Traffic engineering
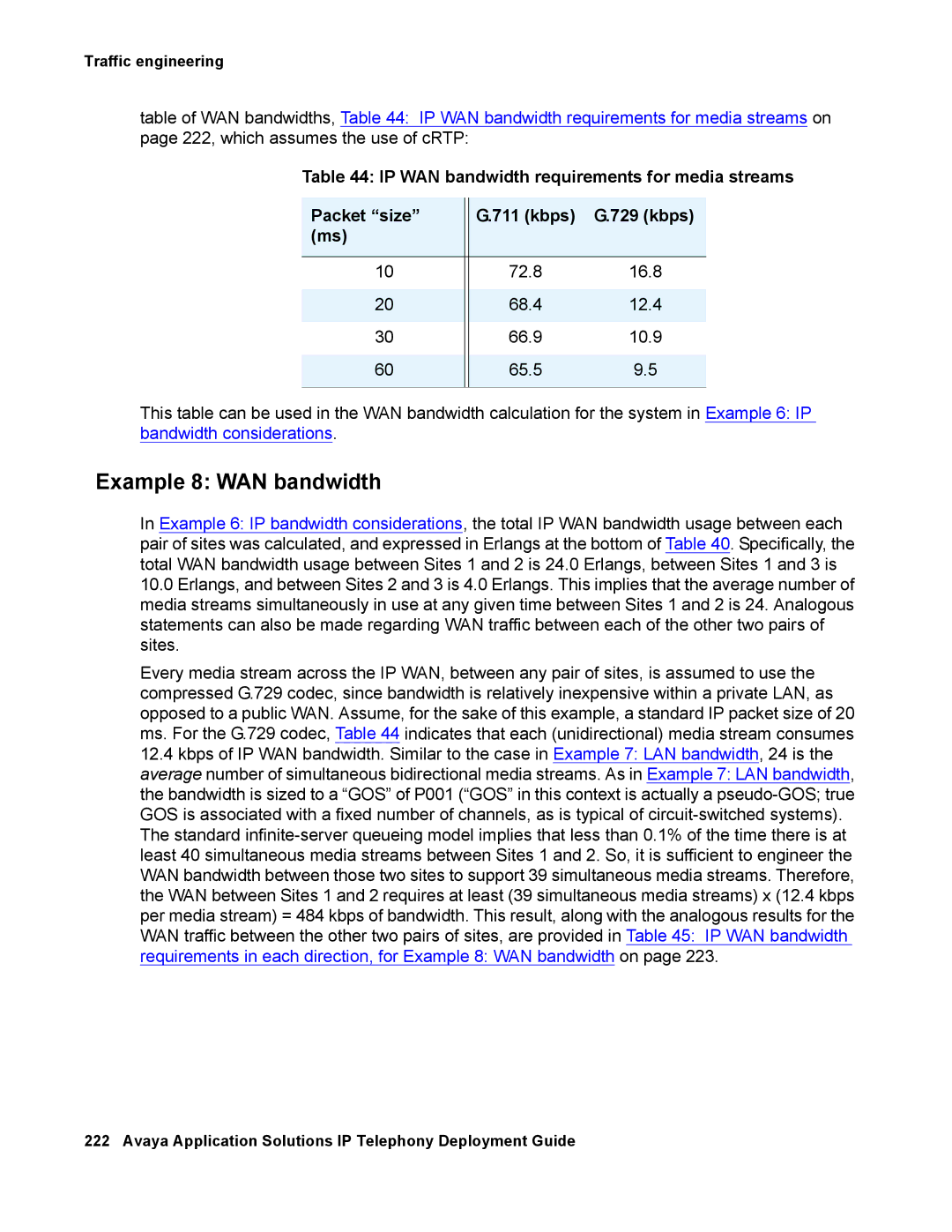
table of WAN bandwidths, Table 44: IP WAN bandwidth requirements for media streams on page 222, which assumes the use of cRTP:
Table 44: IP WAN bandwidth requirements for media streams
Packet “size” |
| G.711 (kbps) | G.729 (kbps) |
(ms) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
| 72.8 | 16.8 |
|
|
|
|
20 |
| 68.4 | 12.4 |
|
|
|
|
30 |
| 66.9 | 10.9 |
|
|
|
|
60 |
| 65.5 | 9.5 |
|
|
|
|
This table can be used in the WAN bandwidth calculation for the system in Example 6: IP bandwidth considerations.
Example 8: WAN bandwidth
In Example 6: IP bandwidth considerations, the total IP WAN bandwidth usage between each pair of sites was calculated, and expressed in Erlangs at the bottom of Table 40. Specifically, the total WAN bandwidth usage between Sites 1 and 2 is 24.0 Erlangs, between Sites 1 and 3 is
10.0Erlangs, and between Sites 2 and 3 is 4.0 Erlangs. This implies that the average number of media streams simultaneously in use at any given time between Sites 1 and 2 is 24. Analogous statements can also be made regarding WAN traffic between each of the other two pairs of sites.
Every media stream across the IP WAN, between any pair of sites, is assumed to use the compressed G.729 codec, since bandwidth is relatively inexpensive within a private LAN, as opposed to a public WAN. Assume, for the sake of this example, a standard IP packet size of 20 ms. For the G.729 codec, Table 44 indicates that each (unidirectional) media stream consumes
12.4kbps of IP WAN bandwidth. Similar to the case in Example 7: LAN bandwidth, 24 is the average number of simultaneous bidirectional media streams. As in Example 7: LAN bandwidth, the bandwidth is sized to a “GOS” of P001 (“GOS” in this context is actually a