Intel® IXP45X and Intel® IXP46X Product Line of Network
7.1.1Selecting VTT Power Supply
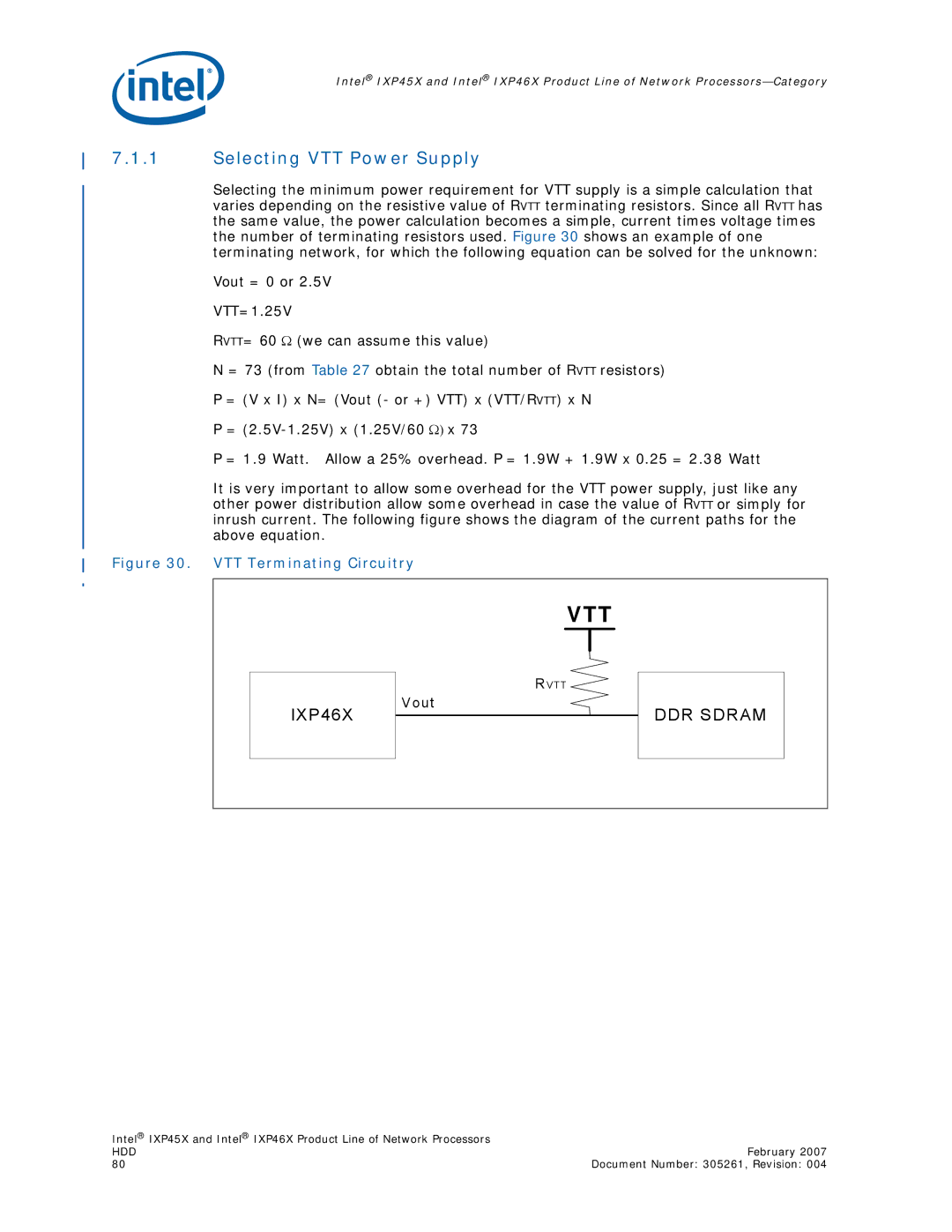
Selecting the minimum power requirement for VTT supply is a simple calculation that varies depending on the resistive value of RVTT terminating resistors. Since all RVTT has the same value, the power calculation becomes a simple, current times voltage times the number of terminating resistors used. Figure 30 shows an example of one terminating network, for which the following equation can be solved for the unknown:
Vout = 0 or 2.5V
VTT=1.25V
RVTT= 60 Ω (we can assume this value)
N = 73 (from Table 27 obtain the total number of RVTT resistors)
P = (V x I) x N= (Vout (- or +) VTT) x (VTT/RVTT) x N
P =
P = 1.9 Watt. Allow a 25% overhead. P = 1.9W + 1.9W x 0.25 = 2.38 Watt
It is very important to allow some overhead for the VTT power supply, just like any other power distribution allow some overhead in case the value of RVTT or simply for inrush current. The following figure shows the diagram of the current paths for the above equation.
Figure 30. VTT Terminating Circuitry
|
| VTT |
|
| RVTT |
IXP46X | Vout | DDR SDRAM |
|
Intel® IXP45X and Intel® IXP46X Product Line of Network Processors |
|
HDD | February 2007 |
80 | Document Number: 305261, Revision: 004 |