SmartSwitch 2200 Series
Page
Page
Enterasys NETWORKS, INC Program License Agreement
Page
Page
Contents
Device Configuration Menu Screens
Port Configuration Menu Screens
Configuration Menu Screens
Layer 3 Extensions Menu Screens
Network Tools Screens
Generic Attribute Registration Protocol Garp
Figures
Xiii
Xiv
Tables
Xvi Tables
Using this Guide
About This Guide
Structure of this Guide
Xix
Related Documents
Document Conventions
Typographical and Keystroke Conventions
Bold type
Page
Introduction
Overview
Management Agent
Local Management Requirements
In-Band vs. Out-of-Band
Navigating Local Management Screens
Local Management Screen Elements
None Defined
Event Message Field
Display Fields
Input Fields
Selection Fields
Command Fields
Local Management Keyboard Conventions
Getting Help
Your email address
Page
Management Terminal Setup
Local Management Requirements
2H252-25R SmartSwitch device is shown in -1as an example
Console Cable Connection
Management Terminal Setup Parameters
VT100ID
Monitoring AN Uninterruptible Power Supply
Telnet Connections
DB9 Port RJ45 COM Port
Page
Accessing Local Management
802.1Q Switching Mode, LM Screen Hierarchy
Using the Exit Command
Using the Return Command
Selecting Local Management Menu Screen Items
Exiting Local Management Screens
Using the Next and Previous Commands
Using the Clear Counters Command
Password Screen
When to Use
How to Access
Screen Example
Enter
Device Menu Screen
Screen Navigation Path
Configuration
Menu Descriptions
Device
Menu
Security
Network
Tools
Cont’d
Section
Overview of Security Methods
Host Access Control Authentication Haca
Overview of Security Methods
14Accessing Local Management
2 802.1X Port Based Network Access Control
Definitions of Terms and Abbreviations
2.2 802.1X Security Overview
MAC Authentication Overview
Authentication Method Selection
Authentication Method Sequence
Concurrent Operation of 802.1X and MAC
Authentication
MAC
20Accessing Local Management
MAC Authentication Control
Security Menu Screen
Refer to -4for a functional description of each menu item
Passwords
Name Services
Authentication
Radius
Passwords Screen
Module Login Passwords Screen
Switch
Field Descriptions
Setting the Module Login Password
Radius Configuration Screen
Timeout
Retries
Last Resort Action/Local Selectable
Last Resort Action/Remote Toggle
Radius Client
IP Address
Setting the Last Resort Authentication
Setting the Local and Remote Servers
Name Services Configuration Screen
Name Services Configuration Screen
Switch Name Modifiable
Name Services
Web Authentication
Secure Harbour IP
System Authentication Configuration Screen
System Authentication Configuration Screen
Authentication
Authenticated , or Unauthenticated
System
Port #
EAP Port Configuration Screen
EAP Port Configuration Screen
Port
Authentication State
Backend State
Port Control
Maximum Requests
Initialize Port
Force Reauth
EAP Statistics Menu Screen
10 EAP Statistics Menu Screen
EAP Session
Authenticator
EAP Diagnostic
EAP Session Statistics Screen When to Use
11 EAP Session Statistics Screen
Authenticate Server or a local Authentication Server Method
SessionID
SessionOctetsRx
SessionOctetsTx
EAP Authenticator Statistics Screen When to Use
Clear Counters Command
Session User Name
Port Number
12 EAP Authenticator Statistics Screen
Clear Counters
EAP Diagnostic Statistics Screen When to Use
13 EAP Diagnostic Statistics Screen
Enters Connecting
Logoffs Connecting
Authenticating
Timeouts
Authenticated
Access Challenges
Backend Statistics Responses
Other Requests To
Counters
MAC Port Configuration Screen
Clear
Port Enable
14 MAC Port Configuration Screen
MAC Supplicant Configuration Screen
SET ALL Ports
Duration
MAC Address
Reauthenticate Sup
Initialize Supplicant
Plicant
False
Device Configuration Menu Screens
Device Configuration Menu Screen
General Configuration
General
Snmp
Resources
Information
General Configuration Screen
0.0
Default Gateway
Subnet Mask
Tftp Gateway IP
Addr
Operational Mode
Device Time
Screen Refresh
Time
Agg Mode
Clear Nvram
IP Fragmentation
WebView
Setting the IP Address
Configuration Warning Screen, IP Address
Setting the Subnet Mask
Configuration Warning Screen, Subnet Mask
Setting the Default Gateway
Setting the Tftp Gateway IP Address
Setting the Module Name
Setting the Device Date
Entering a New Screen Refresh Time
Setting the Device Time
Setting the Screen Lockout Time
Configuring the COM Port
Changing the COM Port Application
COM Port Warning
Clearing Nvram
UPS
Enabling/Disabling IP Fragmentation
Clear Nvram Warning
Snmp Configuration Menu Screen
Snmp Configuration Menu Screen
Snmp Community Names Configuration Screen
Snmp Community Names Configuration Screen
Establishing Community Names
Snmp Traps Configuration Screen
Snmp Traps Configuration Screen
Configuring the Trap Table
Enable Traps
Trap Destination
Trap Community
Access Control List Screen
10 Access Control List Screen
Access Control Lists
IP Addr
Mask
Entering IP Addresses
Entering Single Addresses
Entering Ranges of Addresses
Enable/Disable ACL
System Resources Information Screen
XX KB
Setting the Reset Peak Switch Utilization
Flash Download Configuration Screen
12 Flash Download Configuration Screen
Flash Download Configuration Screen Field Descriptions
Reboot After
Download
Download Server IP
Download File
Image File Download Using Runtime
Configuration File Download Using Tftp
Configuration File Upload Using Tftp
36Device Configuration Menu Screens
Port Configuration Menu Screens
Port Configuration Menu Screen
Port Configuration Menu Screen in Agg Mode, Huntgroup
Ethernet
Interface
HSIM/VHSIM
Redirect
Ethernet Interface Configuration Screen
Intf
Port Type
Config
Link
Speed
Duplex
Ethernet Port Configuration Screen
HDX FC
Refer to -3for a functional description of each screen field
Default Speed
Default Duplex
Interface
Physical Port
10Port Configuration Menu Screens
Full Duplex Flow
Control
Half Duplex Flow
Save to ALL
Selecting Field Settings
Setting the Advertised Ability
Configuration Menu
HSIM/VHSIM Configuration Screen
Redirect Configuration Menu Screen
Redirect Configuration Menu Screen
Port Redirect Configuration Screen
Source Port
Destination Port
Redirect Errors
Frame Format
Source Port n
Status
Changing Source and Destination Ports
Vlan Redirect Configuration Screen
Vlan Redirect Configuration Screen
Source Vlan
Source Vlan n
Changing Source Vlan and Destination Ports
Usage Notes
Aggregation Menu
Rapid Reconfiguration Spanning Tree
Definitions to Know
Link Aggregation
802.3ad Main Menu Screen
1 802.3ad Port Screen When to Use
Aggregator
802.3ad Port Screen
Viewing and Editing 802.3ad Port Parameters
Aggregator
OperKey
MUX
1.1 802.3ad Port Details Screen When to Use
10 802.3ad Port Details Screen
ActorSystemPriority
Port Instance
PartnerAdminSysID
ActorOperState
PartnerOperState
Stats
Displaying Port Statistics
Lagid
1.2 802.3ad Port Statistics Screen When to Use
11 802.3ad Port Statistics Screen
LACPDUsRx
IllegalRx
MarkerPDUsRx
LACPDUsTx
LastRxTimedelta
ActorChurnState
PartnerChurnState
ActorChurnCount
2 802.3ad Aggregator Screen When to Use
12 802.3ad Aggregator Screen
Viewing and Editing 802.3ad Aggregator Parameters
Displaying Aggregator Details
AggInst
SysPri
2.1 802.3ad Aggregator Details Screen When to Use
13 802.3ad Aggregator Details Screen
Instance
Partner
3 802.3ad System Screen When to Use
14 802.3ad System Screen
Broadcast Suppression Configuration Screen
System Identifier
Number of Ports
Number
Port #
Total RX
Setting the Threshold
Setting the Reset Peak
Configuration Menu Screens
802.1 Configuration Menu Screen
802.1 Configuration Menu Screen
802.1p
Spanning Tree
802.1Q Vlan
Spanning Tree Configuration Menu Screen
Tree Configuration Menu
Spanning Tree Configuration Screen
Vlan
AgeTime
Current STP Mode
Configured
Priority
Operation
Configuring a Vlan Spanning Tree
Spanning Tree Port Configuration Screen
Spanning Tree Port Configuration Screen
STP Vlan ID
Switch Address
Age Time
Viewing Status of Spanning Tree Ports
Enabling/Disabling the Default Spanning Tree Ports
Pvst Port Configuration Screen
Port Designated
Corresponding
Port Designated Root
Port Priority
Port Designated Cost
Port State
Port Designated Port
Page
802.1Q Vlan Configuration Menu Screens
Vlan Configuration Menu
Preparing for Vlan Configuration
Summary of Vlan Local Management
802.1Q Vlan Configuration Menu Screen
802.1Q Vlan Configuration Menu Screen
Vlan Port
Static Vlan
Current Vlan
Static Vlan Configuration Screen
Classification
Vlan ID
FDB ID
Creating a Static Vlan
Vlan Name
ADD
DEL Marked
Displaying the Current Static Vlan Port Egress List
Renaming a Static Vlan
Deleting a Static Vlan
Paging Through the Vlan List
Static Vlan Egress Configuration Screen
Static Vlan Egress Configuration Screen
Egress
Setting the Same Egress Type on All Ports Simultaneously
Setting Egress Types on Ports
Setting the Egress Type on One or More Ports Individually
Current Vlan Configuration Screen
Displaying the Next Group of Ports
Vlan Type
Read-Only An example of a dynamic Vlan is a Gvrp Vlan
Current Vlan Egress Configuration Screen
Current Vlan Egress Configuration Screen
Vlan Port Configuration Screen
Policy Pvid
Override is
Pvid
Changing the Port Mode
Configuring the Vlan Ports
Vlan Classification Configuration Screen
Admit Tagged Frames only
VID
VID
Classification
Description
DEL ALL/DEL
Marked
0x0000
0x00000000
000
000.000.000.000
Tftp Http DNS Smtp
Src TCP Port FTP Data
Nlsp IPX WAN Custom
00-00-00-00-00-00
Classification Precedence Rules
Layer
Classification Precedence
Example
Displaying the Current Classification Rule Assignments
Assigning a Classification to a VID
Protocol Port Configuration Screen
Deleting Line Items
Deleting All Classification Rules
Deleting One or More Classification Rules
Protocol Port Configuration Screen
Classify
Classification Rule
Field
Assigning Ports to a VID/Classification
Assigning One or More Ports Individually
Assigning All Ports Simultaneously
SET Ports to
Assigning VID/Classification to Port Vlan Lists
802.1p Configuration Menu
Screen Navigation Paths
802.1p Configuration Menu Screen When to Use
Port Priority Configuration
Port Priority
Traffic Class
Transmit
Queues
Port Priority Configuration Screen
Port Priority Configuration Screen
Set
Setting Switch Port Priority Port-by-Port
Policy Override
Setting Switch Port Priority on All Ports
Traffic Class Information Screen
Traffic Class Information Screen
Traffic Class Information Screen Field Descriptions
Traffic Class Configuration Screen
Traffic Class Configuration Screen
Save
Assigning the Traffic Class to Port Priority
Traffic Class
Transmit Queues Configuration Screen
Transmit Queues Configuration Screen
Weights Q0, Q1
Current Queueing
Mode
Q2, Q3
Setting the Current Queueing Mode
Priority Classification Configuration Screen
PID
PID
18802.1p Configuration Menu Screens
No Change TOS=PID Custom
TCP No Change TOS=PID Custom
Dest IP Address Mask New IP TOS
Tftp
Src TCP Port New IP TOS FTP Data
IP Fragments New IP TOS
IP Fragments2 Start End New IP TOS 00000
Dest TCP Port Start End New IP TOS 00000
SAP
28802.1p Configuration Menu Screens
Layer
About the IP TOS Rewrite Function
Displaying the Current PID/Classification Assignments
Assigning a Classification to a PID
Deleting One or More Line Items
Deleting PID/Classification/Description Line Items
Deleting All Line Items
Protocol Port Configuration Screen
See which ports are set to the PID/Classification indicated
Assigning Ports to a PID/Classification
Solving the Problem
Switch
Rate Limiting Configuration Screen
Priority List
Maximum
Feature
Port Number Modifiable Port Type
Direction
Configuring a Port
42802.1p Configuration Menu Screens
Changing/Deleting Port Line Items
Changing One or More Line Items
More About Rate Limiting
Rate Limiting Configuration Screen
Page
Layer 3 Extensions Menu Screens
Layer 3 Extensions Menu Screen
IGMP/VLAN
Layer 3 Extensions Menu Screen
IGMP/VLAN Configuration Screen
Igmp Version
120
Query Interval
Query Response
Robustness
Last Member Query
Switch Query IP
McastMartPoolSize
Querier Address
Querier Uptime
IGMP/VLAN Configuration Procedure
Igmp State
Page
Device Statistics Menu Screens
Device Statistics Menu Screen
Lists the number of frames received, transmitted, filtered,
Switch Statistics Screen
Rmon
Frames Fltrd
Frames Rcvd
Frames Txmtd
Interface Statistics Screen
Frames Frwded
InOctets
Interface Statistics Screen
InErrors
OutErrors
InUnicast
InNonUnicast
Displaying Interface Statistics
MTU
Rmon Statistics Screen
Rmon Statistics Screen
CRC Align Errors
Rmon Index
Data Source
Owner
Oversized Pkts
Fragments
Jabbers
Total Packets
Index nn
Displaying Rmon Statistics
1024 1518 Octets
Network Tools Screens
Screen ExampleNetwork Tools Help Screen
Refer to -1for a list of the commands
Command
Alias
Examples
Alias Stats
Arp
Arp-a
Syntax Bridge ENABLE/DISABLE IFNUM/ALL Options
Arplearn
Bridge
Syntax Arplearn normal limited status Options
Defroute
Syntax Cdp enable/disable/status Options
Cdp
Vid
Dynamicegress
Syntax dynamicegress action vid Options action
Syntax Enable Group Disable Group Trap #ALL
Commands for Listing Events
Syntax igmpv3drop enable disable status
Gigabitportmode
Igmpv3drop
Syntax gigabitportmode active redundant status
Lgframeadmin
Syntax linktrap enable/disable/status PORT/all
Syntax loopbackdetect enable disable state
Linktrap
Loopbackdetect
Maclock
Syntax maclock show port# all
Syntax Maclock set enable port# all global
Maclock set disable port# all global
Maclock set macaddress port# all create enable disable
Maclock set trap port# all enable disable
Maclock show Stations
Maclock set enable global
Netstat
Nonbridgeifnum
Syntax nonbridgeifnum 0 9999 status
PassiveStp
Ping
Policy
Syntax policy show profile profileindex
Policy show port portnumberorrangeorall
Policy set port portnumberorrangeorall profileindex
Examples Contiued
Policy show port
Radius
11-24Network Tools Screens
Character string for the shared secret code. For security
Radius client
Examples Cont’d
Syntax ratelimitmode status highrange default lowrange
Ratelimitmode
Reset
Syntax reset Options None Example -reset
Syntax Satsize 8 16 status Options
Satsize
Show
Show Appletalk interfaces
Softreset
Syntax softreset Options None
StpEdgePort
Syntax stpEdgePort status
StpForceVersion
Syntax StpForceVersion 0 2 status Options
Syntax stpLegacyPathCost enable disable status
StpLegacyPathCost
Recommended
Value
StpPointToPointMAC
StpRealTimeMsgAge
Syntax stpRealTimeMsgAge enable disable status
StpPort
Syntax Suppresstopologytraps enable disable Options
Suppresstopologytraps
Telnet
Syntax Telnet IP address Port # Options
Timedsoftreset
Timedreset
Syntax timedsoftreset status t seconds resetnv dontresetnv
Syntax timedreset status t seconds resetnv dontresetnv
Traceroute
Syntax Traceroute IP address Options
VrrpPort
EXAMPLE, Effects of Aging Time on Dynamic Egress
Done, quit, exit
Options None Example -done
Vlan Operation and Network Applications
Defining VLANs
Example of a Vlan
Other Vlan Strategies
Types of VLANs
12.2.1 802.1Q VLANs
Ingress
Benefits and Restrictions
Vlan Terms
Default Vlan
Filtering Database
Identifier FDB ID
Tagged Frame
Qcstp
Garp Garp Vlan
Gvrp
Gmrp
Configuration Process
Vlan Operation
Vlan Switch Operation
Defining a Vlan
Classifying Frames to a Vlan
Customizing the Vlan Forwarding List
FID
Receiving Frames from Vlan Ports
Untagged Frames
Tagged Frames
Forwarding Decisions
Known Unicasts
Vlan Configuration
Managing the Switch
Switch Without VLANs
Switch with VLANs
Switch Management with VLANs
12-14VLAN Operation and Network Applications
3069162
Quick Vlan Walkthrough
Assigning a Vlan ID and Vlan Name
Walkthrough Stage One, Static Vlan Configuration Screen
Assigning Ports to the Vlan Egress list
Walkthrough Stage Two, Port 3 Egress Setting
Configuring the Port Parameters
Walkthrough Stage Three, Port 10 Egress Setting
Walkthrough Stage Four, Vlan Port Configuration
Example 1, Single Switch Operation
Examples
For the Red Vlan
11 Switch Configured for VLANs
Frame Handling
Example 2, VLANs Across Multiple Switches
Redco Blue Industries
12-26VLAN Operation and Network Applications
Switch
12-28VLAN Operation and Network Applications
Redco Blue Industries User a
Blue Industries Redco
15 Transmitting to Bridge
Switches 1
Finance Department
Example 5, Using Dynamic Egress to Control Traffic
PCs
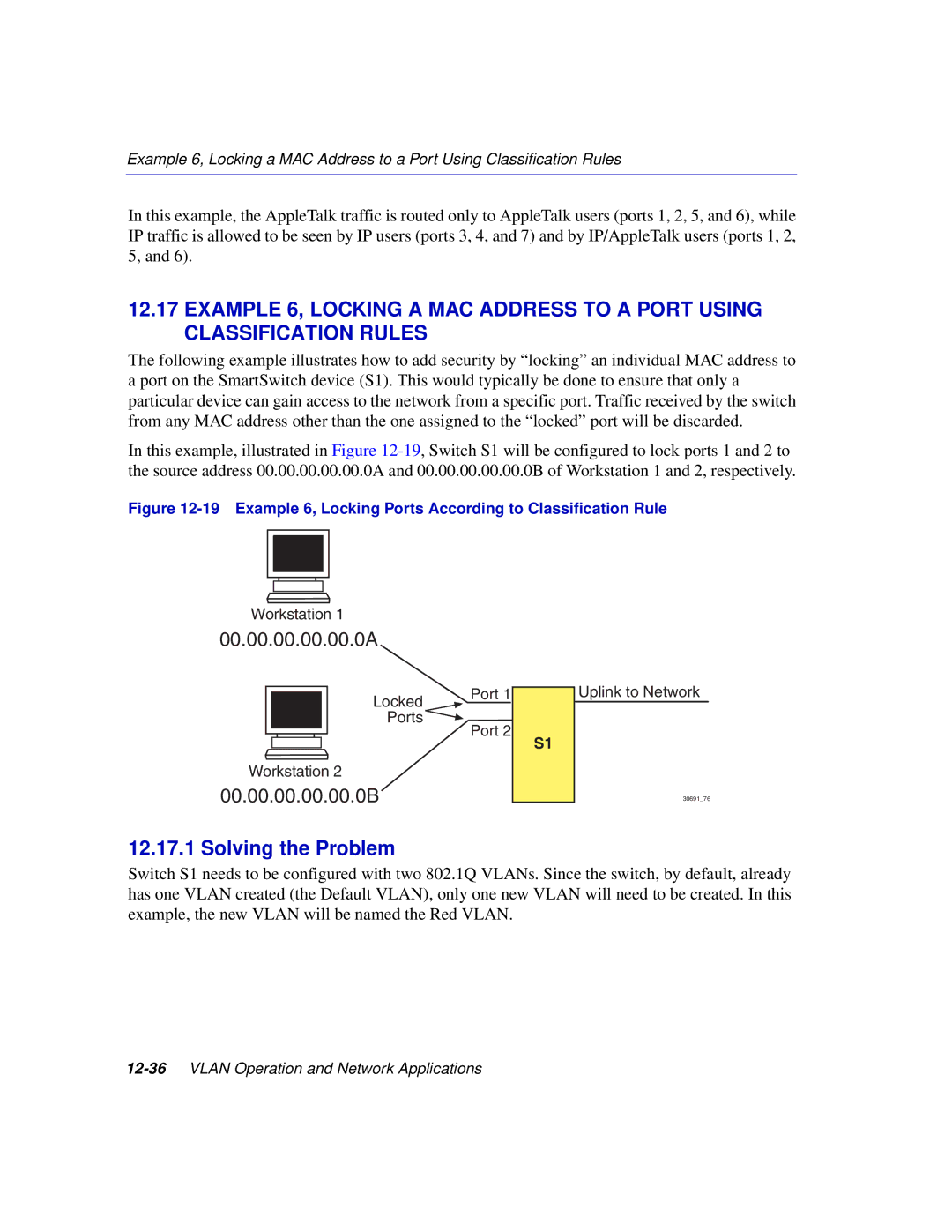
00.00.00.00.00.0A
Switch
SET ALL Ports no
Vlan Operation and Network Applications
Page
Generic Attribute Registration Protocol Garp
HOW IT Works
About Igmp
Supported Features and Functions
Detecting Multicast Routers
Page
Index
Numerics
Index-2
Index-3
Index-4
Index-5
Index-6
Index-7
Index-8
Index-9
Index-10
Index-11