Resource sizing
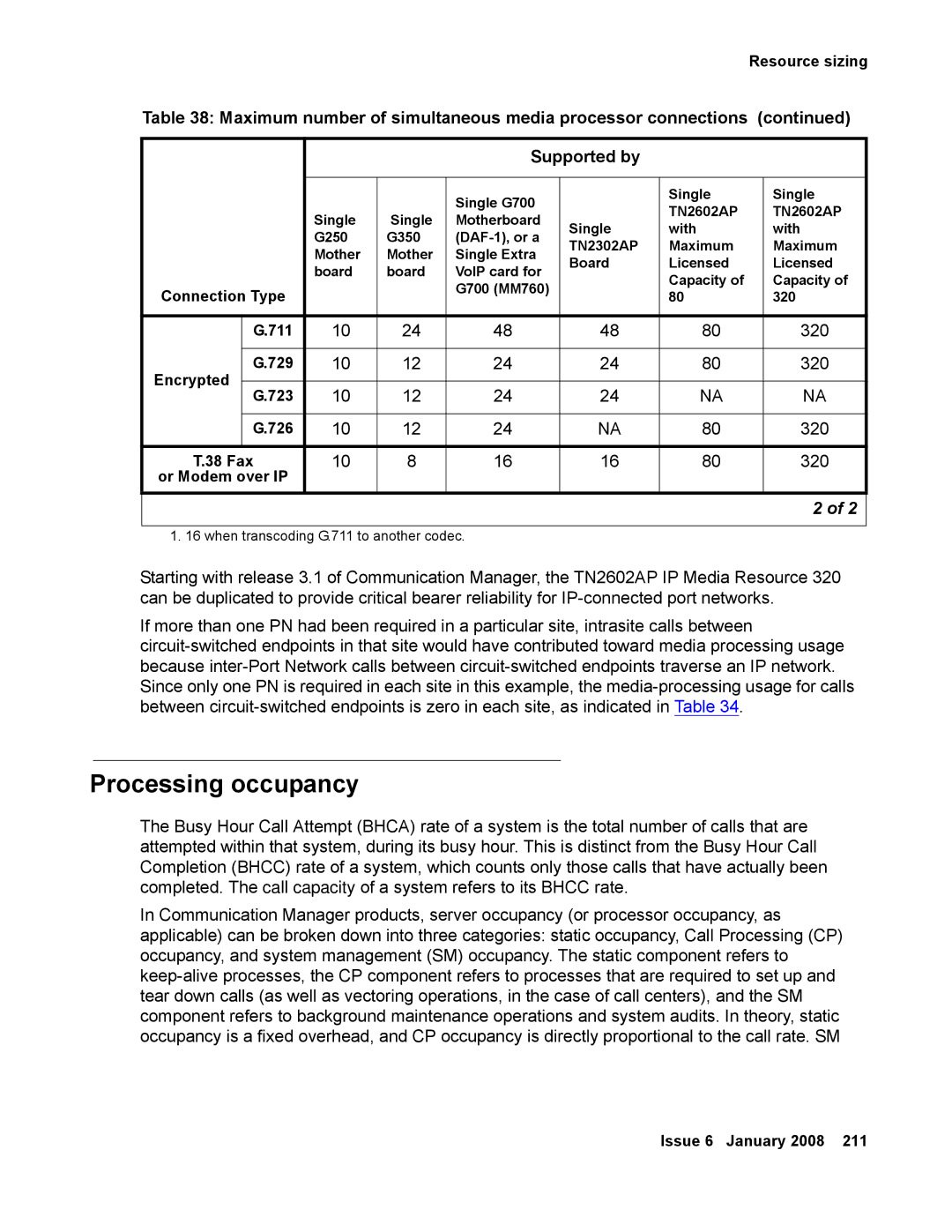
Table 38: Maximum number of simultaneous media processor connections (continued)
|
|
|
| Supported by |
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| Single G700 |
| Single | Single | |
|
|
|
|
| TN2602AP | TN2602AP | ||
|
| Single | Single | Motherboard | Single | |||
|
| with | with | |||||
|
| G250 | G350 | |||||
|
| TN2302AP | Maximum | Maximum | ||||
|
| Mother | Mother | Single Extra | ||||
|
| Board | Licensed | Licensed | ||||
|
| board | board | VoIP card for | ||||
|
|
| Capacity of | Capacity of | ||||
Connection Type |
|
| G700 (MM760) |
| ||||
|
|
| 80 | 320 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| G.711 | 10 | 24 | 48 | 48 | 80 | 320 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Encrypted | G.729 | 10 | 12 | 24 | 24 | 80 | 320 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
G.723 | 10 | 12 | 24 | 24 | NA | NA | ||
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| G.726 | 10 | 12 | 24 | NA | 80 | 320 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
T.38 Fax | 10 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 80 | 320 | ||
or Modem over IP |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 of 2 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
1. 16 when transcoding G.711 to another codec.
Starting with release 3.1 of Communication Manager, the TN2602AP IP Media Resource 320 can be duplicated to provide critical bearer reliability for
If more than one PN had been required in a particular site, intrasite calls between
Processing occupancy
The Busy Hour Call Attempt (BHCA) rate of a system is the total number of calls that are attempted within that system, during its busy hour. This is distinct from the Busy Hour Call Completion (BHCC) rate of a system, which counts only those calls that have actually been completed. The call capacity of a system refers to its BHCC rate.
In Communication Manager products, server occupancy (or processor occupancy, as applicable) can be broken down into three categories: static occupancy, Call Processing (CP) occupancy, and system management (SM) occupancy. The static component refers to
Issue 6 January 2008 211