–If you reboot a system with adapters while the primary path is in a failed state, you must manually disable the BIOS on the first adapter and manually enable the BIOS on the second adapter. You cannot enable the BIOS for both adapters at the same time. If the BIOS for both adapters is enabled at the same time and there is a path failure on the primary adapter, the system will stop with an INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE error upon reboot.
Windows Server 2003 VDS support
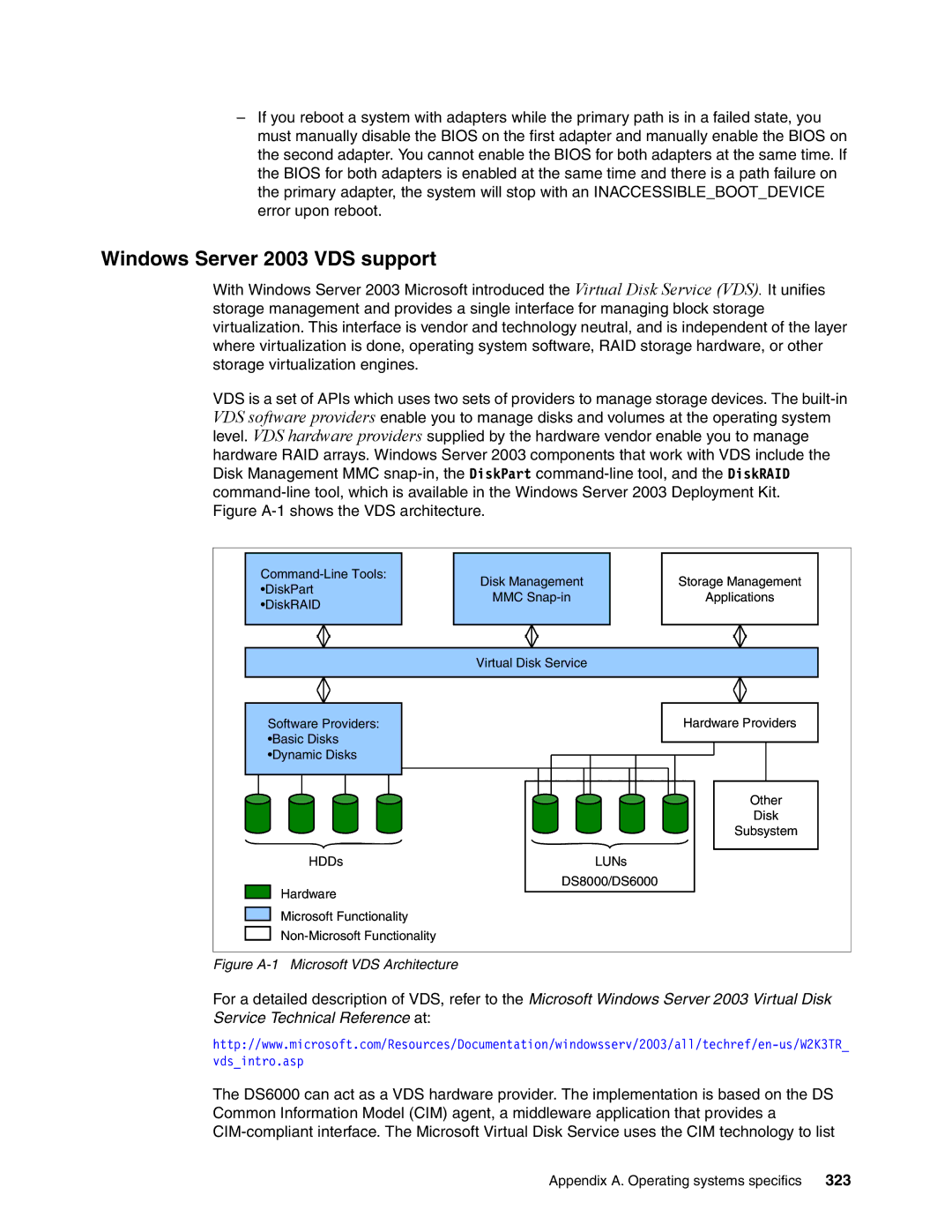
With Windows Server 2003 Microsoft introduced the Virtual Disk Service (VDS). It unifies storage management and provides a single interface for managing block storage virtualization. This interface is vendor and technology neutral, and is independent of the layer where virtualization is done, operating system software, RAID storage hardware, or other storage virtualization engines.
VDS is a set of APIs which uses two sets of providers to manage storage devices. The
hardware RAID arrays. Windows Server 2003 components that work with VDS include the Disk Management MMC
Disk Management | Storage Management | ||
•DiskPart | |||
MMC | Applications | ||
•DiskRAID | |||
|
| ||
| Virtual Disk Service |
| |
Software Providers: |
| Hardware Providers | |
•Basic Disks |
|
| |
•Dynamic Disks |
|
| |
|
| Other | |
|
| Disk | |
|
| Subsystem | |
HDDs |
| LUNs | |
Hardware | DS8000/DS6000 | ||
|
| ||
Microsoft Functionality |
|
| |
|
| ||
Figure A-1 Microsoft VDS Architecture
For a detailed description of VDS, refer to the Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Virtual Disk Service Technical Reference at:
The DS6000 can act as a VDS hardware provider. The implementation is based on the DS Common Information Model (CIM) agent, a middleware application that provides a
Appendix A. Operating systems specifics | 323 |