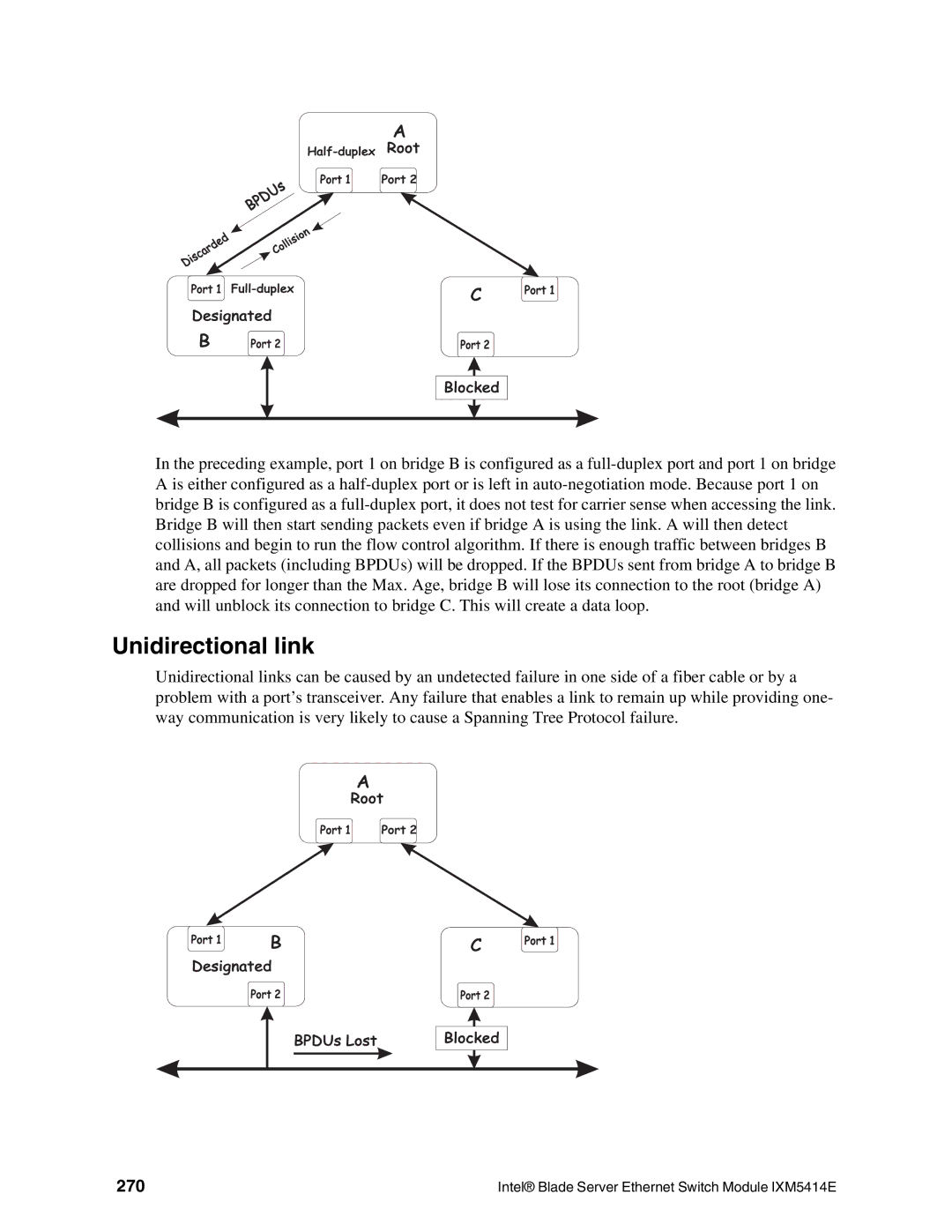
A
Discarded
Port 1 | Port 2 |
BPDUs
Collision
Port 1 | C | |
|
|
Designated
Port 1
B
Port 2 | Port 2 |
Blocked
In the preceding example, port 1 on bridge B is configured as a
Unidirectional link
Unidirectional links can be caused by an undetected failure in one side of a fiber cable or by a problem with a port’s transceiver. Any failure that enables a link to remain up while providing one- way communication is very likely to cause a Spanning Tree Protocol failure.
A
Root
Port 1 | Port 2 |
Port 1 | B | C |
|
Designated
Port 1
Port 2 | Port 2 |
BPDUs Lost
Blocked
270 | Intel® Blade Server Ethernet Switch Module IXM5414E |