NVS
for odd
LSSs
Cache
memory for even LSSs
Controller 0
NVS
for even
LSSs
Cache
memory
for odd
LSSs
Controller 1
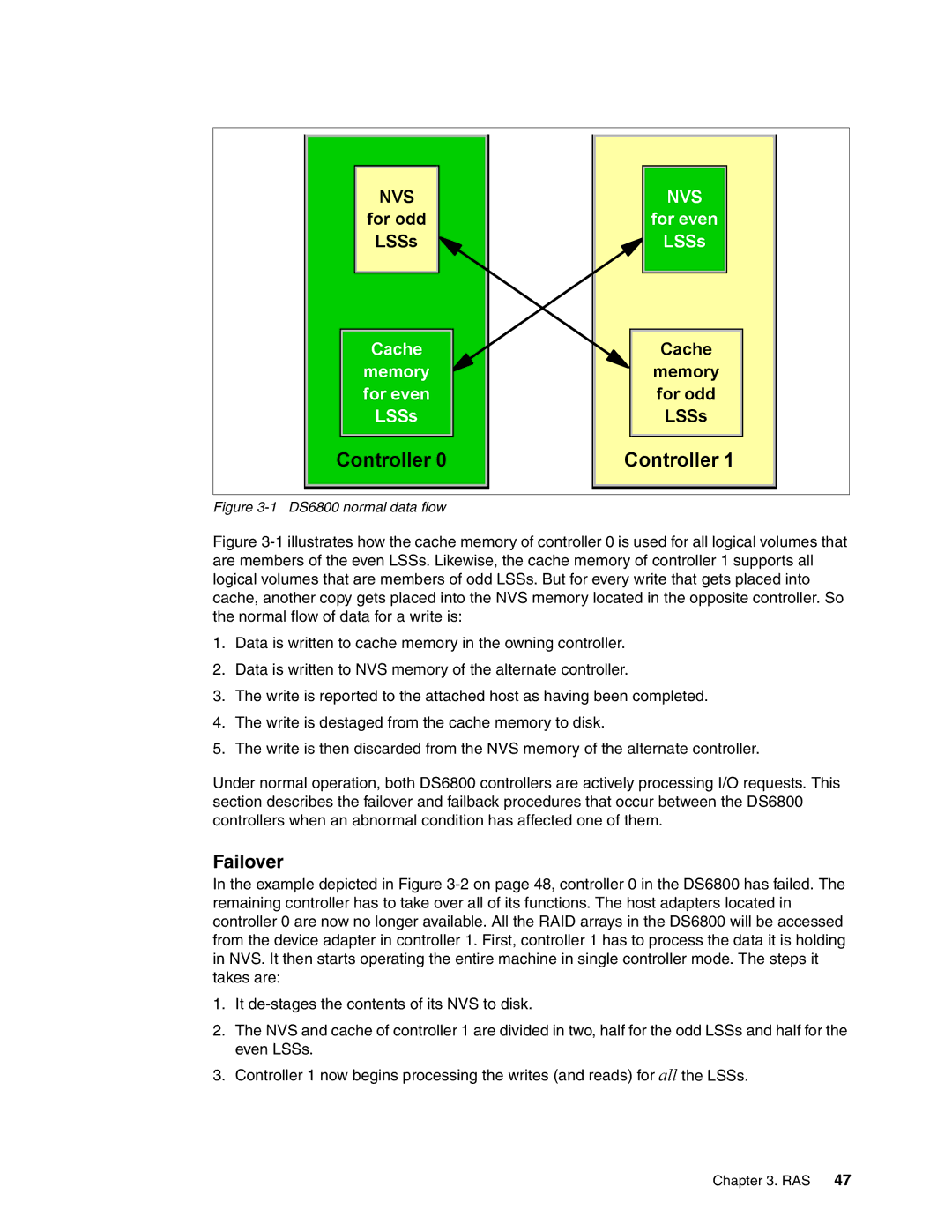
Figure 3-1 DS6800 normal data flow
Figure 3-1 illustrates how the cache memory of controller 0 is used for all logical volumes that are members of the even LSSs. Likewise, the cache memory of controller 1 supports all logical volumes that are members of odd LSSs. But for every write that gets placed into cache, another copy gets placed into the NVS memory located in the opposite controller. So the normal flow of data for a write is:
1.Data is written to cache memory in the owning controller.
2.Data is written to NVS memory of the alternate controller.
3.The write is reported to the attached host as having been completed.
4.The write is destaged from the cache memory to disk.
5.The write is then discarded from the NVS memory of the alternate controller.
Under normal operation, both DS6800 controllers are actively processing I/O requests. This section describes the failover and failback procedures that occur between the DS6800 controllers when an abnormal condition has affected one of them.
Failover
In the example depicted in Figure
1.It
2.The NVS and cache of controller 1 are divided in two, half for the odd LSSs and half for the even LSSs.
3.Controller 1 now begins processing the writes (and reads) for all the LSSs.
Chapter 3. RAS 47