February
Hardware Design Guidelines
HDD
Contents
12.1
Figures
Tables
Control Group Topology Transmission Line Characteristics
Date Revision Description
Revision History
HDD
Chapter Name Description
Content Overview
Title Document #
Related Documentation
List of Acronyms and Abbreviations
Overview
Term Explanation
Smii
Intel IXP465 Component Block Diagram
Dslam
Typical Applications
System Memory Map
System Architecture Description
Intel IXP465 Example System Block Diagram
Signal Type Definitions
Soft Fusible Features
Symbol Description
Soft Fusible Features
Signal Interface
DDR-266 Sdram Interface
DDR Sdram Interface Pin Description Sheet 1
Ddriwen
DDR Sdram Interface Pin Description Sheet 2
Ddrircveninn
Ddrircomp
DDR Sdram Memory Interface
Expansion Bus
DDR Sdram Initialization
Expansion Bus Signal Recommendations
Reset Configuration Straps
Input Pull Name Recommendations Output Down
Name Function Description
Boot/Reset Strapping Configuration Sheet 1
3 8-Bit Device Interface
Boot/Reset Strapping Configuration Sheet 2
4 16-Bit Device Interface
5 32-Bit Device Interface
Bit Device
16/32-Bit Device Interface Byte Enable
Flash Interface Example
Flash Interface
Sram Interface
Uart Interface
Design Notes
Name Input Pull Recommendations Output Down
Uart Signal Recommendations
Uart Interface Example
MII/SMII Interface
MII NPE a Signal Recommendations
Signal Interface MII
MII NPE B Signal Recommendations Sheet 1
MII NPE C Signal Recommendations
MII NPE B Signal Recommendations Sheet 2
Device Connection, MII
MAC Management Signal Recommendations NPE A,B,C
NPE A,B,C
Smii Signal Recommendations NPE A, B, C
Signal Interface, Smii
Device Connection, Smii
Gpio Interface
Gpio Signal Recommendations
I2C Interface
I2C Signal Recommendations
Device Connection
I2C Eeprom Interface Example
USB Interface
USB Host/Device Signal Recommendations
Host Device
USB Device Interface Example
Utopia Level 2 Interface
Utopia Signal Recommendations
Utopia Interface Example
HSS Interface
HSSTXDATA0
High-Speed, Serial Interface
HSSTXCLK0
HSSRXDATA0
HSSTXCLK1
HSSTXDATA1
HSSRXDATA1
HSSRXCLK1
HSS Interface Example
SSP Interface
Synchronous Serial Peripheral Port Interface
PCI Controller Sheet 1
PCI Interface
Input Pull Name Outpu Recommendations Down
PCI Controller Sheet 2
PCI Interface Block Diagram
PCI Interface
Supporting 5 V PCI Interface
PCI Host/Option Interface Pin Description Sheet 1
PCI Option Interface
PCI Host/Option Interface Pin Description Sheet 2
PCI Host/Option Interface Pin Description Sheet 3
Jtag Interface
Clock Signals
Clock Signals
Input System Clock
Clock Oscillator
Power Interface Sheet 1
Power
Name Nominal Description Voltage
Reset Timing
Power Sequence
De-Coupling Capacitance Recommendations
VCC De-Coupling
HDD
HDD
PCB Overview
Component Placement
General Recommendations
Component Selection
Stack-Up Selection
Component Placement on a PCB
Controlled-impedance traces Low-impedance power distribution
Layer Stackup
General Layout Guidelines
General Layout and Routing Guide
General Component Spacing
Signal Changing Reference Planes
Good Design Practice for VIA Hole Placement
Pad-to-Pad Clearance of Passive Components to a PGA or BGA
Clock Signal Considerations
MII Signal Considerations
Smii Signal Considerations
USB Considerations
EMI-Design Considerations
Cross-Talk
Trace Impedance
Power and Ground Plane
HDD
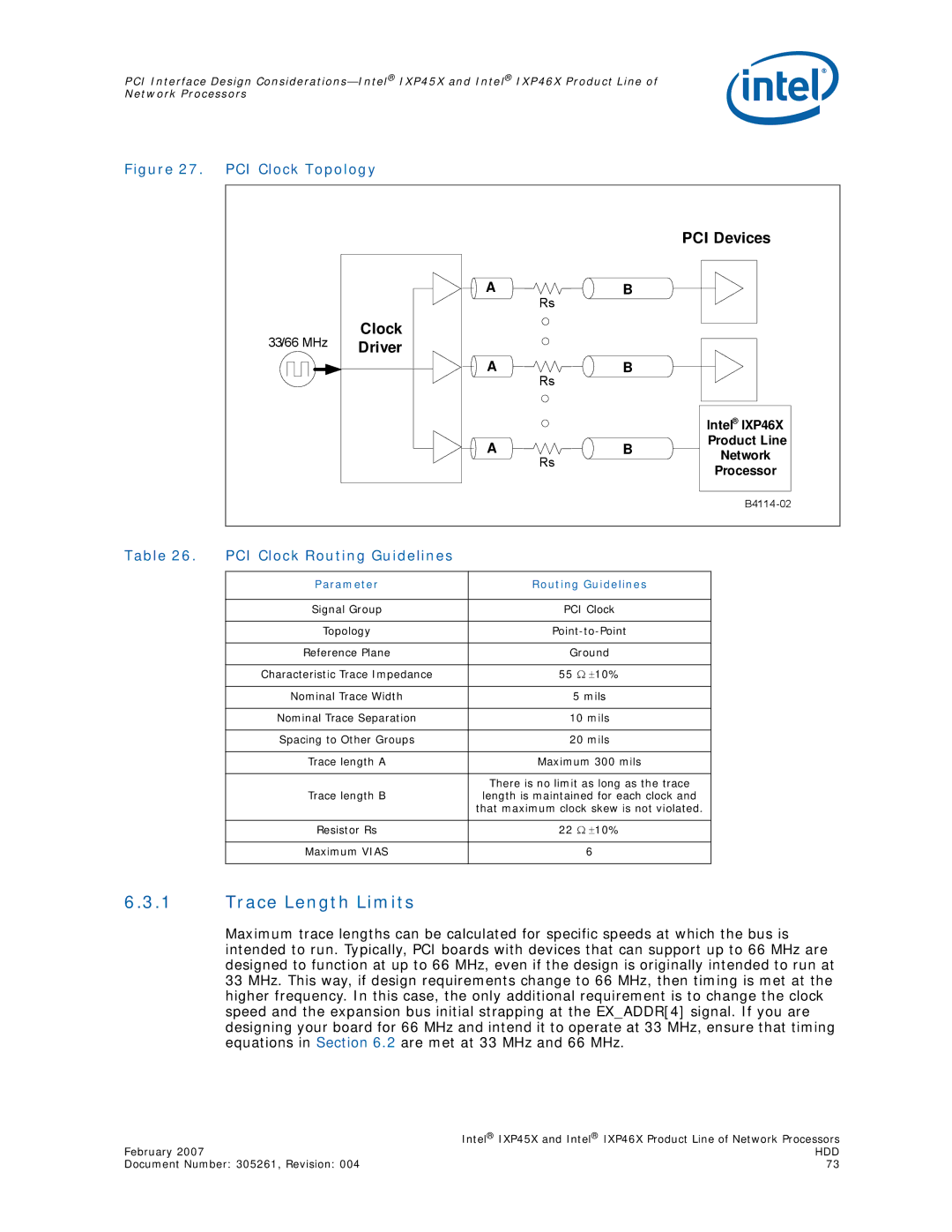
Topology
Electrical Interface
@33 MHz
@66 MHz
PCI Address/Data Routing Guidelines
Clock Distribution
Parameter Routing Guidelines
PCI Clock Routing Guidelines
Trace Length Limits
Routing Guidelines
Signal Loading
Group Signal Name Description No of Single Ended Signals
DDR Signal Groups
Introduction
DDRIDQS40
DDR Sdram
HDD
Clock Banks Memory Size
Supported Memory Configurations
VTT
VTT Terminating Circuitry
Selecting VTT Power Supply
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units
DDR Command and Control Setup and Hold Values
Ddrmclk
DDR Data to DQS Read Timing Parameters
DDR Data to DQS Write Timing Parameters
DDR-Data-to-DQS-Write Timing Parameters
Printed Circuit Board Layer Stackup
Printed Circuit Board Layer Stackup
Printed Circuit Board Controlled Impedance
Printed Circuit Board Controlled Impedance
Timing Relationships
Signal Group Absolute Minimum Absolute Maximum Length
Timing Relationships
Clock Group
Resistive Compensation Register Rcomp
Data, Command, and Control Group Routing Guidelines
Clock Signal Group Routing Guidelines
Parameter Definition
DDRIBA10, DDRIRASN, DDRICASN, Ddriwen
Simulation Results
Clock Group Topology Transmission Line Characteristics
Clock Group
Transmission Line Length
DDR Clock Topology Two-Bank x16 Devices
DDR Clock Simulation Results Two-Bank x16 Devices
Data Group
Data Group Topology Transmission Line Characteristics
DDR Data Topology Two-Bank x16 Devices
DDR Data Write Simulation Results Two-Bank x16 Devices
HDD
HDD
Control Group
Control Group Topology Transmission Line Characteristics
DDR RAS Simulation Results Two-Bank x16 Devices
Command Group Topology Transmission Line Characteristics
Command Group
DDR Command MA3 Topology Two-Bank x16 Devices
DDR Address Simulation Results Two-Bank x16 Devices
DDR Command RAS Topology Two-Bank x16 Devices
104
DDR RCVENIN/RCVENOUT Topology
Rcvenin and Rcvenout
DDR RCVENIN/RCVENOUT Simulation Results Rseries = 0 Ω
DDR RCVENIN/RCVENOUT Simulation Results Rseries = 60 Ω
108