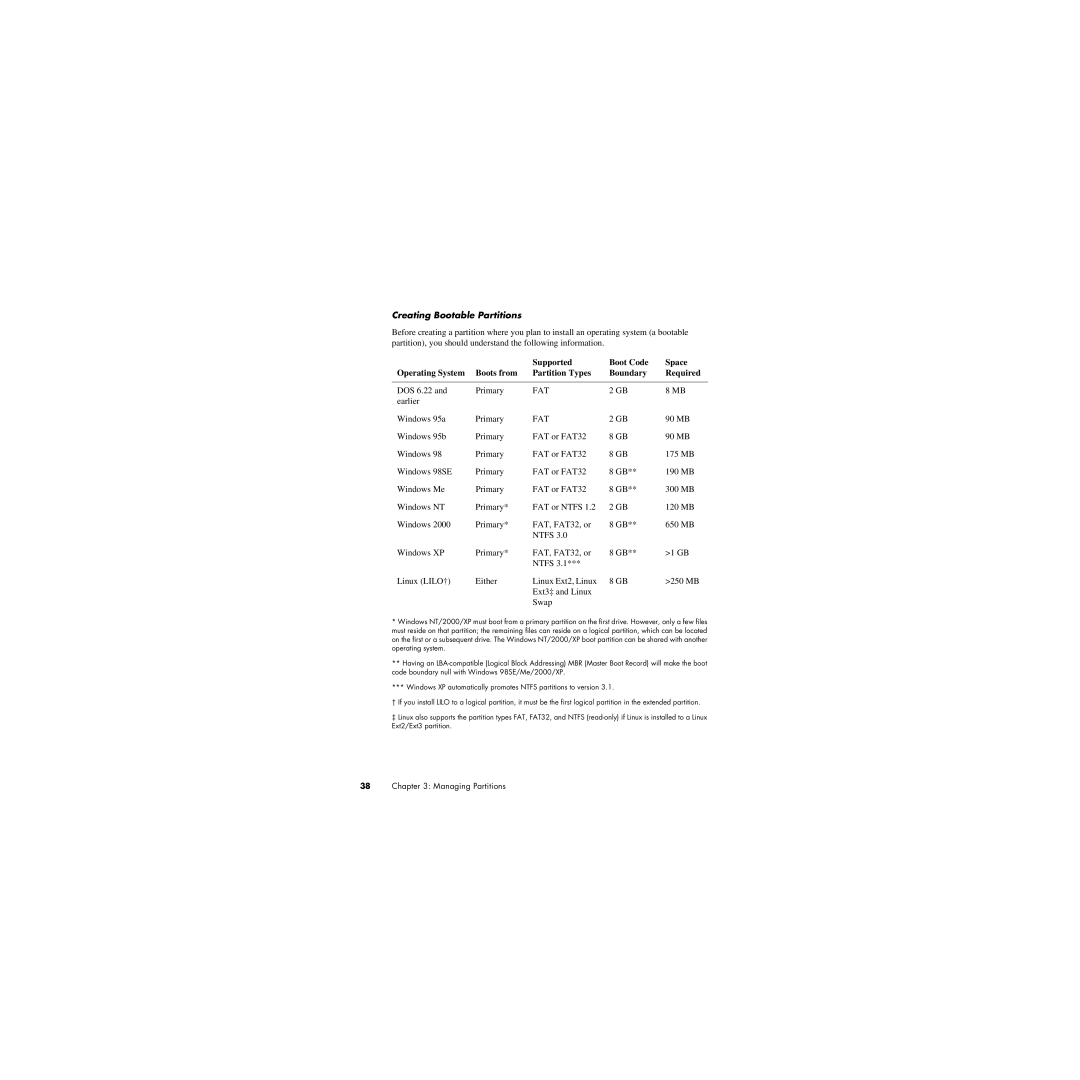
Creating Bootable Partitions
Before creating a partition where you plan to install an operating system (a bootable partition), you should understand the following information.
|
| Supported | Boot Code | Space |
Operating System | Boots from | Partition Types | Boundary | Required |
|
|
|
|
|
DOS 6.22 and | Primary | FAT | 2 GB | 8 MB |
earlier |
|
|
|
|
Windows 95a | Primary | FAT | 2 GB | 90 MB |
Windows 95b | Primary | FAT or FAT32 | 8 GB | 90 MB |
Windows 98 | Primary | FAT or FAT32 | 8 GB | 175 MB |
Windows 98SE | Primary | FAT or FAT32 | 8 GB** | 190 MB |
Windows Me | Primary | FAT or FAT32 | 8 GB** | 300 MB |
Windows NT | Primary* | FAT or NTFS 1.2 | 2 GB | 120 MB |
Windows 2000 | Primary* | FAT, FAT32, or | 8 GB** | 650 MB |
|
| NTFS 3.0 |
|
|
Windows XP | Primary* | FAT, FAT32, or | 8 GB** | >1 GB |
|
| NTFS 3.1*** |
|
|
Linux (LILO†) | Either | Linux Ext2, Linux | 8 GB | >250 MB |
|
| Ext3‡ and Linux |
|
|
|
| Swap |
|
|
*Windows NT/2000/XP must boot from a primary partition on the first drive. However, only a few files must reside on that partition; the remaining files can reside on a logical partition, which can be located on the first or a subsequent drive. The Windows NT/2000/XP boot partition can be shared with another operating system.
**Having an
***Windows XP automatically promotes NTFS partitions to version 3.1.
† If you install LILO to a logical partition, it must be the first logical partition in the extended partition.
‡Linux also supports the partition types FAT, FAT32, and NTFS