Monitoring Network Traffic
Using Traffic Monitor
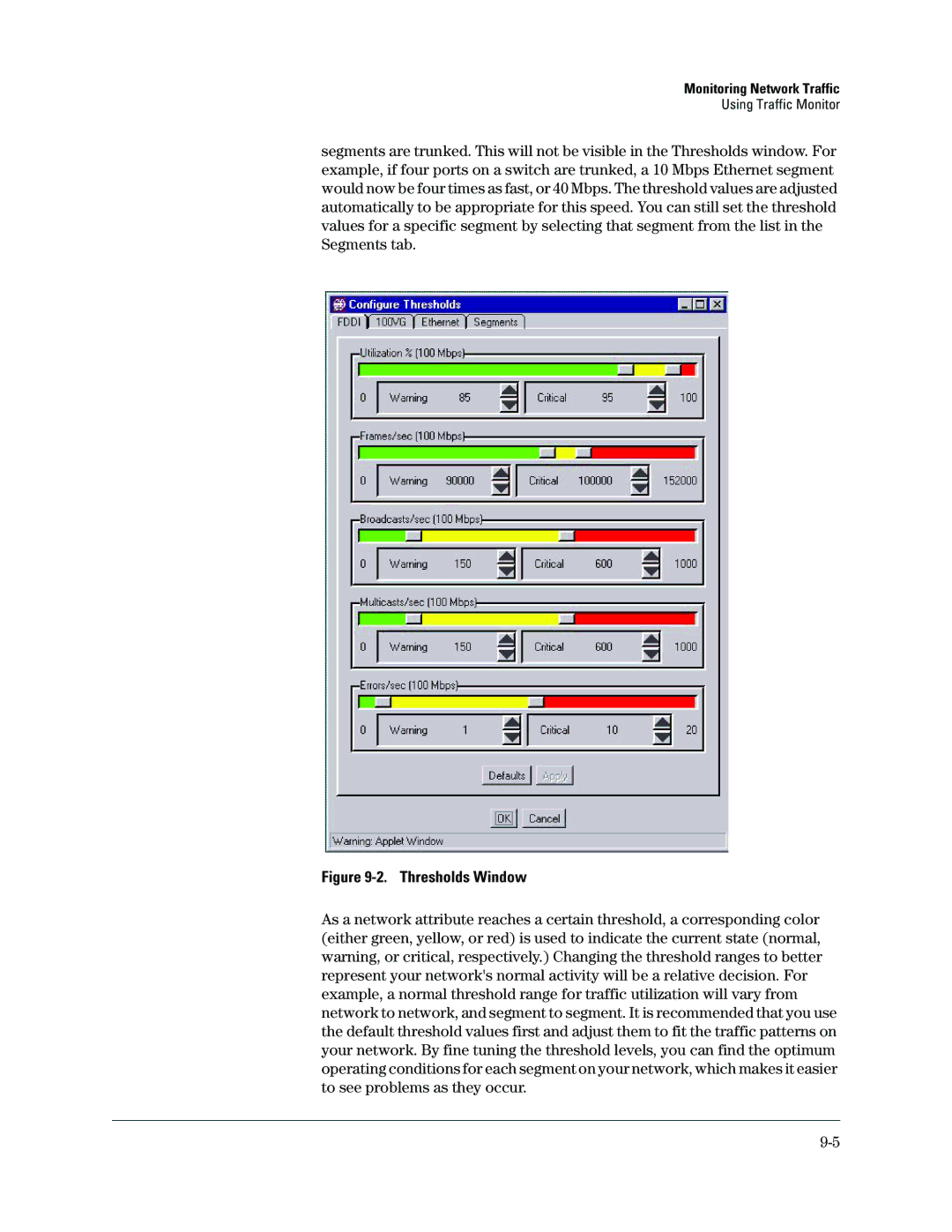
segments are trunked. This will not be visible in the Thresholds window. For example, if four ports on a switch are trunked, a 10 Mbps Ethernet segment would now be four times as fast, or 40 Mbps. The threshold values are adjusted automatically to be appropriate for this speed. You can still set the threshold values for a specific segment by selecting that segment from the list in the Segments tab.
Figure 9-2. Thresholds Window
As a network attribute reaches a certain threshold, a corresponding color (either green, yellow, or red) is used to indicate the current state (normal, warning, or critical, respectively.) Changing the threshold ranges to better represent your network's normal activity will be a relative decision. For example, a normal threshold range for traffic utilization will vary from network to network, and segment to segment. It is recommended that you use the default threshold values first and adjust them to fit the traffic patterns on your network. By fine tuning the threshold levels, you can find the optimum operating conditions for each segment on your network, which makes it easier to see problems as they occur.