WS5100 Series Switch
Motorola, Inc. All rights reserved
Contents
Switch Services
Network Setup
TOC-3
Switch Security
Diagnostics
Switch Management
TOC-5
TOC-6WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Document Conventions
Introduction
Documentation Set
Notational Conventions
Hardware Overview
Overview
System Status LED Codes
Physical Specifications
Power Cord Specifications
Power Protection
Standby
Error Codes
Start Up
Primary
Software Overview
Infrastructure Features
Switch includes the following Infrastructure features
Licensing Support
Installation Feature
Configuration Management
Text Based Configuration
Hardware Abstraction Layer and Drivers
Serviceability
Tracing / Logging
Process Monitor
Secure Network Time Protocol Sntp
Wireless Switching
Password Recovery
Switch includes the following wireless switching features
Rate Limiting
Physical Layer Features 802.11a
802.11bg
HotSpot / IP Redirect
Proxy-ARP
Currently voice support implies the following
IDM Identity Driven Management
Voice Prioritization
Self Healing
Self Healing Actions
Neighbor Configuration
Wireless Capacity
Detector APs
MU Balancing Across Multiple APs
AP Balancing Across Multiple Switches
Wireless Roaming
Fast Roaming
Interswitch Layer 2 Roaming
MU Move Command
L3 Roaming
802.1p Support
Power Save Polling
2.12 QoS
802.11e QoS
Automatic Channel Selection
Wireless Layer 2 Switching
Data QoS
Dcscp to AC Mapping
Ddns
Wired Switching
Switch includes the following wired switching features
Dhcp Servers
Interface Management
Management Features
WS5100 switch supports 32 Wlans
Vlan Enhancements
Switch includes the following wired security features
Security Features
Encryption and Authentication
802.1x EAP
MU Authentication
Keyguard-WEP
Kerberos
MU to MU Allow
Switch-to-Wired
5.7 802.1x Authentication
Secure Beacon
Ieee 802.1AB Lldp
Change Username/Password after AP Adoption
Reset Username/Password to Factory Defaults
Lldp is always enabled and cannot be disabled
Rogue AP Detection
RF scan by Access Port on all channels
Rogue AP Report
Snmp Trap on discovery
Authorized AP Lists
Certificate Management
Access Port Support
5.14 NAT
Web UI Requirements
Accessing the Switch Web UI
Content of this chapter is segregated amongst the following
Connecting to the Switch Web UI
Switch Web UI Access and Image Upgrades
Switch Password Recovery
Upgrading the Switch Image from 1.4.x or 2.x to Version
Upgrading the Switch Image
Auto Installation
Enables are set using the autoinstall feature command
Configuring Auto Install via the CLI
Whenever a string is blank it is shown as --not-set
Downgrading the Switch Image
AP-4131 Access Point to Access Port Conversion
Enables are cleared using the no autoinstall feature
Select the AP Installation main menu item
Select the Special Functions main menu item
10WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
It consists of the following two tabs
Viewing the Switch Interface
Viewing the Switch Configuration
System Name
Troubleshooting
Time Displays the time of day used by the switch Time Zone
Incorrectly could render your switch as operating illegally
Viewing Dashboard Details
Severity Last Occurrence Message # Occurrences
Speed
Viewing Switch Statistics
Name
Status
Associated Number of APs
Utilization issues negatively impacting performance
Avg Signal
Number of MUs
Viewing the Port Configuration
Viewing Switch Port Information
Duplex Displays the port as either half or full duplex
Editing the Port Configuration
Modified
Viewing the Ports Runtime Status
Oper Status
Ethernet ports have a maximum MTU setting
Viewing the Ports Statistics
Name Displays the ports current name MAC Address
Different port could be required
Packets In Error
Indication of a network problem
Network issues
Detailed Port Statistics
With interface is saturated
Viewing the Port Statistics Graph
Output Unicast
Output Packets
Switch Information
Size Bytes
Viewing Switch Configurations
Viewing the Detailed Contents of a Config File
Main screen displays the contents of the configuration file
Editing a Config File
Transferring a Config File
Path
Viewing Switch Firmware Information
Password
Editing the Switch Firmware
Enabling Global Settings for the Failover Image
If using TFTP, use tftp//ipaddress/path/filename
Updating the Switch Firmware
Boot of the switch
Configuring Automatic Updates
Enable
Protocol
Setting
Password Enter the password required to access the server
File Name With
Index
Viewing the Switch Alarm Log
View By
View All
Viewing Alarm Log Details
Possible Causes
Viewing Switch Licenses
Solution
Description
How to use the Filter Option
30WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Displaying the Network Interface
Network Setup
DNS Servers
Resolution Entries
Switch Virtual
Wireless LANs
Select the Domain Network System tab
Configuring DNS
Access Ports
Viewing Network IP Information
Server IP Address
Configuring Global Settings
Adding an IP Address for a DNS Server
Obsolete addresses are periodically removed
Configuring IP Forwarding
Following details display in the table
Active
Adding a New Static Route
Route Metric
Type
Viewing Address Resolution
Select the Address Resolution tab
Typically a Vlan
Viewing and Configuring Layer 2 Virtual LANs
Trunk
Mode It can be either Access or Trunk
Ethernet 1 or ethernet
Is selected, the Allowed VLANs field is unavailable
Editing the Details of an Existing Vlan
Mode drop-down menu
Configuring Switch Virtual Interfaces
Configuring the Virtual Interface
Up or not Down
Following configuration details display in the table
Name Displays the name of the virtual interface
Displays the Vlan ID associated with the interface
To modify an existing virtual interface
Adding a Virtual Interface
Modifying a Virtual Interface
To add a new virtual interface
Viewing Virtual Interface Statistics
Packets, etc
Viewing Virtual Interface Statistics
Only hard-coded at the factory and cannot be modified
Viewing the Virtual Interface Statistics Graph
Click Close to close the dialog
Viewing and Configuring Switch WLANs
Configuring WLANs
Modify the WLAN’s current authentication scheme
Enabled
4094. The default Vlan ID is
Authentication
Editing the Wlan Configuration
Intended function of the Wlan
Value used is unique
Kerberos
No Authentication
Tunnel
802.1X EAP
Refer to the Advanced field for the following information
Configuring 802.1x EAP
Configuring Authentication Types
MU Max Retries
Configuring Kerboros
MU Timeout
28WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Switch Hotspot Redirection
Configuring Hotspots
Configuring an Internal Hotspot
Small Logo URL
Title Text
Header Text
Footer Text
Descriptive Text
Configuring External Hotspot
Main Logo URL
Failed Page URL
Login Page URL
Need to provide correct login information to access the Web
34WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Configuring Advanced Hotspot
Network Setup
Configuring External Radius Server Support
Configuring Dynamic MAC ACL
Radius Server
Address Authentication data source Radius Port
Authentication data source. The default port is
Secret Secondary Radius server Server Timeout
Motorola user privilege values User login source
Configuring the User Login Sources
Configuring Different Encryption Types
Configuring WEP
Key 1011121314 2021222324 3031323334 4041424344
Configuring WEP 128 / KeyGuard
Key
Default hexadecimal keys for WEP 128 and KeyGuard include
Use the Key #1-4areas to specify key numbers
Configuring WPA/WPA2 using Tkip and Ccmp
Bit Key
Ascii Passphrase
From entering the 256-bit key each time keys are generated
Opportunistic Key
Pre-Authentication
Viewing Wlan Statistics
PMK Caching
Last Hr
That may have similar characteristics
Ssid is the Service Set ID Ssid for the selected Wlan
Last 30s
Viewing Wlan Statistics in Detail
Refer to the RF Status field for the following information
Viewing Wlan Statistics in a Graphical Format
Refer to the Errors field for the following information
50WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Viewing Wlan Switch Statistics
Click the VLAN/Tunnel Assignment tab
Edit button on the Configuration tab within the WLANs
Viewing VLAN/Tunnel Assignments
Configuring WMM
Background Optimized for background traffic
WMM enabled
Access
Four Access Category types are
Generic QoS GQoS application programming interface API
Access Category to
Category Network traffic Dscp to Access
Category Network traffic
Read-only and cannot be modified within this screen
Editing WMM Settings
CW Maximum
Viewing Associated MU Details
Viewing MU Status
CW Minimum
Interoperating with
Power Save
This address is burned into the ROM of the MU
Ready
Displays of the Wlan the MU is currently associated with
Similar configurations
Viewing MU Details
Viewing MU Statistics
Address is hard coded at the factory and cannot be modified
Configuration
Selected MU from the access port
Possible network or hardware problems
Viewing MU Statistics in Detail
Hard-coded at the factory and cannot be modified
Refer to the Traffic field for the following information
View a MU Statistics Graph
Viewing Access Port Information
Name Displays a user assigned name for the radio
Configuring Access Port Radios
Access Ports screen consists of the following tabs
Refer to the Properties field for the following
Configuring Layer 3 Access Port Adoption on
Configuring an AP’s Global Settings
Click the Configure Port Authentication button
Port Authentication
Editing AP Settings
Network Setup
MUs that can associate to a radio is
Maximum MUs
Beacon Interval
RTS Threshold
Dtim Periods
Configuring Rate Settings
Self Healing Offset
Adding APs
Viewing AP Statistics
RF Util
Differentiate the radio from other device radios
Average Mbps
Packets that are sent and received
Viewing AP Statistics in Detail
Was encountered on the configured channel
Statistic for the last hour
Viewing AP Statistics in Graphical Format
Click the Wlan Assignment tab
Configuring Wlan Assignment
Its intended coverage area or function
Configurations
Editing a Wlan Assignment
Identifier such as 1/4, 1/3, etc
From the description field in the Radio Configuration screen
Editing WMM Settings
To view existing Radio Configuration information
Viewing Access Port Adoption Defaults
Configuring AP Adoption Defaults
Defaults are 20 dBM for 802.11bg and 17 dBm for 802.11a
Options include Indoor or Outdoor. Default is Indoor
Channel. Default is random
Power dBm
Editing Default Radio Adoption Settings
Stations that can associate to a radio are
Dtim Period
Transmission path
Configuring Rate Settings
Configuring Layer 3 Access Port Adoption
Select/Change Assigned WLANs
Assigned WLANs tab displays two fields Select Radios/BSS
Cannot be modified
Access Category reflects the radios intended network traffic
Higher priority traffic
Editing Access Port Adoption WMM Settings
To edit the existing WMM settings
Viewing Adopted Access Ports
Viewing Access Port Status
Viewing Unadopted Access Ports
Unadopted AP tab displays the following information
Network Setup
96WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Switch Services
NTP Time
Displaying the Services Interface
To display a Services Summary
Dhcp Servers
For information on configuring GRE tunneling, see
Dhcp Server Settings
Configuring the Switch Dhcp Server
Pool Name
Domain
Editing the Properties of an Existing Dhcp Pool
Lease Time
Ddhhmm
Adding a New Dhcp Pool
Click the Add button at the bottom of the screen
Configuring Dhcp Global Options
Configuring Dhcp Server Ddns Values
10WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Client Name
Viewing the Attributes of Existing Host Pools
Can be assigned
Hardware Address
Configuring Excluded IP Address Information
Configuring Dhcp Server Relay Information
14WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Viewing Dhcp Server Status
Refer to the contents of the Status tab for the following
Configuring Secure NTP
Defining the Sntp Configuration
Refer to the Other Settings field to define the following
Adding a New Sntp Symmetric Key
Defining a Sntp Neighbor Configuration
Neighbor Type
When adding or editing an NTP neighbor
Hostname
Support
Adding an NTP Neighbor
Viewing Sntp Associations
Select the NTP Associations tab
Found in some workstations
Viewing Sntp Status
Leap
Transmissions are synchronized
Root Dispersion
Configuring Switch Redundancy
Root delay
26WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Discovery Period
Redundancy Switch
Redundancy ID
Mode
Reviewing Redundancy Status
Redundancy Group License Aggregation Rules on
Configuring Redundancy Group Membership
Values
Do not match this switch’s parameters
Not Seen The member is no more seen by this switch
Module
Displaying Redundancy Member Details
Adoption Capacity
Complimentary with this switch’s version?
Updates Sent
Updates Received
Adding a Redundancy Group Member
Redundancy Group License Aggregation Rules
Layer 3 Mobility
Configuring Layer 3 Mobility
36WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Switch Services
Defining the Layer 3 Peer List
Select the Peer Statistics tab
Reviewing Layer 3 Peer List Statistics
Reviewing Layer 3 MU Status
Configuring GRE Tunnels
Assigning priority to different types of traffic
Destinations IP
To configure GRE tunnelling on the switch
Source IP
Interface IP
Disabled
Editing the Properties of a GRE Tunnel
Adding a New GRE Tunnel
Select the Enable Neighbor Recovery checkbox
Configuring Self Healing
Select the Neighbor Details tab
Configuring Self Healing Neighbor Details
Editing the Properties of a Neighbor
Switch Services
Configuring Discovery Profiles
Configuring Switch Discovery
Network devices is conducted
Profile Name
To be located
Start IP Address
Adding a New Discovery Profile
Viewing Discovered Switches
New search
Assigned using the Switch Configuration screen
Different profile for the switch discovery process
Discovery profile and launching a new search
Displaying the Main Security Interface
Switch Security
Trustpoints
Wireless Filters
Detection
Certificates
AP Intrusion Detection
Enabling and Configuring AP Detection
To configure AP Detection
BSS MAC Address
Timeout
Unapproved AP
Refresh Time
Address Particular index
Adding or Editing an Allowed AP
Any MAC Address
Specific MAC
To review the attributes of allowed APs
Approved APs Reported by APs
Dbm
Unapproved APs Reported by APs
Therefore interpreted as a threat on the network
Address to a new Allowed AP index
Essid to a new Allowed AP index
Unapproved APs Reported by MUs
Seconds Detecting AP
As a threat
Configuring MU Intrusion Detection
To configure MU intrusion detection
MU Intrusion Detection
Mobile Unit
Switch columns
Contents of the MUs that have been filtered thus far
Violation Type
Identifier
Click on Revert to rollback to the previous configuration
Viewing Filtered MUs
Configuring Wireless Filters
Refer to the Associated WLANs field for following
Filters field contains the following read-only information
Editing an Existing Wireless Filter
Enter the a hex value for the Starting MAC address
Adding a new Wireless Filter
Associating an ACL with Wlan
Configuring ACLs
For more information, see
Switch supports the following ACLs to filter traffic
ACL Overview
Router ACLs
Port ACLs
Precedence Order
Wireless LAN ACLs
ACL Actions
Adding a New ACL
Configuring an ACL
Adding a New ACL Rule
22WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Editing an Existing Rule
Eth2
Adding a New ACL Configuration
Attaching an ACL
Eth1
Click on the Attach tab Click on the Add button
Attaching an ACL on a Wlan Interface/Port
Direction
Adding a New ACL Wlan Configuration
Displays the IP ACL configured
Displays the MAC ACL configured
Reviewing ACL Statistics
Click on the Dynamic Translation tab
Configuring NAT Information
Defining Dynamic NAT Translations
Type Displays the NAT type as either
Anywhere on the Internet
LAN over the switch managed network
Access List
Adding a New Dynamic NAT Configuration
Click the Static Translation tab
Defining Static NAT Translations
Click on the Static Translation tab
Adding a New Static NAT Configuration
Switch Security
Available from the drop-down menu for use as the interface
Configuring NAT Interfaces
Viewing NAT Status
Inside Local
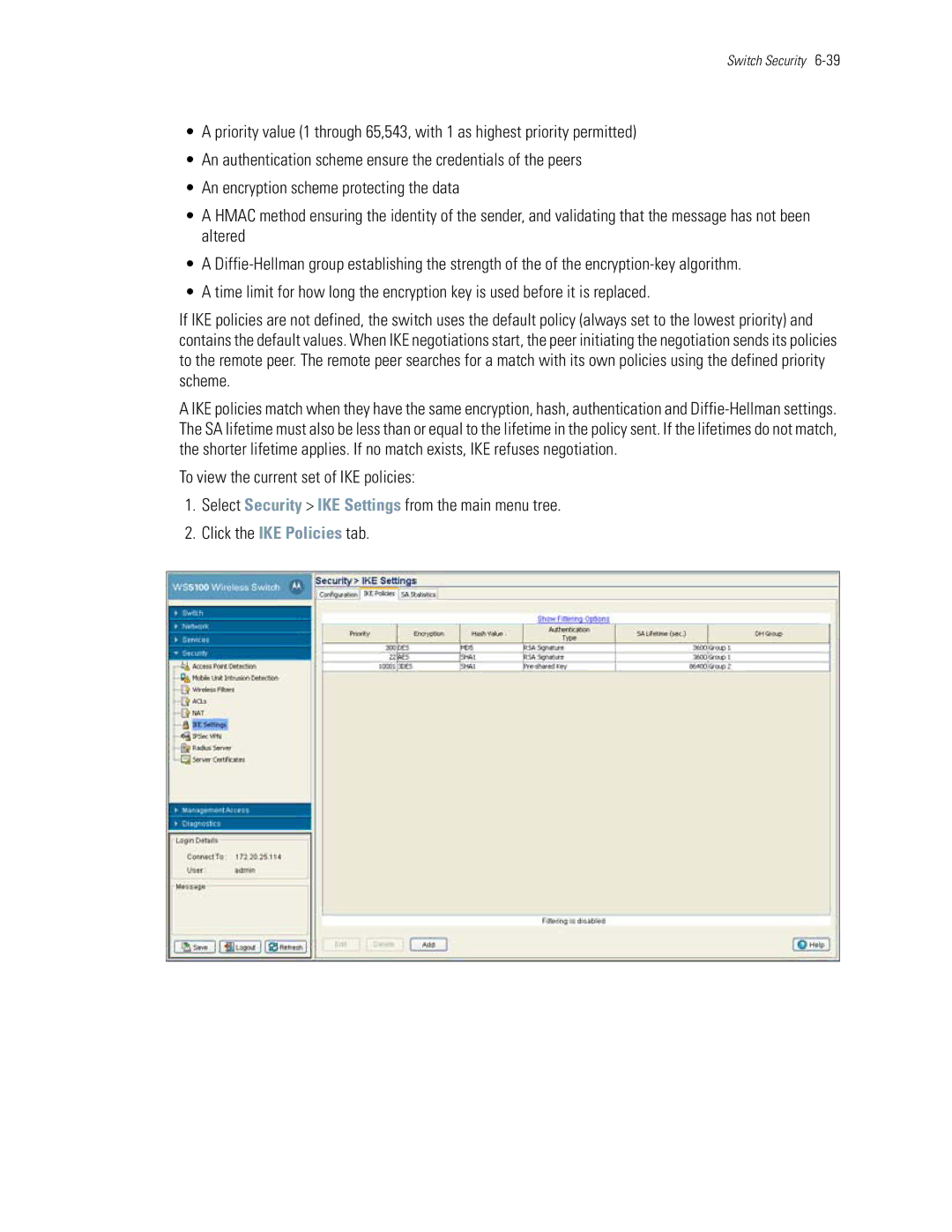
Configuring IKE Settings
Inside-Global
World
Click the Configurations tab
Defining the IKE Configuration
Peers
Setting IKE Policies
Aggressive Mode
Peer IP Address
Switch Security
Highest priority value
SHA The default value
Default value
Priority
Secret without transmitting it to one another
Include
Options include
Viewing SA Statistics
Configure a Dhcp Sever to give public IP address
Configuring IPSec VPN
Configure security associations parameters
Defining the IPSec Configuration
Transport
Editing an Existing Transform Set
Tunnel or Transport
AH Authentication
Adding a New Transform Set
ESP Encryption
Scheme Include None No AH authentication is used
Click the IP Range tab to view the following information
Defining the IPSec VPN Remote Configuration
Configuring Ipsec VPN Authentication
Shared Secret
Click the Authentication tab
Default port is
Port
Configuring Crypto Maps
Priority / Seq
Crypto Map Entries
Click the Crypto Maps tab and select Crypto Map Entries
ACL ID
Mode Config
Crypto Map Peers
Peer Name
Click the Crypto Maps tab and select Peers
Priority / Seq #
Higher the priority
Set for protecting the data flow
Crypto Map Manual SAs
Transform Set
Crypto Map Transform Sets
Protecting the data flow
Crypto Map Interfaces
Viewing IPSec Security Associations
Index from others with similar configurations
TLS and MD5 Ttls and PAP
Configuring the Radius Server
Setting up Radius on the switch entails the following
Radius Overview
Ttls and MSCHAPv2 Peap and GTC Peap and MSCHAPv2
User Database
Using the Switch’s Radius Server Versus an External Radius
Defining the Radius Configuration
Radius Proxy Server Configuration
Radius Client Configuration
Configuring Radius Authentication and Accounting
EAP and Auth Type Specify the EAP type for the Radius server
Activity is detected
Configuring Radius Users
Cert Trustpoint
CA Cert Trustpoint
Their Radius privileges expire
User
Guest User
Configuring Radius User Groups
Guest Group
Select the Groups tab
Available WLANs
Configured WLANs
Time of access
Viewing Radius Accounting Logs
Size
Creating Server Certificates
Select the Accounting Logs tab
Automatically once they reach their limit
Within the State/Prov stated
Using Trustpoints to Configure Certificates
Certificate was issued
City L
Creating a Server / CA Root Certificate
Key for you new certificate
Using the Wizard to Create a New Certificate
78WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Organization Unit
City
Organization
Requests
Using the Wizard Delete Operation
To use the wizard to delete trustpoint properties
Click the Next button to complete the trustpoint removal
Configuring Trustpoint Associated Keys
Key Label
Adding a New Key
Select the Keys tab Keys tab displays the following
Transferring Keys
84WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Displaying the Management Access Interface
Switch Management
Log Output
Configuring Access Control
To configure access control settings on the switch
Enable Snmp Retries
Enable Telnet
Network. This setting is enabled by default
Long as the Enable Telnet option remains enabled
360 is associated with the SSH-Server
Configuring Snmp Access
Community Name
Configuring Snmp v1/v2 Access
Access Control
Editing an Existing Snmp v1/v2 Community Name
Configuring Snmp v3 Access
User Name
Unique SNMPv3 usernames and passwords include
Select Management Access Snmp Access from the main menu tree
Editing a Snmp v3 Authentication and Privacy Password
V2/V3 Metrics
Accessing Snmp v2/v3 Statistics
Read-Only errors
Usm Statistics Values
To configure Snmp trap definitions
Configuring Snmp Traps
Enabling Trap Configuration
Mobility
Wireless
Redundancy
Miscellaneous
Generation
Configuring Trap Thresholds
To configure Snmp trap threshold values
Threshold Name
14WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Radio Range Wlan Range Wireless Units
Wireless Trap Threshold Values
To configure the attributes of Snmp trap receivers
Configuring Snmp Trap Receivers
To add a new Snmp trap receiver
Editing Snmp Trap Receivers
Adding Snmp Trap Receivers
Configuring Local Users
Configuring Management Users
Creating a New Local User
Modifying an Existing Local User
Provides read-only permissions
Redundancy/clustering and control access
Creating a Guest Admin and Guest User
Assign the guest-admin WebUser Administrator access
Configuring Switch Authentication
Assignment is from 1
Not a DNS name
Modify the following Radius Server attributes as necessary
Modifying the Properties of an Existing Radius Server
Session. The available range is between 0
Adding a New Radius Server
Address Not a DNS name Radius Server Port
Is from 1
Switch Management
28WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Displaying the Main Diagnostic Interface
Diagnostics
Switch Environment
CPU Performance
Usage
Switch Memory Allocation
Switch Disk Allocation
Buffer
Switch Memory Processes
Other Switch Resources
Select the Other Resources tab
Configuring System Logging
Log Options
8WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
Date
File Management
Log level
Made, they have been accounted for
Viewing the Entire Contents of Individual Log Files
Transferring Log Files
Reviewing Core Snapshots
File extension is always .core for core files
Troubleshooting issues
Transferring Core Snapshots
Select a target file, and select the Transfer Files button
Reviewing Panic Snapshots
Panic actually occurred
Remaining nine are renamed so the newest can be saved as
Size Displays the size of the panic file in bytes Created
Transferring Panic Files
Viewing Panic Details
Debugging the Applet
Select Diagnostics Applet Debugging from the main menu
Configuring a Ping
New ping test is required
Timeout sec
Not received by the switch from its target device
Time between the switch and its connected device
Adding a New Ping Test
Modifying the Configuration of an Existing Ping Test
Timeoutsec
Test description to convey the overall function of the test
Within the Configuration tab
Between the switch and its connected device
Test Name
Viewing Ping Statistics
Last Response
Average RTT
24WS5100 Series Switch System Reference Guide
General Information
Motorola’s Enterprise Mobility Support Center
Customer Support Web Site
2WS5100 Series System Reference Guide
Page
Motorola INC