2 Gbps Fibre Channel ports |
|
|
| 2 Gbps Fibre Channel ports |
Host adapter | Controller |
| Controller | Host adapter |
Card 0 |
| Card 1 | ||
chipset |
| chipset | ||
Server 0 |
| Server 1 | ||
|
|
| ||
Power PC | Processor | Interconnect | Processor | Power PC |
chipset | memory |
| memory | chipset |
| Volatile |
| Volatile |
|
Device adapter |
|
| Persistent | Device adapter |
chipset | Persistent |
| chipset | |
| 2 Gbps Fibre Channel ports |
| 2 Gbps Fibre Channel ports |
|
|
| Fibre Channel switch |
|
|
| To next | ooo |
|
|
| switch | 16 DDM |
|
|
|
| Fibre Channel switch | Server enclosure | |
|
|
| ||
|
| Fibre Channel switch |
|
|
|
| ooo |
|
|
|
| 16 DDM |
|
|
|
| Fibre Channel switch | Expansion enclosure | |
|
|
| ||
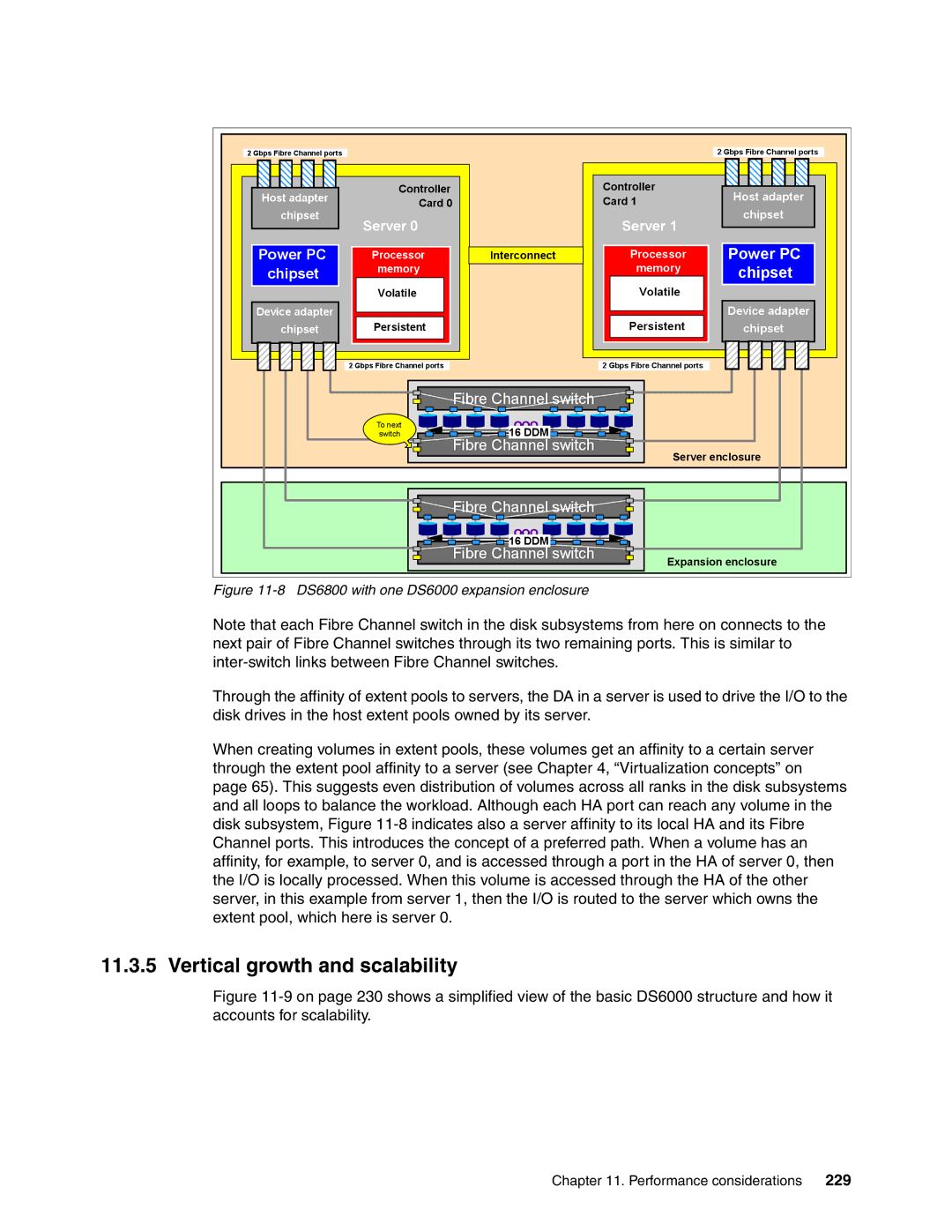
Figure 11-8 DS6800 with one DS6000 expansion enclosure
Note that each Fibre Channel switch in the disk subsystems from here on connects to the next pair of Fibre Channel switches through its two remaining ports. This is similar to
Through the affinity of extent pools to servers, the DA in a server is used to drive the I/O to the disk drives in the host extent pools owned by its server.
When creating volumes in extent pools, these volumes get an affinity to a certain server through the extent pool affinity to a server (see Chapter 4, “Virtualization concepts” on page 65). This suggests even distribution of volumes across all ranks in the disk subsystems and all loops to balance the workload. Although each HA port can reach any volume in the disk subsystem, Figure
11.3.5 Vertical growth and scalability
Figure 11-9 on page 230 shows a simplified view of the basic DS6000 structure and how it accounts for scalability.
Chapter 11. Performance considerations | 229 |