headers
The IEEE 802.1Q standard restricts the forwarding of untagged packets to the VLAN of which the receiving port is a member.
The main characteristics of IEEE 802.1Q are as follows:
•Assigns packets to VLANs by filtering
•Assumes the presence of a single global spanning tree
•Uses an explicit tagging scheme with
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN packet forwarding
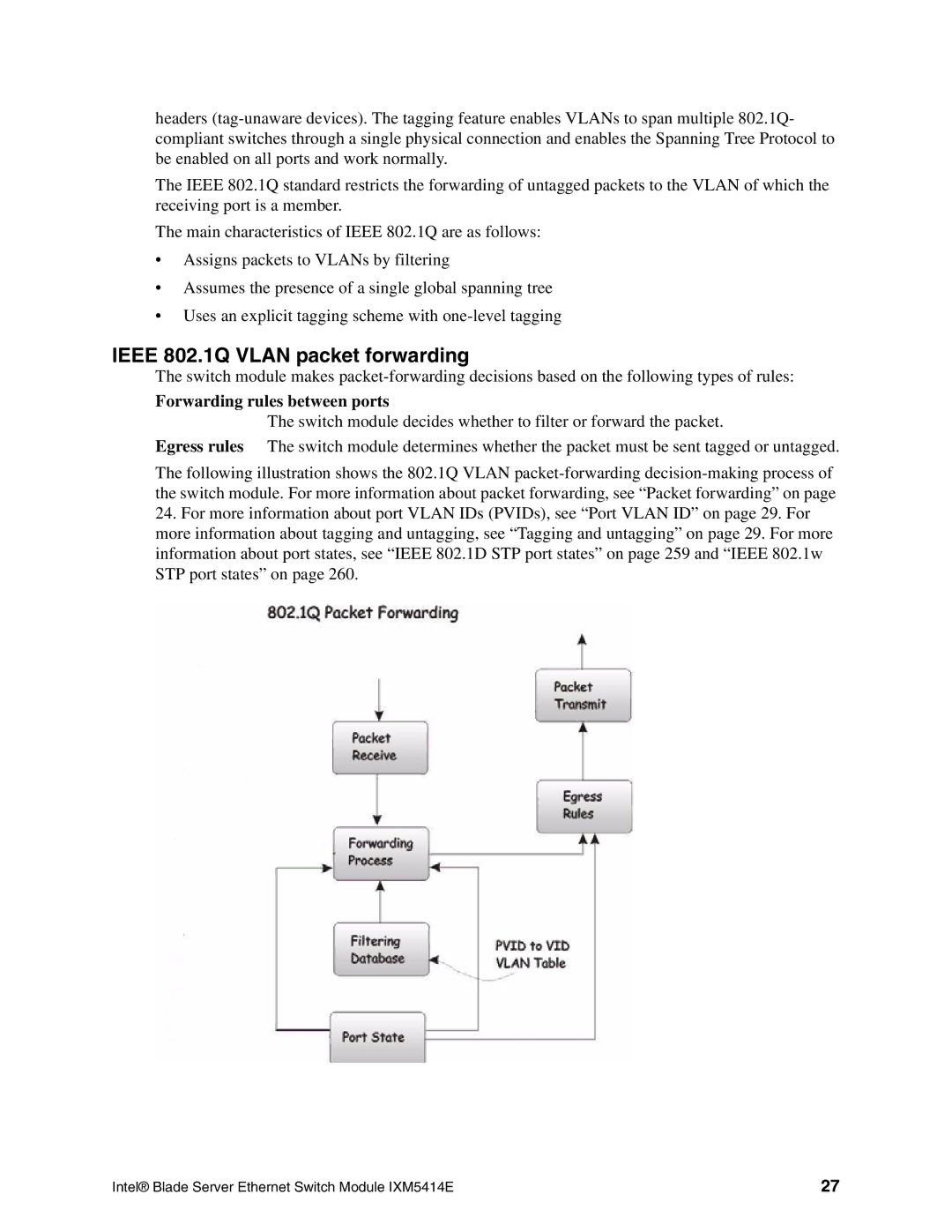
The switch module makes
Forwarding rules between ports
The switch module decides whether to filter or forward the packet.
Egress rules The switch module determines whether the packet must be sent tagged or untagged.
The following illustration shows the 802.1Q VLAN
24.For more information about port VLAN IDs (PVIDs), see “Port VLAN ID” on page 29. For more information about tagging and untagging, see “Tagging and untagging” on page 29. For more information about port states, see “IEEE 802.1D STP port states” on page 259 and “IEEE 802.1w STP port states” on page 260.
Intel® Blade Server Ethernet Switch Module IXM5414E | 27 |