash Memory
Setting The Read/Reset State
Specifying Addresses
Writing Data
Writing to the Flash Memory
370
1 Example of the Flash Memory Write Procedure
Erasing All Data Erasing Chips
How to enable the Flash Security Feature
Flash Security Feature
How to disable the Flash Security Feature
Behavior under the Flash Security Feature
Program Access to Flash Memory
Software Reset, Watchdog Timer Reset
Flash Content Protection
374
Appendix
Appendix a I/O Map
Appendix a I/O Map
Table A-1 Map 1
377
Table A-1 Map 2
378
Table A-1 Map 3
Explanation on read/write
Table A-1 Map 4
Explanation on initial value
379
Appendix B Overview of the Instructions
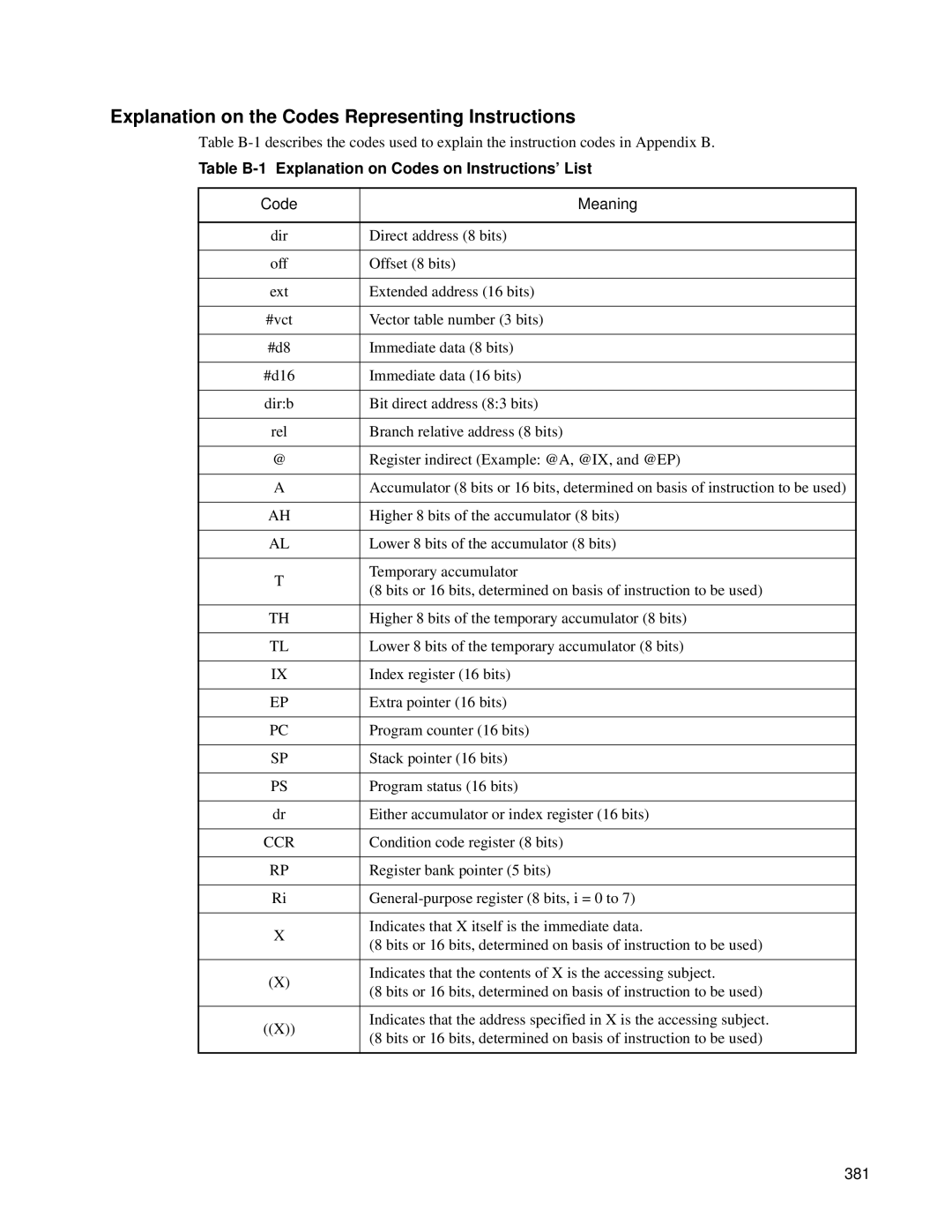
Table B-1 Explanation on Codes on Instructions’ List
Explanation on the Codes Representing Instructions
Code Meaning
CCR
Table B-2 Explanation on Items of Instructions’ List
Explanation on the Items of Instructions’ List
382
Direct addressing
Addressing
Extended Addressing
Pointer Addressing
Index addressing
384
Immediate Addressing
General-purpose Register Addressing
Vector Addressing
Table B.1-1 Vector Table Address Corresponding to vct
Inherent addressing
Relative Addressing
386
JMP @A
Special Instructions
Movw A, PC
Divu a
Mulu a
388
389
Xchw A, PC
390
Appendix B Overview of the Instructions Callv #vct
Table B.3-1 Bus Operation at Bit Manipulation Instructions
Bit Manipulation Instructions Setb and Clrb
Code Mnemonic
RMW
Table B.4-1 List of Transfer Instructions 1
F2MC-8L Instructions List
393
Table B.4-1 List of Transfer Instructions 2
Table B.4-2 List of Operation Instructions 1
Operation Instructions
394
395
Table B.4-2 List of Operation Instructions 2
396
Table B.4-2 List of Operation Instructions 3
Table B.4-2 List of Operation Instructions 4
Branch Instructions
Table B.4-3 List Branch Instructions
397
Table B.4-4 List of Other Instructions
Other Instructions
398
Instruction Map
Instruction Map
Table B.5-1 shows the instruction map of the F2MC-8L
Instruction Map of the F
Table C-1 Mask Options
Appendix C Mask Options
Eprom for use
Appendix D Programming Eprom with Evaluation Chip
Programming Eprom
Appendix E Pin State of the MB89202/F202RA Series
Table E-1 Pin States in Each Operation Mode
Appendix E Pin State of the MB89202/F202RA Series
P37/BZ/PPG
403
Index follows on the next This is listed in alphabetic order
Numerics
Aden
ADC
CCR
Bzcr
Cntr
DDR
Comr
EIC
EIE
Fmcs
F2MC-8L
ILR
Interrupt Level Setting Registers
Interrupt Enable Bits
Interval Timer
Memory Access
OUT
PDR
P37/BZ/PPG
RCR
PUL
RST
Rsfr
SDR
SMC
Sidr
SMR
Sodr
Tccr
Tbtc
TCR
TDR
Wrarh
Wdtc
Wrarl
Wrdr
418
CM25-10153-2E
Fujitsu Semiconductor Controller Manual