Agilent Technologies. All rights reserved
Agilent Technologies 16760A Logic Analyzer
Sampling Mode on
Captures input signals as low as 200 mV p-p
Agilent Technologies 16760A Logic Analyzer
Probing
Concepts on
Reference on
Glossary see
See Also
Contents
Choosing the Sampling Mode
110
Using Symbols 101
112
114
152
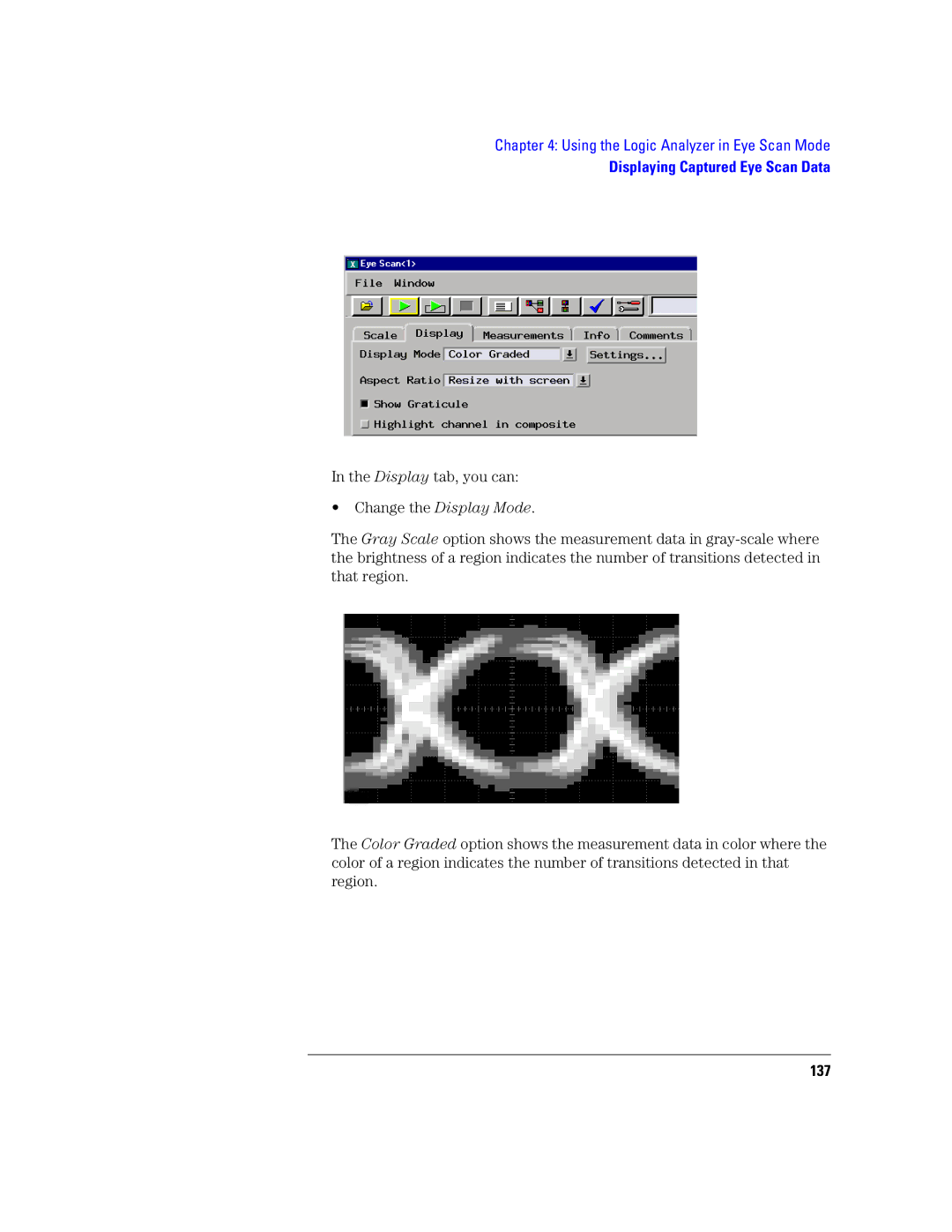
Displaying Captured Eye Scan Data
155
Format Tab 174
211
Eye Scan Tab 204
210
259
Specifications and Characteristics
240
Glossary Index
Contents
Getting Started
Eye scan sampling mode, measurements will have these steps
Connect logic analyzer to the device under test
Probing and Sampling Mode Selection Steps
Next . Choose the sampling mode on
To choose the sampling mode
Choose the sampling mode
If you chose State Mode
If you chose Timing Mode
If you chose Eye Scan Mode
Next . Format labels for the probed signals on
Either Timing Mode or State Mode
Format labels for the probed signals
To specify threshold voltages
To assign pods to the logic analyzer
To assign names to logic analyzer channels
Next
Defined threshold voltage Select the Close button
Define the trigger condition
Timing Mode or State Mode Steps
Next . Run the measurement on
Run the measurement
To open Waveform or Listing displays
Display the captured data
Next . Display the captured data on
To add display tools via the Workspace window
Next For More Information... on
Select channels for the eye scan measurement
Eye Scan Mode Steps
Next . Set the eye scan range and resolution on
Set the eye scan range and resolution
Next . Run the eye scan measurement on
Run the eye scan measurement
Next . Display the captured eye scan data on
Display the captured eye scan data
Eye Scan display window, use the following subtabs
For More Information
For More Information
Probing and Selecting the Sampling Mode
Probing and Selecting the Sampling Mode
Probing the Device Under Test
Using the E5378A Single-Ended Probe
Number
Single-ended signal
Numbers
Either
Using the E5379A Differential Probe
Independent threshold adjustment
Or single-ended signals
Negative data inputs
Reference voltage
Or AMP
Using the E5380A Mictor-Compatible Probe
Using the E5382A Single-ended Flying Lead Probe Set
Additional Accessories
Using an Analysis Probe
Probing the Device Under Test
Selecting the Timing Mode Asynchronous Sampling
Choosing the Sampling Mode
To select the conventional/transitional configuration
To select the timing mode
Sample rate is the inverse of the sample period
To specify the sample period
State Mode Sampling Position
Selecting the State Mode Synchronous Sampling
To automatically adjust sampling positions on
To manually adjust sampling positions on
To select the state speed configuration
To select the state mode
For the clock input signal that will be used
To set up the sampling clock
Run simultaneously
To automatically adjust sampling positions
Automatically sets the sampling position
To run eye finder repetitively
Choose the labels that you wish to run eye finder on
To save/load eye finder data
To view eye finder data as a bus composite
To view eye finder data as a stack of channels
Eye finder data must be saved and loaded separately
To manually adjust sampling positions
Eye Finder Advanced Settings Dialog on
To set acquisition memory depth
Either Timing Mode or State Mode
To specify the trigger position
To turn an analyzer off or on
To name an analyzer
You can give more descriptive names to a logic analyzer
You can also name analyzers in the Pod Assignment Dialog on
To select the eye scan mode
Selecting the Eye Scan Mode
To select the eye scan mode speed configuration
High-speed or high-bandwidth oscilloscope
To set up the eye scan mode reference clock
To assign pods to the analyzer
Format tab has activity indicators that show signal levels
Formatting Labels for Logic Analyzer Probes
To set pod threshold voltages
Capturing Data on 17 Channels in State Mode
To set up qualified eye scan measurements on
To set clock threshold voltages
To assign probe channels to labels
To delete labels
Maximum of 32 channels can be assigned to a label
Label off
To import label names and assignments from a netlist
Signals
E5378A and E5380A probe types to be selectable
Label
Label Definition File Format Examples
To import label definitions from an Ascii file
To assign label name Blue to channel 5 on pod A2
Channel 5 on pod A2, and channel 6 on pod A1
To export label definitions to an Ascii file
To change the label polarity
Changing the label polarity does not affect
To reorder bits in a label
Changing the label polarity will have the following effects
To turn a label off
To turn labels off or on
To turn a label on
To display a label that was off
Using the Logic Analyzer in Timing or State Mode
Using the Logic Analyzer in Timing or State Mode
General
Setting Up Triggers and Running Measurements
Use trigger functions for basic measurements
To select a trigger function
Using Trigger Functions
To specify a label pattern event Timing only
To specify a label edge event
To enter symbolic label values on Symbols Selector Dialog on
To compress a trigger function
To expand a trigger function
To copy trigger function libraries between systems
To load/unload trigger function libraries
To count time, states, or turn counting off
Using Other Trigger Features
To assign pods to the analyzer on
To specify default storing
Reduced by half in order to store the required time tags
If you chose Custom
To clear default storing changes
Trigger tabs Default Storing subtab, select the At start
Default storing is initially on or off
To insert a store action state mode on
Acquisition option button and choose either On or Off
To clear the trigger sequence on
To insert/replace/delete sequence levels
To insert sequence levels
To replace sequence levels
To cut/copy-and-paste sequence levels
Setting Up Triggers and Running Measurements
Example system14 Slot C Analyzer C has triggered
To view a picture of the trigger sequence
To restore default trigger settings
To clear the trigger sequence
Trigger tab, select the Overview subtab
To specify a time duration for events timing only
To specify a duration or occurrence count for events
To insert timer actions/events
To insert a store action state mode
To insert a timer action
Available
To insert counter actions/events
To insert a timer event
To insert a counter action
To insert a counter event
To insert flag actions/events
To insert a flag event
To drive the Port Out signal with a flag
To use named events
To insert a reset occurrence counter action
To group events
To save a trigger setup
Saving/Recalling Trigger Setups
To give an event list a name
To insert a named event
Running Measurements
To recall a trigger setup
To clear the trigger save/recall list
To start/stop measurements
To stop a measurement
If nothing happens when you start a measurement
Select the Stop or Stop All button
Waiting for Trigger on
To view the trigger status
To open Waveform or Listing displays
Displaying Captured Data
To use other display tools
Help volume
Windows
Search for particular data values captured on labels
Displaying Captured Data
Intermittent Data Errors Unwanted Triggers
Analyzer help volume
If the captured data doesnt look correct
Into parallel words which are easier to view and analyze
This situation will occur in these cases
If there are filtered data holes in display memory
To view symbolic values in a listing display
To display symbols for data values
To view symbolic values in a waveform display
100
To cancel the display processing of captured data
Select the Cancel button
101
Using Symbols
You can use symbol names in place of data values when
102
To load object file symbols
To reload object file symbols
Object file symbols are reloaded
To adjust symbol values for relocated code
Whose symbols you wish to relocate
To create user-defined symbols
To replace user-defined symbols
104
When entering label values in the trigger sequence
To enter symbolic label values
To delete user-defined symbols
To load user-defined symbols
106
To create an Ascii symbol file
General-Purpose Ascii GPA Symbol File Format on
Create the reader.ini file on your workstation or PC
ReadOnlyTicoffPage
StabsType
AppendTicoffPage
Examples Example for Elf/Stabs
109
Example for Coff/Stabs using Ticoff reader
Example for Ticoff
You can print captured data from display tool windows
Printing/Exporting Captured Data
Select the Read File button
Select the file name and automatic file sequencing options
Icon to view the imported data
111
112
Cross-Triggering
To cross-trigger with another instrument
113
When the logic analyzer drives the arm signal
To test the logic analyzer hardware
Solving Logic Analysis Problems
To test the logic analyzer hardware on
114
115
Service Center for assistance
System help volume
To save logic analyzer configurations
Saving and Loading Logic Analyzer Configurations
To load logic analyzer configurations
116
117
Using the Logic Analyzer in Eye Scan Mode
118
Eye Scan tab lets you set up and run Eye Scan measurements
Setting Up and Running Eye Scan Measurements
To select channels for the eye scan
119
120
To set the eye scan range and resolution
Scan Settings Subtab on
To run an eye scan measurement
To quickly set up another measurement using the scale see
To set advanced eye scan options
121
122
To set up qualified eye scan measurements
Advanced Subtab on
123
Requirements Signal Timing Burst Transfers
Memory device versus a memory controller
Burst
Has adjustable sampling positions on each input channel
After the rising edge of the clock
Before the clock edge to after it
125
Clock cycle of the next burst
Are supported
126
127
Be sure that the thresholds are set correctly
Not already expanded
For correct state mode acquisitions
Start your target system and select Run Eye Finder
Display
129
Now, set up eye scan mode
130
Select the Eye Scan tab Select the Qualifier subtab
131
Select the Qualify eye scan sampling using... button
To comment on the eye scan settings
133
Displaying Captured Eye Scan Data
To open the Eye Scan display
Tool
To select the channels displayed
Within the data captured on the bus
134
Scale tab, you can
To scale the Eye Scan display
To use the scaling options
Eye Scan display window, select the Scale tab
To set Eye Scan display options
To quickly set up another measurement using the scale
To clear the captured eye scan data
To open the Eye Scan display on
137
138
139
140
To change the Eye Scan color scale
141
Is zero by default
Make measurements on the eye scan data on
142
To make measurements on the eye scan data
About the captured measurement data
143
144
145
146
147
148
Scroll bars to navigate through the information
To display information about the eye scan data
Eye Scan display window, select the Info tab
149
150
Info tab, you can
151
To comment on the eye scan data
152
Loading Logic Analyzer Configurations on
Saving and Loading Captured Eye Scan Data
153
Sampling Tab on Format Tab on Trigger Tab on
154
155
Sampling Tab
Sampling tab lets you choose between the logic analyzers
Conventional Transitional
Timing Mode
Acquisition
156
Will be stored
How Samples are Stored in Transitional Timing
Period and other times more than two sample periods apart
Samples with transitions
158
State Mode
State Speed
159
Sampling Positions Dialog
160
Sampling Positions Tab
File menu Lets you save/load eye finder data
Display Area
Label buttons
Sampling Position
161
How the Suggested Position Behaves
How the Selected Position Behaves
XX% complete
Cannot run the Eye Finder at this time
Characterizer cannot be loaded
Cannot run the Logic Analyzer at this time
Complete Date
163
Select one or more labels in the Eye Finder Setup tab
This channel appears to be completely quiet
Timeout N K clocks in 5 sec
Two common possibilities exist
165
See individual channels for messages
Run Eye Finder to characterize this channel
Stable region extends beyond the limits of the display
166
Disk is probably full
Numerical value for the item XXX could not be read
File Name already exists. Overwrite?
Failed to open file for reading/writing Name
Invalid true/false flag
Unsupported revision level AA.BB
169
Eye Finder Setup Tab
170
Eye Finder Advanced Settings Dialog
171
File Info Tab
Reload
Eye Scan Mode
Save
Save As
173
Selecting the Eye Scan Mode on
Format Tab
Expander cards which cannot be used in the clock setup
Data
Specify the logic analyzer pod and clock threshold voltages
Name
Pod Assignment Dialog
Type
Pods
176
Trigger Tab
177
Trigger Functions Subtab
178
General Timing Trigger Functions
179
180
General State Trigger Functions
181
Find pattern1 eventually followed by pattern2
182
183
Advanced Trigger Functions
184
State Trigger Functions
Turbo State Trigger Functions
Advanced pattern1 or pattern2
Searched for
186
187
Half Channel State Trigger Functions
Count
Settings Subtab
Intermodule Control
188
189
Overview Subtab
This tab gives a picture of the trigger sequence
Event Specification List
Default Storing Subtab
At start Acquisition
Group events
191
Status Subtab
Save/Recall Subtab
192
Creating trigger function libraries
Two kinds of symbols are available
Symbols Tab
That you use to set up resource terms
Multiple files
194
Object file versions See Also
195
Symbols Selector Dialog
Matching Symbols
Address masking is done by the Align to x Byte option
Search Pattern
Offset By Option
Align to x Byte Option
Symbol File Formats
Byte option allows you to mask off an address
Qualifies any address from 100C through 100F
198
General-Purpose Ascii GPA Symbol File Format
107 file
199
GPA Record Format Summary
Format
200
Records
Definitions in the file
Symbol representing the function name
Symbol representing the name of the section
First address of the section, in hexadecimal
Last address of the section, in hexadecimal
Name of a file
You can specify symbols for variables using
Number of a line in the file, in decimal
202
203
Comments
Labels Subtab
Eye Scan Tab
Expand
Collapse Shows labels only Select All Selects all channels
Run Mode
Scan Settings Subtab
Scan Range
Time
206
Advanced Subtab
Medium
Short
Long
Custom
Qualification
Qualifier Subtab
Clock Edge to Sample
Names for
209
Comments Subtab
Calibration Instructions
Calibration Tab
Calibration Status
Calibration Messages
211
Error Messages
212
Branch expression is too complex
General Guidelines
213
Specific Guidelines 200 Mb/s State and all Timing Modes
This one may
If the following sequence does not compile
Specific Guidelines 400 Mb/s State Modes
214
215
216
Specific Guidelines 800 Mb/s State Mode
Specific Guidelines 1250/1500 Mb/s State Mode
217
Hardware Initialization Failed
Goto action specifies an undefined level
Possible Causes
Last sequence level calls goto next
Must assign another pod pair to specify actions for flags
Maximum of 32 Channels Per Label
No more Edge/Glitch resources available for this pod pair
Timing sampling mode, flags are are always available
No more Pattern resources available for this pod pair
Possible Solutions
Phrase some of the edges as patterns
220
221
No Trigger action found in the trace specification
Slow or Missing Clock
222
Trigger function initialization failure
Trigger Specification is too complex
Trigger inhibited during timing prestore
Then the approximate time is 32 seconds
223
224
Combiner resource allocation guidelines
Event
225
Waiting for Trigger
Misaligned boundaries for addresses
226
To save a trigger setup on
Operating temperature 0 to 45 degrees C
Specifications and Characteristics
Probes
227
E5379A Differential Probe Specifications Characteristics
E5378A Single-Ended Probe Specifications Characteristics
All specifications are marked by * asterisk
E5378A Input Equivalent Circuit
229
E5379A Input Equivalent Circuit
230
1500 Mb/s Sampling Mode Specifications and Characteristics
E5380A Input Equivalent Circuit
231
Characteristics
232
233
400 Mb/s Sampling Mode Specifications Characteristics
234
200 Mb/s Sampling Mode Specifications Characteristics
Transitional Timing Mode Specifications and Characteristics
Conventional Timing Mode Specifications and Characteristics
All specifications are marked by * asterisk
235
236
What is a Specification?
What is a Function Test?
What is a Characteristic?
Referred to as an operational accuracy calibration
237
238
239
Concepts
240
Understanding Logic Analyzer Triggering
Conveyor Belt Analogy
241
Conveyor belt analogy
Sequence Levels
Summary of Triggering Capabilities
Next Summary of Triggering Capabilities on
Next Sequence Levels on
243
Addr Data
244
Boolean Expressions
Edges
Branches
Ranges
Next Ranges on
Occurrence Counters and Global Counters
Flags
Next Flags on
Trigger Sequence for Module
Next Timers on
Timers
An example trigger sequence to set up this measurement is
An edge followed by an edge with a time limit
Storage Qualification
Default Storage
Next Storage Qualification on
Needed
250
Sequence Level Storage
Next Strategies for Setting Up Triggers on
Strategies for Setting Up Triggers
Trigger Functions
251
252
Agilent 16715A trigger user interface
Pattern2 occurring immediately after Pattern1
253
Same trigger as If/Then statements
Store range until pattern occurs
Next Setting Up Complex Triggers on
Setting Up Complex Triggers
Document Your Trigger Sequences
Next Document Your Trigger Sequences on
Different parts of the trigger to describe how they work
Conclusions
Next Conclusions on
Inline documentation on an Agilent logic analyzer
256
Understanding State Mode Sampling Positions
To accurately capture data on a bus
257
258
Window
259
Understanding Eye Scan Measurements
260
261
Using the Logic Analyzer in Eye Scan Mode on
Voltage resolution that can be set is 1 mV
Are multiple logic analyzer cards in a module in this case
Measurements run simultaneously in parallel
263
Glossary
Asterisk * See edge terms, glitch, and labels
264
Divided into 1K 64-state records
265
Debug mode See monitor
266
Ethernet address See link-level
267
268
269
Module/probe interconnect cable
270
By the channel width of the instrument
Processor probe See emulation
271
Measurements
272
273
274
275
Index
251
276
247
277
122
278
180
279
280
Label values, symbolic, 105 labels, 22
Positive logic
281
242
282
107
283
Wait for other machine to trigger
284
Publication Number 5988-9044EN January 1