IPmux-1, IPmux-1E
Page
International Headquarters RAD Data Communications Inc
IPmux-1, IPmux-1E
Limited Warranty
Please observe the following precautions
General Safety Instructions
General Safety Practices
Connection of AC Mains
Connection of DC Mains
Connection of Data and Telecommunications Cables
Ports Safety Status
Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC
Canadian Emission Requirements
Supplementary Information
Safety
Manufacturers Name Manufacturers Address
Product Name
Manual Organization
Foreword
Conventions
Page
IPmux-1, IPmux-1E
Limited Warranty
General Safety Instructions
Handling Energized Products
Connection of Data and Telecommunications Cables
Electromagnetic Compatibility EMC
Canadian Emission Requirements
Declaration of Conformity
Preface
Conventions
To operate the IPmux-1/1E
Setting Jumpers IPmux-1E Isdn Version Only
IPmux-1/1E Operation
To set the IPmux-1E ISDN-S module jumpers
IPmux-1/1E Configuration
Configuration
General
Contents
Overview of Menu Operations
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Iii
List of Tables
Overview
Versions
IPmux-1 with E1 interface
Options
Applications
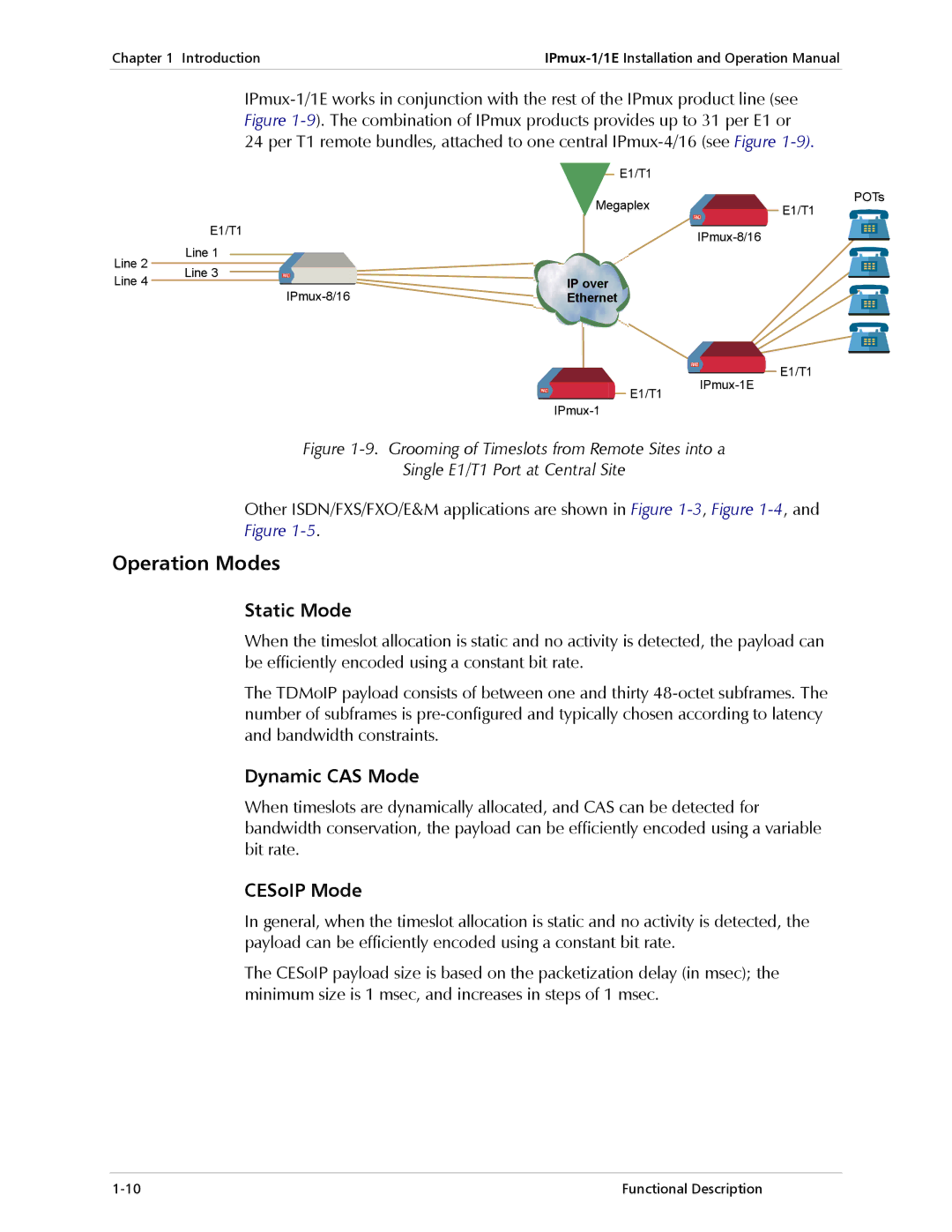
E1/T1 Circuit Extension over an IP/Ethernet Network
Digital Isdn Application V5.1 Concentration of Remote BRIs
Management
Features
Ethernet Ports
Isdn BRI
To calculate Distance
Fiber Options
There is no user port, the network fiber option is SC
To calculate Optical Budget
Physical Description
QoS
Timing
Functional Description
Front Panel
Rear Panel
Operation Modes
Static Mode
Dynamic CAS Mode
CESoIP Mode
Unframed Transparent
TE Mode
NT Mode
E1/T1
First Channel Second Channel
Timeslot Assignment in a Bundle
Timing Modes
Testing
External Network Timing
Network Timing Schemes
Single Source Clock Network
12. IPmux-1 in External Clock Mode
15. TDMoIP Frame Structure
Frame Format
Ethernet Frame Structure
Layer
Layer IP Layer
Layer Data
Packet Delay Variation
Vlan Support
UDP Support
Pdvt Jitter Buffer
Pdvt Buffer Effect on Delay
Intrinsic PDV in Static Mode
To configure jitter buffer depth
Ethernet Throughput
Intrinsic PDV in Dynamic CAS Mode
Intrinsic PDV in CESoIP Mode
Ethernet Throughput in Static Mode
Vlan + frame overhead + payload *
Ethernet Throughput in Dynamic CAS Mode
Unstructured
Structured
Preamble field 7 bytes
Round Trip Delay
Ethernet Throughput in CESoIP Mode
Frame overhead does not include
Reorder and Duplication of Ethernet Frames
Round Trip Delay in Static Mode
Round Trip Delay in Dynamic CAS Mode
Packet Delay in CESoIP Mode
End-to-End Alarm Generation
OAM Connectivity
Duplicated Frames
Packet Type Source IP Check Vlan Check
Vlan Traffic Behavior
Vlan Check for Packets that are Received by IPmux-1/1E
Vlan Check for Packets that are Sent by IPmux-1/1E
Internal Switch Operation Modes
Ethernet User Port
Rate Limiter Option
Switch Behavior
Basic Mode
Frame Action Switch Action
User Tagged Mode
User Untagged Mode
10. Rate Mode
Rate Mode
Rate + User Untagged Mode
Rate + User Tagged Mode
11. Rate+User Tagged Mode
Typically connected to another switch
Lease Length
12. Rate+User Untagged Mode
Manager Option
Technical Specifications
Optional user port is present
B8ZS, B7ZS, AMI
Line Impedance Balanced 120Ω Unbalanced 75Ω
Number of Ports
Compliance 168
Ms tail support
Local alarm
On power supply is OK
On port is synchronized no alarm
OFF signal loss, LOF or AIS is detected
Power
Introduction
Introduction
Chapter Installation
Site Requirements and Prerequisites
Package Contents
IPmux-1
Installation and Setup
Setting Jumpers
Equipment Needed
IPmux-1E ISDN-S Jumpers
IPmux-1 Front Panel for Two Ethernet Ports
Connecting Interfaces and Cables
Fuses
Grounding
Pin Designation Direction Function
Location of Connectors
E1/T1 Port Connectors Pinout
Ethernet Port Pinout
Control Port Pinout
Pin Number Signal Name
Pin Number Designation Function
Connecting the Control Port
E&M Interface Pin Assignments for RJ-11
FXS/FXO Interface Pin Assignments for RJ-11
Pin Number Signal Name Function
Connecting the Power
AC Power Connection
To connect AC power to IPmux-1/1E
DC Power Connection
Installation Installation and Setup
Chapter Operation
Front Panel Controls, Connectors, and Indicators
Name Type Function
IPmux-1 Front Panel LEDs
IPmux-1E Front Panel Indicators
With Control Terminal
Operating Instructions
Turning IPmux-1/1E On
Without Control Terminal
Login
User Name and Password
Turning IPmux-1/1E Off
Getting Started
Overview of Menu Operations
Navigating
Main Menu
IPmux-1 E1/T1 Terminal Menu Tree
IPmux-1E ISDN-S Terminal Menu Tree
IPmux-1E FXS/FXO/E&M Terminal Menu Tree
Configuration Connection Configuration Connection Mode
Activation Criterion
Main Menu
Connection Mode Configuration Connection Configuration
IPmux-1/1E Main Menu
To access the System menu
System Menu
IPmux-1/1E Main Menu Options
System
Setting IPmux-1/1E Configuration Options
To access the Configuration menu
Configuration
14. IPmux-1E ISDN-S Configuration Menu
Performance Monitoring
To view Performance Statistics
Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring
Operation Overview of Menu Operations
Error Detection
Using Front Panel LEDs
Working with the Alarm Buffer
Event Description Corrective Action
Event Types
LOS END
IPmux-1 Troubleshooting Chart
Troubleshooting
E1/T1 Statistics
Performance Monitoring and Troubleshooting Statistics
LOS
LCV
AIS Febe BES SES UAS Lomf
LOS LOF RED LCV
Alarm Description
E1/T1 Alarms
LCV
Febe
SES
Main Menu Æ Performance Monitoring Æ LAN Statistics
LAN Statistics
One Ethernet Port
To view the LAN statistics
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Parameter Description
LAN Statistics Parameters
Parameter Description Frames Transmitted
LAN Statistics
With User Ethernet Port
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Check the network interface card
Parameter Description Frames Transmitted
Bundle Connection Statistics
To view the Bundle connection status
Bundle Connection Status
Bundle Connection Status Parameters
To Chapter
Synchronous and constant flow
Transmitting them all at once
External Loop
Diagnostic Tests
↓ Internal/External /Disable
E1/T1
To run a test
Remote Loopback
Tone Injection
To run a loopback test
Answer
Frequently Asked Questions
UDP Destination Port
ToS
Answer
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Frequently Asked Questions
Booting IPmux-1/1E
Boot Sequence
General
To access the file system
Accessing the File System
Exist
Boot Menu
Page
Using Telnet to Manage the IPmux-1/1E
Starting a Telnet Session
To open a Telnet application
Telnet Operation
System Security
To establish a Telnet session
Telnet Access
Appendix B Telnet Using Telnet to Manage the IPmux-1/1E
Snmp Environment
Snmp Principles
Snmp Operations
Management Information Base MIB
MIB Structure
MIBs Supported by the IPmux-1/1E Snmp Agent
Snmp Communities
Management Domains under Snmp
Network Management Stations
Authentication
Figure D-1. Tftp Downloading Procedure
Inband Tftp Download Procedure
Table D-1. Browse MIB Fields
Preliminary Procedure
Before performing Tftp download
Log in as Superuser su
Checking the Download
To check the download
Press Start Query
Figure D-3. System Description
Appendix E Configuration Menus
Performance Monitoring
Configuration
Main Menu
System
Viewing the IPmux-1/1E System
General Information
General Information
Figure E-3. General Information Window Isdn
Self-Test Results
For details
Reset
To reset the IPmux-1/1E configuration
System Event Log
Logfile Events
Logfile Events
Ping
To ping
Vlan ID
General Configuration
General Configuration Menu
Ping
Host IP
Default Gateway
To configure the Host IP address and IP Mask
To change a configured Host IP
Management Configuration
Authentication/Community
Dhcp Status
Off
Table E-3. Authentication/Community Parameters
To access additional manager-list parameters
Manager List
Alarm Traps Mask
Alarm Traps Mask
Table E-4. Manager List Parameters
Alarm ID Alarm Description Trap Sent to NMS
Ascii Terminal Configuration
Table E-6. IPmux-1/1E Alarms
To configure Telnet Access
To Download/Upload using Xmodem
Time/Date Update
Download/Upload Using Xmodem
Table E-7. Ascii Terminal Configuration Parameters
DOWNLOAD/UPLOAD Using Tftp
DOWNLOAD/UPLOAD Using Xmodem
View Transfer Status
Table E-10. Download/Upload Using Tftp Parameters
To save the parameters and start the transmission process
0.0 to
Figure E-21. Reset Default Warning
Set Default Parameters
IPmux-1 E1/T1 Configuration
E1 Configuration
E1 Configuration
CRC4 Disable
Default Disable
Default -10 dB
CRC4 Enable
Default FF
CAS enable
CAS disable
Default CAS Enable
B8ZS
T1 Configuration
T1 Configuration
T1-ESF
Default B8ZS
Framer will be configured to T1-ESF mode. Operation
Mode will be set by signaling mode field #6 to either
Default T1-ESF
Default 7F
IPmux-1E Configuration
Isdn Configuration
Isdn Configuration
Table E-15. Isdn Channel Parameters
Isdn Channel Configuration
Table E-14. Isdn Configuration
Isdn Channel Configuration
Valid only for FXO
Analog Configuration
Analog Configuration
Wiring Wire, 4-Wire Valid only for E&M
Channel Configuration
Analog Channel Configuration
Signaling Profile Configuration
Signaling Profile Configuration
ESC
Connection Configuration Static Mode
To configure the Connection
Connection Configuration
Bundle Connection Configuration Static Mode
Bundle Connection Configuration
IP TOS
Primary
Default 0.0.0.0 not configured
To 300 milliseconds
None, Secondary
None
Protection Switching Configuration
Protection Switching Configuration
Disable, Immediate Msec to 1 sec
Connection Configuration Dynamic CAS Mode
Bundle Connection Configuration Dynamic CAS Mode
24 to
Disable Default Disable
Criterion
Connection Configuration CESoIP Mode
Activation Criterion
Activation
Figure E-37. Connection Configuration
Bundle Connection Configuration CESoIP Mode
1796 to
First define the bundle
To 63 msec
1796
LAN Configuration
LAN Configuration No User Port
100BaseT Full-duplex
Table E-25. LAN Configuration Parameters
SET
10 DS0 Bundle Configuration
DS0 Bundle Configuration
Active Echo Cancellation Timeslots
Performance Monitoring
To save the change
Compliance to Standards
Table E-27. E1/T1 Statistics Parameters
Alarm Failure Comments
Table E-27. E1/T1 Statistics
Table E-28. Link Status Parameters
Parameter Description
Isdn Statistics
Isdn Statistics in IPmux-1
Table E-29. Isdn Statistics Parameters
To view statistics for the next interval
Analog Status IPmux-1E with FXS/FXO/E&M
On hook Off hook Ringing
Analog Status
To reset counters
LAN Status no User port
Table E-30. LAN Status
Frames transmitted to the network
Statistics Values Description Frames received from the user
Bundle Connection Statistics
Bundle Connection Status /Statistics
Parameter Possible Values / Remarks
Table E-31. Bundle Connection Status/Statistics Parameters
Aging Time
Ethernet Configuration/Status with Ethernet User Port
Default 120 seconds
Switch Configuration
Figure E-49. LAN Configuration Two Ethernet Ports
LAN Configuration
Rate+user untagged modes
Table E-32. LAN Configuration Two Ethernet Ports
Default 100 Mb
This item is displayed only in user tagged, user untagged
To erase the MAC Table
Vlan Configuration
Vlan Configuration Vlan ID
Erase MAC Table
Parameter Values Remarks
Table E-34. Vlan Configuration Rate+User Tagged Mode
LAN Status
Maximum number of allowed entries is
To view statistics for next channel
Figure E-53. LAN Status Menu Two Ethernet Ports Internal
Table E-35. LAN Status Two Ethernet Ports
Page
Index
Datagram, 1-16 date, E-13
Configuration menu, 3-14 connection
Jabber, E-57
FXS
Max Capability, E-52 menu tree
QoS
Packet delay
Version, D-3
Timeslot, 1-12, E-40 timing
DC Power Supply Connection Terminal Block Connector
TB Plug with Captive Screws optional
DC Power Supply Wire Voltage Polarity
XMODEM, E-13
Index
Excellent Good Fair Poor Very Poor
Customer Response Form
Page
Error Report
Page
Page
International Headquarters