J300 Series
Definitions and Symbols
Safety
Precautions
Page
Iii Pollution degree Aug
Revision History Table
Table of Contents
Installation
Safety Precautions
Inputoutput
Input phase failure protection
Noise filter Fuse Good example Power supply
Bad example
Control and operation
Maintenance, inspection and part replacement
Appendix
Megohm-meter
Earth leakage breaker Mgo
Turn on and OFF Good example
Earth LeakageSurge absorber breaker Power
Supply Leading power factor capacitor
Motor
General Caution
To be grounded or shielded wire
Inspection Upon Unpacking
Contents of Specifications Label
Names of Parts
Appearance and Names of Parts
Installation
Be sure to check the ambient temperature
Vent hole Cm or more
Precaution for installation and wiring
Wiring
Power supply
ELB
Wiring the Power Supply and Motor
L3 RB + T1 T2 T3 PE
Dynamic Braking Resistor Braking Units
Inverter At the site
Improper grounding Proper grounding Inverter
Wiring of Control Circuit Terminals
FM CM1 PLC P24 CM2 AL2 AL1 AL0
CM2 AL2 AL1 AL0
Page
Connection to the Programmable Controller
200V class
Wiring Equipment, Options EMI filter, etc
Standard equipment Power supply
Magnetic
Inverter
RB P
Terminal
Run signal 27 VDC Intelligent output signal
Free run input signal
Current frequency command
Common for frequency command Output
PLC
Control Circuit Terminals
Cosø=0.4 10 mA 30 VDC Resistor load
Abnormal, Power off
AL0-AL1 open
Contact rating 250 VAC Resistor load
Terminal Connection Diagram
Before Starting Operation
Operation
Page
Operating with digital operator
Running from external command
For sink type wiring
Test Run
Key to
Key and then press Press
Key to set Press
Key to Key to set Press
Contact b Contact a
Contact specification
Resetting Any one of A, B and C is possible
Func Function key Up key, Down key
Power Lamp Monitor LED display
STOP/RESET key
Operation of the Digital Operator
Key Description
Key is pressed, the extension function mode can be selected
Explanation of Screen Display
Monitor mode
Transition of Each Code
Output frequency
Digital Operator Initialization List
Screen display
Explanation of Modes
Monitor mode contents
Is displayed
10.00 to 100.00 to
Trip current
Trip cause
Function mode
Setting
Frequency
Direction
Running
Tion time 1 Manual torque boost
Accelera- tion time 1 Decelera
Run
Extension function
Motor receiving voltage setting
How to Delete Trip History Data ,
Extension function mode contents
Initial value Constant between 99.9 is set in units
Start frequency adjustment
Extension Function Code
Speed control response constant
Frequency upper, lower limiter
Multispeed setting
Extension Function Code Contents and display
Carrier frequency setting
Frequency command sampling frequency setting
100 150
Setting method 20% 120%
Motor poles setting for motor speed monitor
Initial value Func
Same as A26
Setting end
Initial value Setting method
400 External frequency
External
Operation will be stopped
Inverter requiring an external resistor
T1 + t2 + t3 100 Model 055, 075LF
Terminal connection example
Output full-scale value
Current monitor
Torque monitor 200% of the rated torque
Only optionally set frequency
Frequency arrival signal output method
At the time of constant
Speed arrival
Swfw
Swjg
Base frequency setting
Maximum frequency
Frequency at the start of running
PID
This function is valid when 0 is set for Setting method
Auto tuning setting
Motor data selection
Ro-T- option selection
Unusable
Input
Terminal Setting
Extension Function Code Function name
Frequency arrival signal
Signal during running Setting method is the same
Overtorque signal Note As that of the input terminals
Input
Protection Functions
Other display
Error Messages and Diagnosis
Troubleshooting
BRD%ED
Ground fault on
Symptom
Display on
Check Countermeasure
Appropriate value
Trouble shooting
HRW-OJ
Page
Insulation resistance tests, withstand voltage tests
Maintenance and Inspection
Maintenance and Inspection Precautions
Inspection Items
10-2
Applied voltage Good example Time Megohm-meter
Bad example Time
Location Daily Periodic
10-3
Daily Inspection and Periodic Inspection 1/3
Instruments
Daily Inspection and Periodic Inspection 2/3
10-4
Replacement
Daily Inspection and Periodic Inspection 3/3
No blown out LEDs
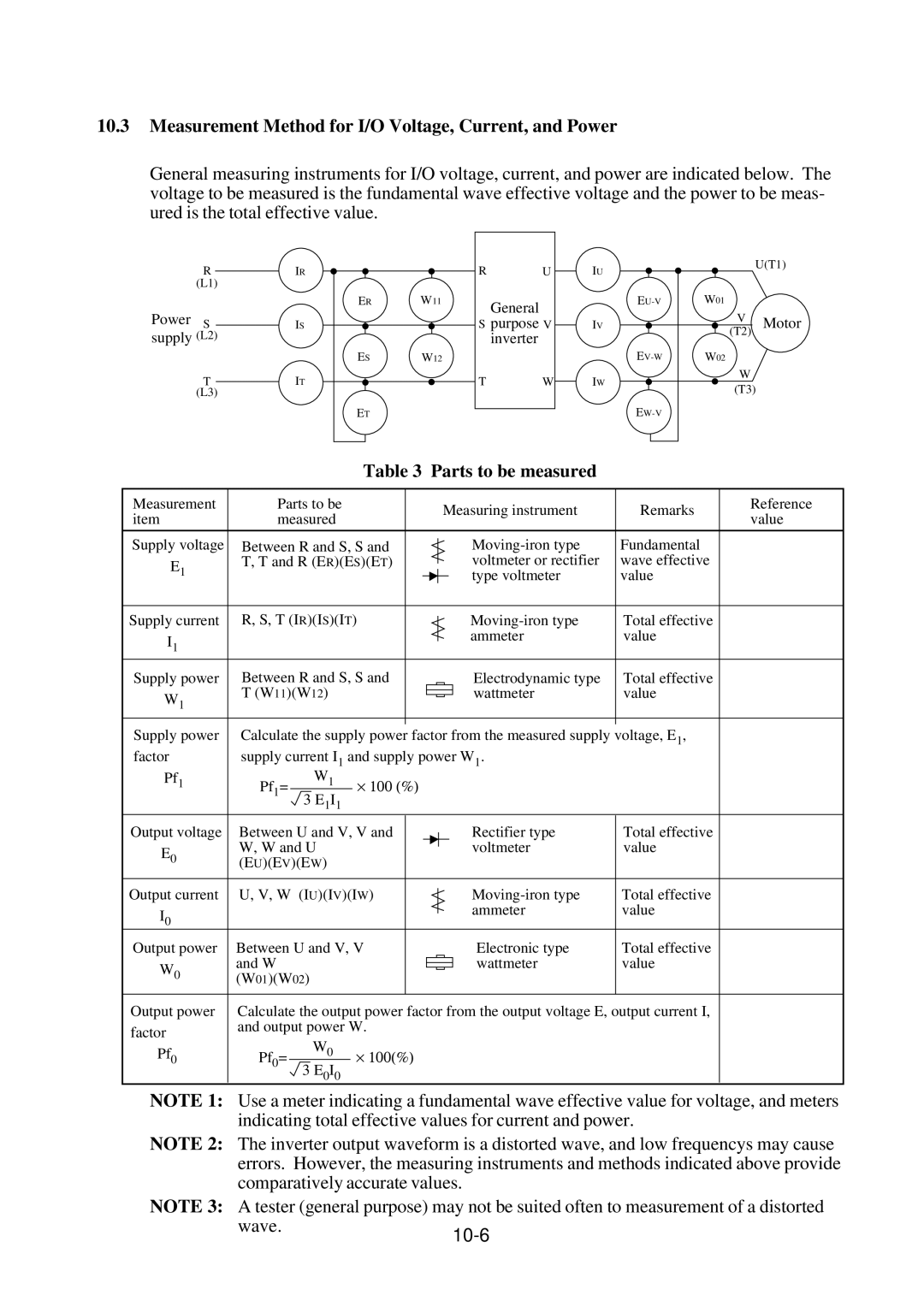
Parts to be measured
Measurement Method for I/O Voltage, Current, and Power
Measurement method for output voltage
10-7
Standard Specifications
Common Standarsd Specifications
11-1
Description Input voltage Class Model Name Type
11-2
11-3
Individual Specification USA version J300
Functions When Using the Optional Remote Operator
Connecting the remote operator
12-1
Switch Model J300 series
12-2
Same as VWA, J100
12-3
Monitor mode
Term Lllllllll
12-4
12-5
Function mode
12-6
12-7
12-8
12-9
12-10
12-11
12-12
12-13
12-14
12-15
For error contents, see
Other displays
12-16
Fmax Fch
Forced rewriting Description Alarm
Value. Note that when Automatically rewritten
12-17
Dimensions
Remote operator, copy unit
12-18
12-19
Copy Unit Function
12-20
Data to be copied by the copy unit Precautions for copying
13-1
Service
Page
Precautions
Autotuning start Setting method
Select 2 Motor in the third hierarchy
New remote operator
Select 3 Function in the first hierarchy
Select 1 Control in the second hierarchy
Tuning END
Tuning NG
Display in the failure state
Select Sensorless vector control by Control method
Running method by autotuning data
0VC to 4SLV in the fourth hierarchy
Change the content of 6 Mode from
When the data is changed, press Key
Select 1 V/f in the third hierarchy
Carrier
50% Range where the energy conservation is effective
Energy conservation running Outline of the function
Large load
Initial display
SPD
Precautions
Principle
Setting process
Digital operator Select Running mode selec Tion
STR Mode 2GOD
IPS Trip OFF
IPS Powr
Alarm
Time chart for retry mode
Digitaloperator
Commercial power source switching
Set TRM terminal mode
Function mode F-34
Elbc
Appendix 3 Capacitor Life Curve
Ambient Temperature Hours Operation/day Capacitor life year
Deceleration
Appendix 4 Acceleration/Deceleration Curve Constants
Curve
RU curve Acceleration
AUX
When V/f control is selected Function mode
When sensor-less vector control is selected Function mode
Operation conditions
Load varies
Operation conditions Phenomena Improvements Display, etc
Quickly varying load
Motor revolution varies when
AUX K 022.00 kW 005.50 kW Select the most approximate value
Select the motor capacity which is the most approxi
Mate to the total capacity of the motors used
For example, 7.5 kW, 5.5 kW, and 3.7 kW
Function name Second function setting
Appendix 6 Supplementaly Explanation of the Function Mode
Monitor mode
HOP, HRW DOP, DRW
HRW DRW
SET Selectrem
4RESET
Initreseton
1F-SET
3LINE Acclinel
Controlvc
1AUTO 0NOR
2DATA 0NOR
2FRS 1ZST Runfrs ZST
3LINE Decline L
4GAIN Decgain
2TIME
2LIMH
1LEVEL
2CONST1.0
1LIML
IN-TM4FRS
IN-TM1RS
IN-TM2AT
IN-TM3JG
1RYA 3RUN
1BAUD
2NUMBER1
0EVN
Wiring Sketch
Appendix 8 PID Function
PID Gain
Data Setting Method