It is not recommended that you use the smallest cluster size on partitions containing a single, large file, such as a database or swap file.
Choosing a smaller cluster size may resize the partition smaller, creating unallocated space next to the partition. You can use this unallocated space to create a new partition.
FAT16 partitions are resized automatically to fit the cluster size.
WARNING! Do not choose the 64 K cluster size unless you have Windows NT, Windows 2000, or Windows XP. Partitions of this type are incompatible with Windows 9x and DOS.
4Click OK.
Default Cluster Sizes
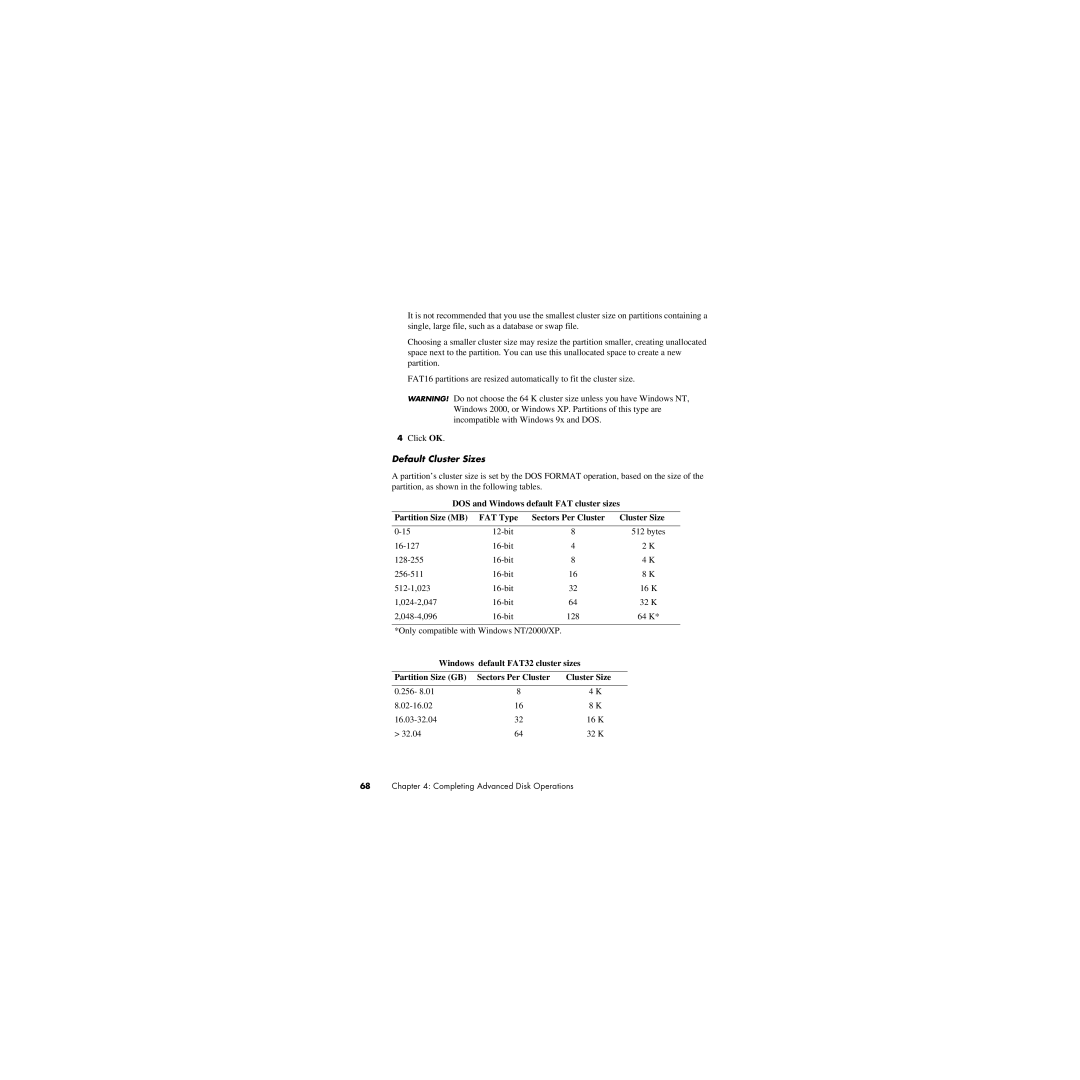
A partition’s cluster size is set by the DOS FORMAT operation, based on the size of the partition, as shown in the following tables.
DOS and Windows default FAT cluster sizes
Partition Size (MB) | FAT Type Sectors Per Cluster | Cluster Size | |||
|
|
|
|
| |
8 |
| 512 bytes | |||
4 | 2 | K | |||
8 | 4 | K | |||
16 | 8 | K | |||
32 |
| 16 K | |||
64 |
| 32 K | |||
128 | 64 | K* | |||
|
|
|
|
| |
*Only compatible with Windows NT/2000/XP. |
|
|
|
| |
Windows default FAT32 cluster sizes |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Partition Size (GB) | Sectors Per Cluster | Cluster Size |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.256- 8.01 | 8 | 4 K |
|
|
|
16 | 8 K |
|
|
| |
32 | 16 K |
|
|
| |
> 32.04 | 64 | 32 K |
|
|
|
68Chapter 4: Completing Advanced Disk Operations