Designing Access Controls
Choose the Access Control Methods
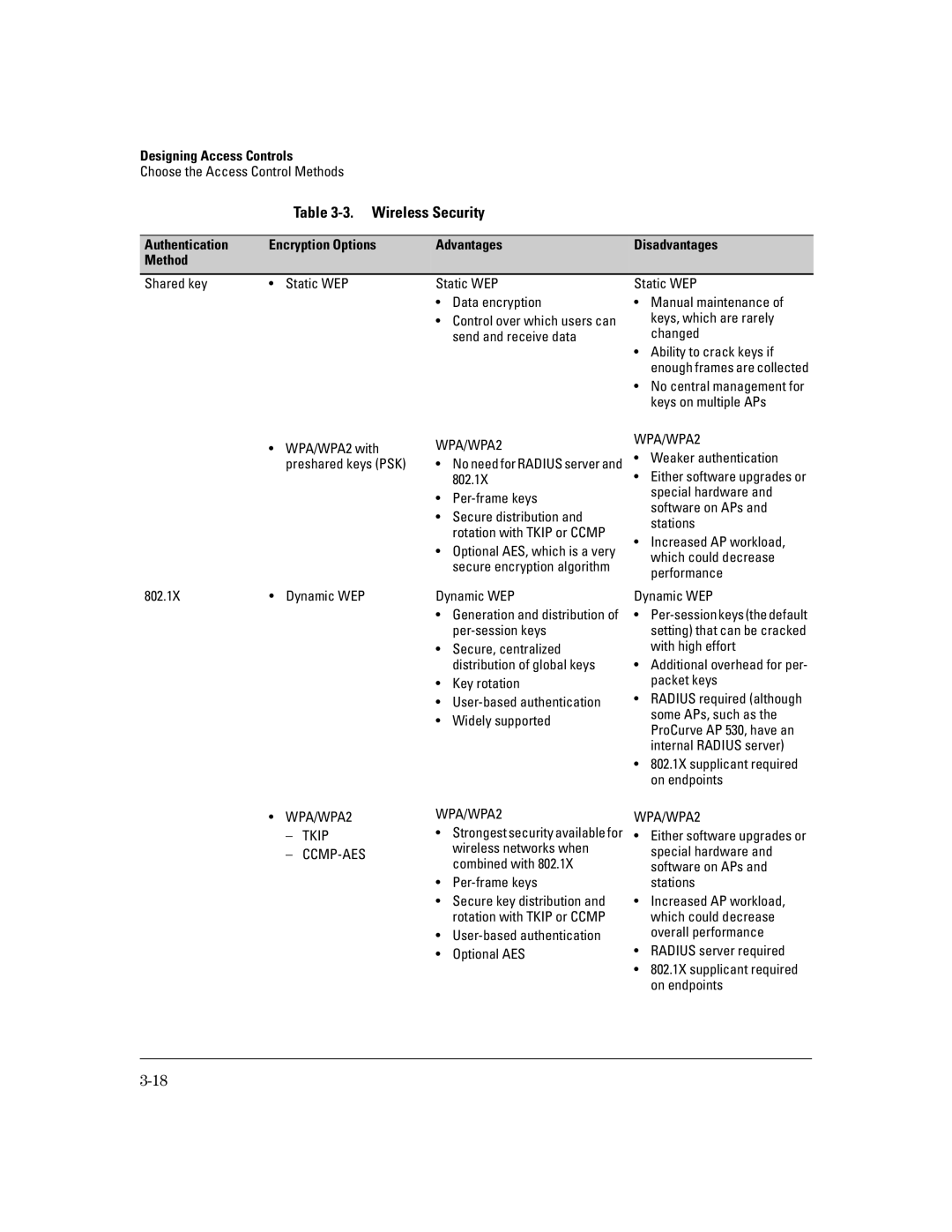
Table 3-3. Wireless Security
Authentication | Encryption Options | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shared key | • Static WEP |
Static WEP
•Data encryption
•Control over which users can send and receive data
Static WEP
•Manual maintenance of keys, which are rarely changed
•Ability to crack keys if enough frames are collected
•No central management for keys on multiple APs
•WPA/WPA2 with preshared keys (PSK)
802.1X | • Dynamic WEP |
•WPA/WPA2
–TKIP
–CCMP-AES
WPA/WPA2 | WPA/WPA2 | |||
• | Weaker authentication | |||
• No need for RADIUS server and | ||||
| 802.1X | • Either software upgrades or | ||
• |
| special hardware and | ||
| software on APs and | |||
• | Secure distribution and |
| ||
| stations | |||
| rotation with TKIP or CCMP |
| ||
| • | Increased AP workload, | ||
• Optional AES, which is a very | ||||
| which could decrease | |||
| secure encryption algorithm |
| ||
|
| performance | ||
|
|
| ||
Dynamic WEP | Dynamic WEP | |||
• Generation and distribution of | • | |||
|
| setting) that can be cracked | ||
• | Secure, centralized |
| with high effort | |
| distribution of global keys | • Additional overhead for per- | ||
• | Key rotation |
| packet keys | |
• | • | RADIUS required (although | ||
• | Widely supported |
| some APs, such as the | |
| ProCurve AP 530, have an | |||
|
|
| ||
|
|
| internal RADIUS server) | |
|
| • | 802.1X supplicant required | |
|
|
| on endpoints | |
WPA/WPA2 | WPA/WPA2 | |||
• Strongest security available for | • Either software upgrades or | |||
| wireless networks when |
| special hardware and | |
| combined with 802.1X |
| software on APs and | |
• |
| stations | ||
•Secure key distribution and rotation with TKIP or CCMP
•
•Optional AES
•Increased AP workload, which could decrease overall performance
•RADIUS server required
•802.1X supplicant required on endpoints