SMV
Copyright 1999 by Honeywell Inc Revision 0 January 18
Copyright, Notices, and Trademarks
About This Publication
Conventions and Symbol Definitions
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Table of Contents
111
103
119
137
Figures and Tables
100
Table A-9
Acronyms
Parameters
Technical Assistance
References
Overview First Time Users Only Introduction
Section Contents About This Section
This section includes these topics
Topic
About Conformity
CE Conformity Europe
SMV 3000 Smart Multivariable Transmitters
Meter Body Factory Characterization Data Electronics Housing
SMV Operating Modes
Transmitter adjustments
Smartline Configuration Toolkit
Smartline Configuration Toolkit SCT
Smart Field Communicator SFC
Using the SFC with the SMV
About SFC Communications
Smart Field Communicator SFC
Order Components
Transmitter Order
Smart Field Communicator Model STS103 Operating Guide
Quick Start Reference Introduction
Task Description Reference Section
Getting SMV 3000 Transmitter On-Line Quickly
Preinstallation Considerations Introduction
Electronic pressure transmitters
Considerations for SMV 3000 Transmitter
Evaluate conditions
Operating Temperature Limits
Thermocouple requirements
RTD requirements
Type Rated Range Limits Standard
SCT 3000 Requirements
Considerations for SCT
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Installation Introduction
Mounting SMV 3000 Transmitter
Mounting SMV 3000 Transmitter to a Bracket
Action If you are using an… Then…
Bracket mounting
Step
Step Action
Leveling a Transmitter with a Small Absolute Pressure Span
Flange for manifolds on 2, 2-1/8, or 2-1/4 inch centers
Piping SMV 3000 Transmitter
Pressure lines to the transmitter
Process to be measured. shows the transmitter located above
Suggested mounting location for the transmitter depends on
Drain away from the transmitter
Transmitter location
Piping SMV 3000 Transmitter
General piping guidelines Installing flange adapter
Installing 1/2 inch NPT Flange Adapter
Considerations CE Conformity Special Conditions Europe
Installing RTD or Thermocouple
CE Conformity Special Conditions Europe Summary
Wiring SMV 3000 Transmitter
Polarity
For the given probe type
Refer to .2 CE Conformity Europe Notice for special
Conditions
TPS/TDC 3000 reference
Optional meter Wiring connections
If input is from … Then…
Wiring connections Step
RTD Input Wiring Connections
Green covered wire
AWG American Wire Gauge or KCM Kilo Circular Mils bare or
Optional lightning protection
Ground Connection for Lightning Protection
Conduit seals and Hazardous Location Installations
Getting Started Introduction
Off-line Configuration Procedures SCT Hardware Connections
Off-line Versus On- line SMV Configuration
Establishing Communications
SCT 3000 On-line Connections to
Establishing On-line Communications with the SMV
Making On-line Connections to
DE Communication Mode
Checking Communication Mode Firmware Version
Changing Communication Mode
Making Initial Checks
Want to change it
Write Protect Option
Module for SMV 3000 transmitters
Write Protect Option
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Configuration Introduction
To Print On-line Manual and Help Topics
About Configuration
Changing database parameters configuration
Configuration Summary
Overview
Overview
Using the SCT for SMV 3000 Configuration
Configuring the SMV 3000 with The SCT
SMV Process Variable SCT Template Tab Card
PV1 Priority
Device Configuration
Background Device Data Fields
PV Type Selecting PVs for Broadcast
General Configuration
If You Select PV Type
These PVs are Broadcast to Control System
Background Analog Output Selection
To represent the output
Determine which PV is desired as SMV Output
Then Select…
Line Filter Background
Engineering Units
DPConf Configuration PV1
Engineering Unit
Meaning
LRV and URV PV1 DP Range Values
About Square Root Output
Output Conformity Background
Flow 0utput Full MA dc Scale
About Square Root Output Square Root Dropout
Differential Pressure % Full Scale
Damping Background
Absolute Pressure
AP/GPConf Configuration PV2
STG170
Gauge Pressure
Pressure reading
Flow calculation
PV2 AP/GP or SP Range Values LRV and URV
Selecting PV3 Engineering Units
TempConf Configuration PV3
Engineering Unit Meaning
Cold Junction Compensation Background Output Linearization
Sensor Type
Sensor Type Rated Temperature Range Limits
Fault Detect Background
Typical RTD Range Configuration
PV3 Temperature Range Values LRV and URV
Range Settings After LRV is Changed to Zero
Current Range Settings
Damping Background
FlowConf Configuration PV4
PV4 Engineering
Pre-programmed Mass Flow Engineering Units for PV4
PV4 Flow Upper Range Limit URL Range Values LRV and URV
Lower Range Limit LRL and Upper Range Limit URL identify
About URL and LRL
LRV and URV set the desired zero and span points for your
Typical Volumetric Flow Range Setting Values
About LRV and URV
M3/h
Low Flow Cutoff for PV4
Damping
Graphic Representation of Sample Low Flow Cutoff Action
Using Custom Units for PV4 Flow Measurement
Using Custom Engineering Units
Description Standard Equation
Flow Compensation Wizard
Dynamic Compensation Equation
Primary Element
Flow = N
Dynamic compensation flow equation for mass applications is
Saving, Downloading Printing a Configuration File
Saving, Downloading and Printing a Configuration File
Verify Flow Configuration
Verifying Flow Configuration
Startup Introduction
Startup Tasks
About Startup Step Procedures
BAD PV displayed on TPS/TDC systems
Running Output Check
Background Analog Output Mode Procedure
Output Check Procedure for SMV Transmitters in DE mode
Procedure Step
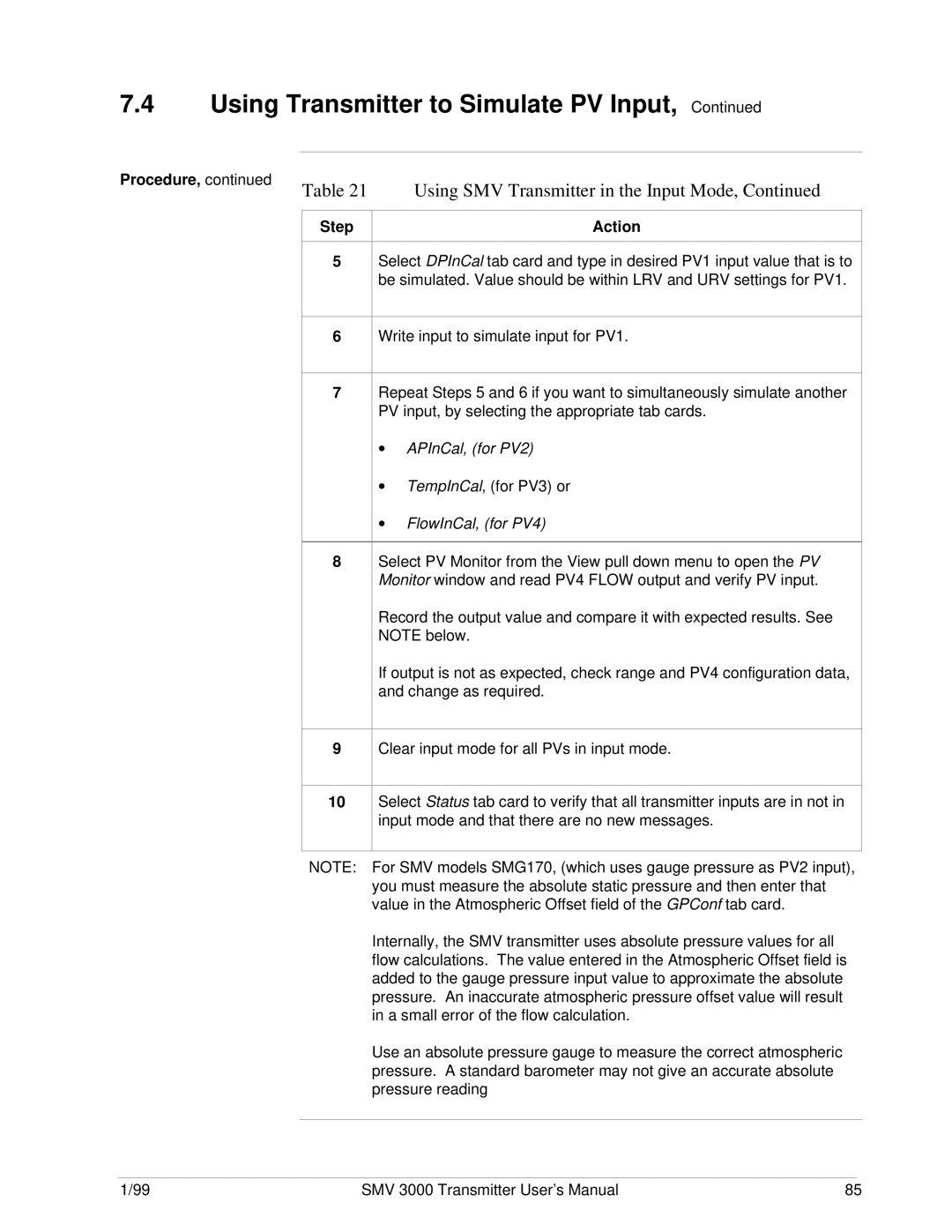
FlowOutCal, for PV4
Output Check for SMV Transmitters in DE Mode
Using SMV Transmitter in Input Mode
Using Transmitter to Simulate PV Input
APInCal, for PV2
SMV Model SMA125 Start-up Procedure
Procedure
Starting Up Transmitter
Starting Up Transmitter
SMV Draft Range Start-up Procedure
Starting Up Transmitter
Black
SCT
Operation Introduction
Summary Procedure
Accessing Operation Data
If you want to view… Select the SCT
Select the SCT Window or Tab Card
If you want to view…
TempConf
Background Analog and DE Mode Differences
Changing Default Failsafe Direction
Jumper on the main PWA of the electronics module
Cutting Failsafe Jumper
Main PWA
Saving and Restoring a Database
Saving and Restoring SMV Configuration Database
Section Contents
Maintenance Introduction
Topic See
Maintenance Routines And Schedules
Preventive Maintenance
Background Procedure
Inspecting and Cleaning Barrier Diaphragms
22519
Replacing Electronics Module or Prom
Prom number using the SCT See .2 in this manual for details
Plug-in Prom on the main PWA is uniquely characterized to
Required Replacing Electronics Module or Prom
104 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
If you are replacing the… Then…
Main PCB If the new electronics module has the write protect
Main PCB
Center section is supplied with a new matching Prom
Replacing Meter Body Center Section
Matching Prom
Replacing Meter Body Center Section
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual 109
22519
Calibration Introduction
About Calibration
Test Equipment Required
Using the SFC or SCT for Calibration
Using the SFC
Calibrating Analog Output Signal
Calibrating PV1 and PV2 Range Values
Typical PV1 or PV2 Range Calibration Hookup
About Reset Accuracy for PV1 and PV2
Resetting Calibration
118 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Troubleshooting Introduction
Diagnostics Troubleshooting Tools
You can clear fault conditions
Troubleshooting Using the SCT
Diagnostic Messages Diagnostic Message Table Headings
Diagnostic Messages
Diagnostic Messages
Critical Status Diagnostic Message Table
124 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual 125
Status TAG ID.# Corrects RST PV1
Non-Critical Status Diagnostic Message Table
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual 127
128 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual 129
130 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Non-Critical Status Diagnostic Message Table
TAG no Illegal Response URV 3 . TAG ID Invalid Request
Communication Status Message Table
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual 133
Informational Status Message Table
Status TAG ID Wire RTD PV3
SFC Diagnostic Message Table
Page
Part Identification
Parts List Replacement Parts
138 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
SMV 3000 Electronics Housing
Quantity Per Unit
Key Part Number Description
Key
Parts Identification for Callouts in Figure
Quantity Per Kit
Key Part Number
SMV 3000 Terminal Block Assembly
Description Quantity Per Unit
SMV 3000 Meter Body
K10 K11
Quantity Per Unit Flange Adapter Kits two heads
K10 K13
Process Head Kits one head with Viton head gasket
Part Number Description Reference
Summary of Recommended Spare Parts
Spares for
SMV Multivariable Transmitter Wiring Diagrams for
Wiring Diagrams
Using Mounting Bracket Type
See Drawing Number
148 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Appendix a PM/APM/HPM SMV 3000 Integration Overview
Appendix Contents
This appendix includes these topics
Purpose of this appendix
Definition Communications Link Compatibility
Description
DE/ Digital
Diagram Typical Integration Hierarchy
SMV3000 Transmitter
Exchange of data over the bi-directional data path between
Data Exchange Functions
SMV 3000 transmitter and the PM/APM/HPM is based on imaging
Stimv IOP for each transmitter PV. This is done by mapping
SMV 3000 Transmitters
Points per Stimv IOP
Four Points Per Transmitter
Figure A-4 AI Point for Each Transmitter Input
Application. Table A-1 shows what PVs represent in the SMV
Broadcast using the SCT
See Deconf parameter in subsection A.5 and Deconf Changes
SMV PV Number
About Database Broadcast
Other Smartline transmitter. See in the PM/APM Smartline
Installation
Mounting Assumptions
Connection Rule
Figure A-5 Connection Rule Example
About Configuration Getting Started
Configuration
Building Points
Point Building Rules
Eudesc Parameter
PED Entries
If Process Variable Number is…
Then base engineering unit is …
Table A-5 PV Characterization Selections for SMV 3000 PVs
Listed in Table A-5
So the value is the same regardless of EU
Mind, that the URL, LRL, URV, and LRV are displayed in base
URL Parameter
If PED Deconf entry is …
Then URL is …
Then Damping Value can be …
If Process Variable Number is… PV1 or PV2
Piuotdcf Parameter Cjtact Parameter
After Point is Built
Generic Operations Detail Display Difference
Operation Notes
Database Mismatch Parameters
Deconf Changes
Figure A-7 Example of Deconf Download Error Message
Table A-10 Conversion Values for PV3 Temperature
Conversion Multiplier
Engineering Unit Conversion for PV4
Conversion Offset
Conversion Offset Secondary Variable Reference
Table A-12 Conversion Values for PV4 as Mass Flow Rate
Status Messages
Problem
Message
Corrective Action
170 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Appendix B SMV 3000 Configuration Record Sheet
1b. Static Pressure PV2 Configuration Section
Appendix B- Configuration Record Sheet
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual 173
174 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Reference Data Sources
Appendix C -PV4 Flow Variable Equations Overview
Standard Flow Equation
Example Air Through a Venturi
178 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Example Superheated Steam Using an Averaging Pitot Tube
Standard Flow Equation
Dynamic Compensation Flow Equation
Table C-3 Liquid Propane Configuration Example
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual 183
184 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Example Air
Table C-4 Air Configuration Example
186 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual 187
Example Superheated Steam
SMV Operation in a Steam Application
Table C-5 Superheated Steam Configuration Example
190 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
Dynamic Compensation Flow Equation
Page
SMV 3000 Smart Multivariable Transmitter
# in User Sub-Section Description of Change
Torque Table Process Head Bolts/Nuts
································
···································
34-SM-99-01 Addendum to 33-SM-25-02 03/04
Psi
03/04 34-SM-99-01 Addendum to 33-SM-25-02
Index
Cont’d
194 SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual
SMV 3000 Transmitter User’s Manual 195
Industrial Automation and Control