9.1.2 Summary of the DS Storage Manager logical configuration steps
It is our recommendation that the client consider the following concepts before performing the logical configuration. These recommendations are discussed in this chapter.
Planning
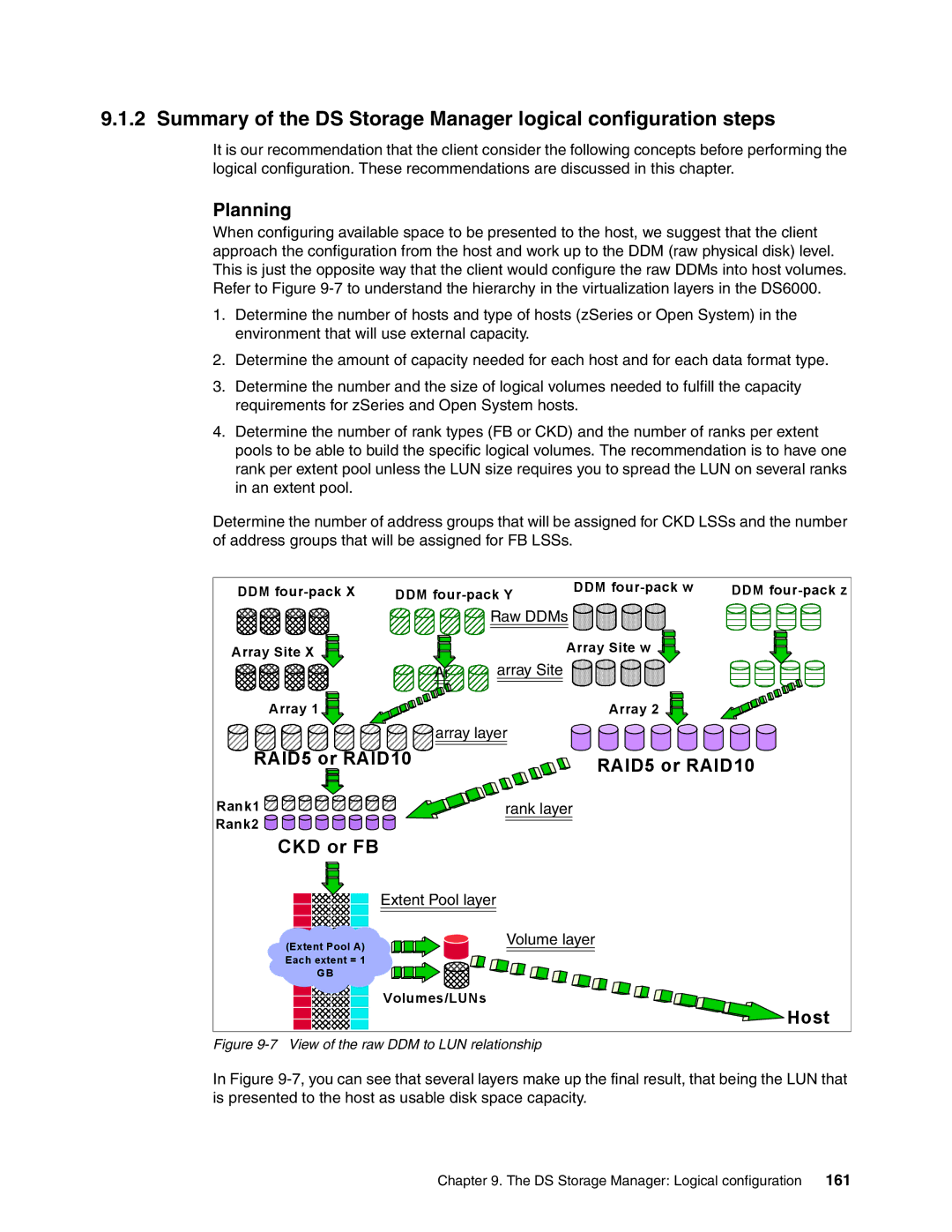
When configuring available space to be presented to the host, we suggest that the client approach the configuration from the host and work up to the DDM (raw physical disk) level. This is just the opposite way that the client would configure the raw DDMs into host volumes. Refer to Figure
1.Determine the number of hosts and type of hosts (zSeries or Open System) in the environment that will use external capacity.
2.Determine the amount of capacity needed for each host and for each data format type.
3.Determine the number and the size of logical volumes needed to fulfill the capacity requirements for zSeries and Open System hosts.
4.Determine the number of rank types (FB or CKD) and the number of ranks per extent pools to be able to build the specific logical volumes. The recommendation is to have one rank per extent pool unless the LUN size requires you to spread the LUN on several ranks in an extent pool.
Determine the number of address groups that will be assigned for CKD LSSs and the number of address groups that will be assigned for FB LSSs.
DDM | DDM | DDM | DDM | |
|
| Raw DDMs |
|
|
Array Site X |
| Array Site w |
| |
| Ar | array Site |
|
|
Array 1 |
|
| Array 2 |
|
| array layer |
|
| |
RAID5 or RAID10 |
| RAID5 or RAID10 | ||
|
|
| ||
Rank1 |
| rank layer |
|
|
Rank2 |
|
|
|
|
CKD or FB
(Extent Pool A) |
Each extent = 1 |
GB |
Extent Pool layer 6
Volume layer
Volumes/LUNs

 Host
Host
Figure 9-7 View of the raw DDM to LUN relationship
In Figure
Chapter 9. The DS Storage Manager: Logical configuration 161