RAID 50 – Striping of Distributed Parity
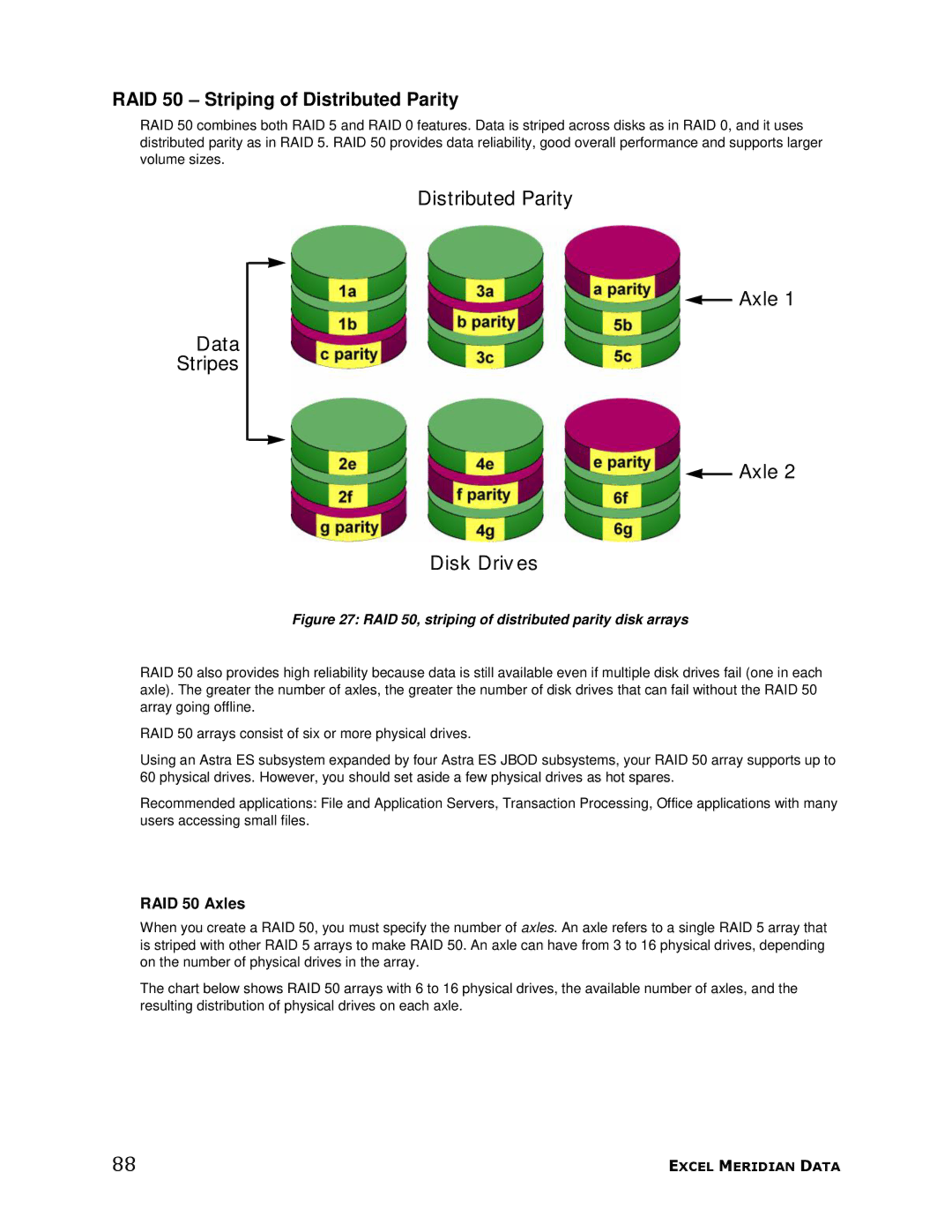
RAID 50 combines both RAID 5 and RAID 0 features. Data is striped across disks as in RAID 0, and it uses distributed parity as in RAID 5. RAID 50 provides data reliability, good overall performance and supports larger volume sizes.
Data Stripes
Distributed Parity
 Axle 1
Axle 1
![]() Axle 2
Axle 2
Disk Driv es
Figure 27: RAID 50, striping of distributed parity disk arrays
RAID 50 also provides high reliability because data is still available even if multiple disk drives fail (one in each axle). The greater the number of axles, the greater the number of disk drives that can fail without the RAID 50 array going offline.
RAID 50 arrays consist of six or more physical drives.
Using an Astra ES subsystem expanded by four Astra ES JBOD subsystems, your RAID 50 array supports up to 60 physical drives. However, you should set aside a few physical drives as hot spares.
Recommended applications: File and Application Servers, Transaction Processing, Office applications with many users accessing small files.
RAID 50 Axles
When you create a RAID 50, you must specify the number of axles. An axle refers to a single RAID 5 array that is striped with other RAID 5 arrays to make RAID 50. An axle can have from 3 to 16 physical drives, depending on the number of physical drives in the array.
The chart below shows RAID 50 arrays with 6 to 16 physical drives, the available number of axles, and the resulting distribution of physical drives on each axle.
88 | EXCEL MERIDIAN DATA |