Manual
Card
Programs
Symbols used in this Manual
View of chapters
205 Road Plus 249 File Editor 303 Monitoring 333 Index 341
Contents
Introduction Search Point Coarse Positioning
Introduction Measure Mode Results Configuration
Select Stakeout Method Plot Configuration
Stakeout
Area Computation of Area 117
Remote Height 105
Hidden Point 111
Sets of Angles 129
205
Local Resection 165
Road line 171
Road Plus 249
Monitoring 333
File Editor 303
Index 341
Introduction
General
Installation in the PC
Hardware and software required
On the diskette bearing the label TPS 1000/2000/5000
TPS-WORKBENCH
Diskette bearing the label TPS
System Firmware
Characters for version release number
Application programs ?????VVV.PRG
????? Maximum of 5 characters for name Application
System textsSYS?VVV.SS
RESECVVV.LENetc Stakeout
PrtxtVVV.LSP Orientation
TIEVVV.LENetc
STAKEVVV.LENetc
Loading files into the TPS1000 instruments
Applications Name Art.No Licence Code Version Language
Loading system texts
Select the command Transfer files in the Utilities
Menu
Loading application
Programs
Licence code Solving problems
List
Select Main Menu
Licence code for TPS 1000 applications
No. of application Licence code Remarks
General notes
Settings
Units in this manual Preparation
Instrument field setup
Using the program
Data exchange
Calling up the program
Designation of keys
Target eccentricity
Orientation and Height Transfer
Introduction
Target Point
Enter the target point number and height of the reflector
Retrieved several times
Point List
Enter a maximum of 10 points. The same point can be
Return to the dialog Target Point
Measure Mode
Calculates the orientation, the elevation
Calculation
Respective standard deviations
Display the residuals of individual measurements. You
Can also disable points from the calculation
More Information
Orientation or height as well as delete erroneous
Point no
Use for Ht
Status
Easting, Northing, Elevation Target coordinates used
Plot
Recalculate the result and return to the dialog
Configuration Editor
Configuration
Start the Configuration Editor from the Target Point dialog
Log File
Two Faces
User Disp
Log FlName
Data will always be appended to the specified Log
Dual-face Measurement
Log file
File
Record
For each measurement, a record will be
TPS System 1000 theodolite series
Resection
This manual describes the Resection program
Pt2 00000
Station Data
Proceed to the dialog Target PoinT Start the Configuration
Enter station point number and height of the instrument
Enter the target point number and height
Reflector
RESEC\ Measure MOD GSI
This dialog the calculated station coordinates are
Shown with the orientation
TPS-System 1000 Programs-2.3.1en
Start the Configuration Editor from the Station Data dialog
TPS-System 1000 Programs-2.3.1en
Be stored containing
Data will always be appended to the specified Log-file
For each measurement, a record will
Station coordinates and orientation
Typical log file entry in the Resection program
Tie Distance
Radial Mode
TIED\ First Point
TPS-System 1000 Programs-2.3.1en
Results
TPS-System 1000 Programs-2.3.1en
Start the Configuration Editor from the First Point dialog
TPS-System 1000 Programs-2.3.1en
Log File
FILE12.GSI
Stakeout
Introduction Search Point
For positioning are only displayed after two stakeout
Coarse Positioning
Line Offset
Points
Line
Target no
Azimuth
Offset
Orthogonal
Hz Angle
STAKE\AZIMUTH & Distance
Leica TPS-System 1000 Programs-2.3.1en
Stakeout
Polar Stakeout
Dist
Reflector. Positive in sign if point is
Transversal displacement
Right
Reflector. Positive in sign if stakeout
Longitudinal displacement
Point is further away from station
Stakeout with auxiliary points
Target no Point number of the point to be staked
Distance from the first auxiliary point
Angle from the first auxiliary point to
Stakeout point
To the stakeout point
Stakeout from Coordinate Differences
Leica TPS-System 1000 Programs-2.3.1en
Coarse Meth
Select Stakeout Method
Stakeout M
Plot is generated of the stakeout situation with a list
Numeric values, corresponding to
3D Stake
Difference in the log file
Recording of design
Coordinates, setout height and height
Coordinates, setout coordinates und
Typical log file entry in the Stakeout program
Free Station
Station Data Target Point
Same point number can be used several times
Without new input
FREST\MEASURRE Mode GSI1403
Calculates the 3D station coordinates and orientation as
Well as the standard deviation of the results
Orient Standard deviation of the Orientation
Or height as well as delete erroneous measured points
Can also disable points from the calculation of position
Distance error
Sequence number of the current point
Easting, Northing, Elevation Target coordinates used
Top of the sketch shows the direction of Grid north.
Configuration. The station point is in the center
Generates a plot showing the measurement
Sketch is true in angular but not true in distances. Points
FREST\ Configuration
Leica TPS-System 1000 Programs-2.3.1en
Northing
Easting
Height of station
Next
Typical log file entry in the Free Station program
Reference Line
ΔSpat.dist
ΔLine
ΔPerp.l
Baseline Points
Determine Base Points
1403 Puoint no
Change the theodolite face Exit the program
Alpha
Length of perpendicular
Height reference point
ΔPerp.lngth
Spatial distance
100
Line / α
Height
If set to Inter, the Line / a option is
Configuration
Each modification of baseline Reference line is stored
104
Remote Height
Horizontal direction from the remote
Measure Base Point
Point number of the base point
Point to the base point
107
Slope dist
109
REMHT\ Configuration
Hidden Point
Reflector 1 + Reflector Reflector 3 + Reflector
Start the Configuration Editor from the Measure dialog
Measure ROD Configuration
Measure Rod
Horizontal direction to the hidden
Point number
Point
Slope. Dist
This manual describes the Area program of the TPS
Area Computation of Area
System 1000 theodolite series
Straight line
119
Than 180 200 gon
Arcs
Ensure the central angle of any arc is always smaller
Three Points
Select arc defined by 2 points and radius Exit the program
Radius Arc
Accept the input. Continue with dialog Measure
Calculation
Shows a plot of the present area
Area results recording format
Return to the dialog Results
Set YES for dual-face measurement
Code
126
Point and end point, horizontal
For each section of the area, start
Distance and azimuth are stored
128
Sets of Angles
Sets Menu
Sets menu view
A new instrument station. The point number for
Measure Mode
Measure First Set
Targets must be entered in Dialog First SET
ALL Dist
Measure Further Set
ΔHz
Calculate Mode
Calculate Horizontal and Vertical Sets
Formats and Data Recording
Number of measurements and accuracies
Code Target number Average of all sets
Directions averaged from all valid sets
Differences or residuals for the points observed
More Information
SETS\ More Info HZ
139
Examples and used formulae
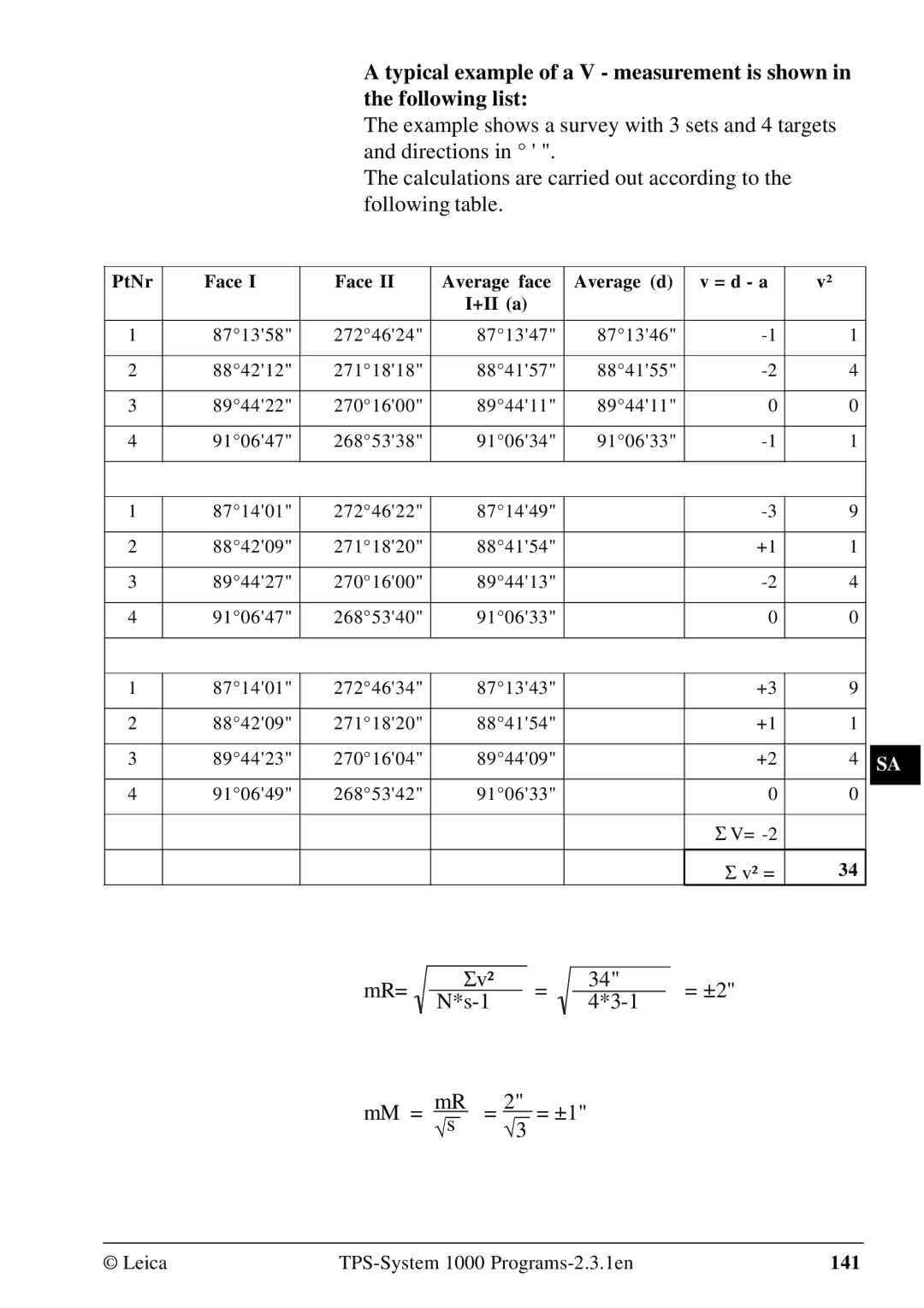
MR= Σv² = ±2 1s-1 13-1 MM = = ±1
MR= Σv² = ±2 MM = = ±1
PtNr Face Average face Average d = d a +II a
Used formulae and designations
Start the Configuration Editor from the Sets Menu dialog
Hz Tol
Angle Tol
Deviation for one measurement
Average horizontal and vertical
Angles of all sets, the standard
Standard deviation of an angle
146
Traverse
Traverse Menu
Traverse menu
New traverse
Select method of orientation
Calculate Azimuth
Enter Backsight Azimuth
Occupy station
154
Traverse Point / Sideshot Point
Close traverse
157
Number of traverse points
Examples Codeblock with results of the traverse closure
Code
Length of traverse sum of legs
Plot
Return to the dialog Closure Results
No for the single measurement
Mult Meas Set YES for the multiple
Measurement
Input of code number for recording
Desired to achieve a higher accuracy or reliability.
Multiple Measurement
Measurement to a point can be repeated as often as
Mean value of the measurements and the respective
162
Instrument, the name of the data file
Header line will contain the name
This program, information about
Date and time
164
Local Resection
LRES\ Station Data
Target Points
Station no
LRES\ Configuration
170
Leica TPS 1000 series
Road line
Manual describes the program Road Line for
Centre-line offset
File name CRS?????.GSI
File name ALN?????.GSI
File name PRF?????.GSI
Permitted elements in the Hz-alignment Straight
Parabola
Permitted elements in V-alignments Straight
Permitted elements in cross sections
Program concept
Alignment Calculation program only
Selection of files
Out or inspected in two dimensions. Without
Alignment
If no V-alignment is selected, points can only be set
Checking files
Are found, the inspection is aborted
177
Program flow
Element
Cross sections Selecting points in the cross section
Offset of the centre of the X-section
Horizontal displacement centre-line
By this amount
Plot
Returns to dialog Cross Section
Stakeout
ROADL\ Point Coords
Section Check
ROADL\ X-SECTION Check
Display of results
Chainage
Result of the road station and offset is stored
Start the Configuration Editor from the Select
ALN Files dialog
189
Measurement
191
Data format
Hz-alignment
193
Data block
Lasttmpl
195
110002+00000000
Example S-line with a straight connection
410001+Example1
00100000 73....+Tmpl0123
Alignment V-alignment definition = V-alignment
198
72 = 00000NON
01142936 83..10+00422500
Example Crest and dip
410001+Example1 +0VALIGNM
+02091126 83..10+00415000
Cross sections
Aspect Chainage increasing
202
Empty
Road Data Entry program
Leica ROADDATA.EXE for providing setting-out data files
Using the ROADDATA.EXE program
\roaddata
Cogo
206
Direc. Type
Call up the Configuration-Editor
Computes distance and direction between two points
Search Given
Call up the function in the Cogo Menu dialog
Southwest
From
Horiz.Dist
Computes a new point given a direction and distance
Traverse
From a known point
Call up the function from the Cogo Menu
Northeast
Defining direction by magnetic bearing
Quadrant
Polar calculation
Add
Multiply
Divide
Subtract
Defining direction by
Azimuth
Display of corrected Azimuth
Display of entered Azimuth ref. to
Accept displayed values and proceed to dialogue Traverse
Entering horizontal distance
Defining horizontal distance
Horiz Dist
Call up of a distance which has been
Correction
Display of entered horizontal distance
Entering distance for a positive
Entering distance for a negative
Following dialog box shows the result of the traverse
Intersections
Bearing-Bearing Intersection
Call up the function from the menu
Intersections
Straight lines
Configuration during Direc.Type
Enter quadrant First or second
Enter magnetic bearing First or
Azimuth if Azimuth is selected
Configuration during Direc
Enter bearing, mangnetic bearing resp
Type
COGO\BRG-BRG Results
Bearing-bearing coordinates
Bearing-Distance Intersection
Search
S1 and S2 Y
COGO\ Bearing from
Can be entered
Enter quadrant
Then the azimuth of the straight line
Determining the direction by means of the function
Enter bearing, mangnetic bearing
Selected in the configuration during
Resp. azimuth if Azimuth is
Entering radius
Enter distance from point
Call up of a radius which has been
COGO\ BRG-DIST Results
Point 1 Y, X, radius
Distance-Distance Intersection
Point 2 Y, X, radius
COGO\ Distance #1 from
Enter distance from points
COGO\ DIST-DIST Results
Offsets
Call up the function in the Cogo Menu
Baseline End Point 2 Y
Distance-Offset
Baseline Start Point 1 Y
Lateral point 3 Y
Call up the function from the menu Offsets
Following dialog box shows the results
Offset Display lateral deviation/ordinate Q
Orthogonal point calculation
Lateral point 3 coordinates Y
242
Entering distance along baseline
Using the function Polar
Enter distance along baseline L
Call up of a distance along baseline
Entering lateral deviation/distance
Stored using the function Polar
Enter lateral deviation/distance from start Q
From start
Display of north coordinate
Entering point number of the lateral
Display of east coordinate
Entering height optional
Circle centre coordinates
Three Point Arc
Arc point 1 Y
COGO\ First PT on ARC
Following dialog box shows the results of the calculation
Road Plus
Alignment Definition Data Files
250
Parameters of parabola
Defined by chainage and height
= crest + = dip
Creating Data Files Program Overview
Number of points in a cross section
Getting Started
ROAD+\ Configuration
255
List Help Conf
Horizontal alignment file contains the following elements
Negative offset Positive offset
Cross Section Definition
Cross section Cut
Cross section Fill
Cross Section Assignment File
Cross Section name Starting Chainage
Interpolation along a cross section
Cross Section Interpolation
Interpolation between cross sections
Superelvation governed by cross sections
Superelevation/Widening
Cross Section D Full Superelevation Cross Section C
Station Equation File
File Checking
Stakeout Using Horizon- tal Offset
Preparing for the example
265
266
Template SCLO
Slope extends well beyond expected Catch Point
Tutor 35.000 16.700 500 030 TypCut 16.630
ROAD+\ Chainage & Offset
Hght Offset
Access the cross section options
Offset
Interpolated
Horizontal offset to apply to current
Previous Element
Horizontal
Interpolated
Stakeout and Record point
Activates the stakeout program
1403 Target no 00000 Dist 007 Height
Stakeout Next point on Cross Section
276
Check Xsec Help
25.000
500 Easting 331.000 Northing 340.500 Elevation 31.200
Start Roadplus & Set Configuration Options
Horizontal Offset Stake Out Summary
Select Alignment Files
Horizontal file must be selected
Set offset value and select point to stakeout
Stakeout the point
Select new chainage
Plan View
Slope Staking
Cross Section +200.000 Centerline
CL Offset Catch Point ΔXS Hgt Diff
Catch Centr Help Plot
287
Slope Staking Menu Function Key Summary
Reference Point
290
Following geometric elements are supported
Data Formats
Horizontal Alignment
Element Definition Declaration Alignment file
Comments
Example of a Horizontal Alignment
Parabola length End of project Coordinate Km,H 00000EOP
Vertical Alignment
Tangent Coordinate Km,H to Coordinate Km,H
Vertical Alignment File Header
Example of a vertical alignment file
Element Definition
Cross Sections
Geometric elements supported
Header of the cross section file
Example
+TEMPLATE
Elements supported Definition
Cross Section Assignments
Header of the Cross Section Assignment file
+CRSASKER
Header of the Station Equation file
Station Equations
Elements supported
Data block for a station equation is structured as follows
301
302
File Editor
Creation of files
Editing files
It is possible to insert also a new data set
Menu Programs dialog
Open file
Start program File Editor from the Main
File Type Select type of file Coordinate, refer to chapter
Coordinates
Insert code block, see dialog
Call function Insert Point Coordinates in menu Insert Record
Goto start of file Goto end of file
Save
Input of code number
Call function Insert Code Block in menu Insert
Sequence number of current point
Info
Start dialog Search in dialogs View / Edit
File pages 307
Insert new Header, see dialog
File Id
Job Id
File Type
Insert Curve In, see dialog
Radius
Station
Ele Type
Template
315
Searching for station
Start dialog Search in the dialogs View / Edit
Direction Forward
Input of station chainage Search for station
0VALIGNM
Display for the vertical alignment file
Insert Tangent Insert Circular Curve
Input of parabola parameter
Call function Insert Parabola in menu Insert
Parameter
Input of elevation
File pages 317
Template
Display of cross section file
Cut/Fill
ΔHz-Dist
SO Ht diff
Slope ratio
File pages 322
Station Equation
Input of job identificaton
Display for the station equation file
Ahead
Sta. Eqn
Back
Start dialog Search in dialogs View / Edit File
Pages 326
Cross-section Assignment
CRS File
Display of section assignment file
Selection of relevant cross section file
Selection of template
Input of start station for this template
Pages 330
Station Input of station chainage
Monitoring
334
Main menu
Selecting points
Measurement menu
Points will be saved in the set measurement file
Selecting the points to be measured
Timer selection
Point measurement End monitoring
Index
342
343
Transfer
Section Check 184
ISO standard
664901-2.3.1en