Designing Access Controls
Choose the Access Control Methods
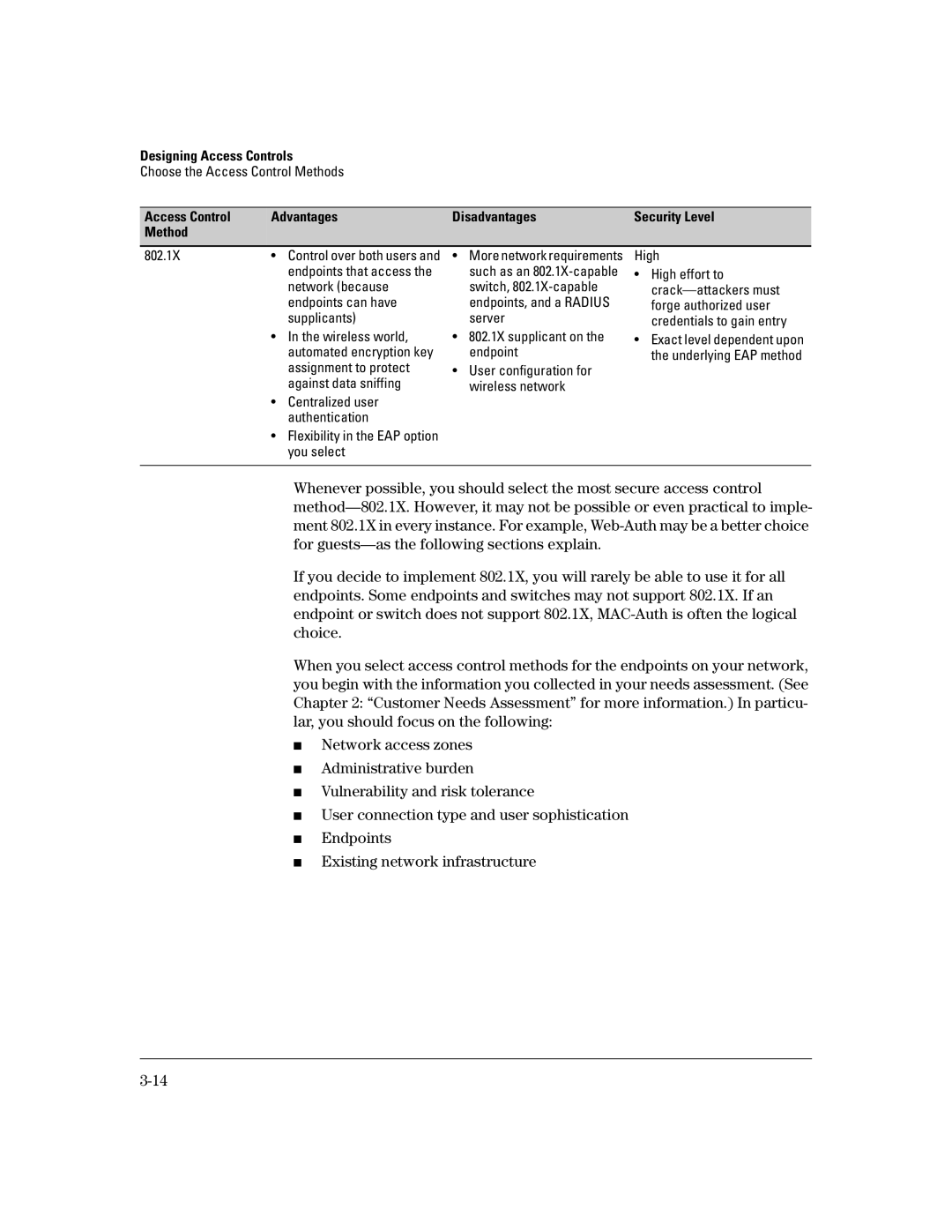
Access Control | Advantages | Disadvantages | Security Level |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
802.1X | • Control over both users and | • More network requirements | High |
| endpoints that access the | such as an | • High effort to |
network (because | switch, | |
endpoints can have | endpoints, and a RADIUS | forge authorized user |
supplicants) | server | credentials to gain entry |
•In the wireless world, automated encryption key assignment to protect against data sniffing
•Centralized user authentication
•Flexibility in the EAP option you select
•802.1X supplicant on the endpoint
•User configuration for wireless network
•Exact level dependent upon the underlying EAP method
Whenever possible, you should select the most secure access control
If you decide to implement 802.1X, you will rarely be able to use it for all endpoints. Some endpoints and switches may not support 802.1X. If an endpoint or switch does not support 802.1X,
When you select access control methods for the endpoints on your network, you begin with the information you collected in your needs assessment. (See Chapter 2: “Customer Needs Assessment” for more information.) In particu- lar, you should focus on the following:
■Network access zones
■Administrative burden
■Vulnerability and risk tolerance
■User connection type and user sophistication
■Endpoints
■Existing network infrastructure