Traffic engineering
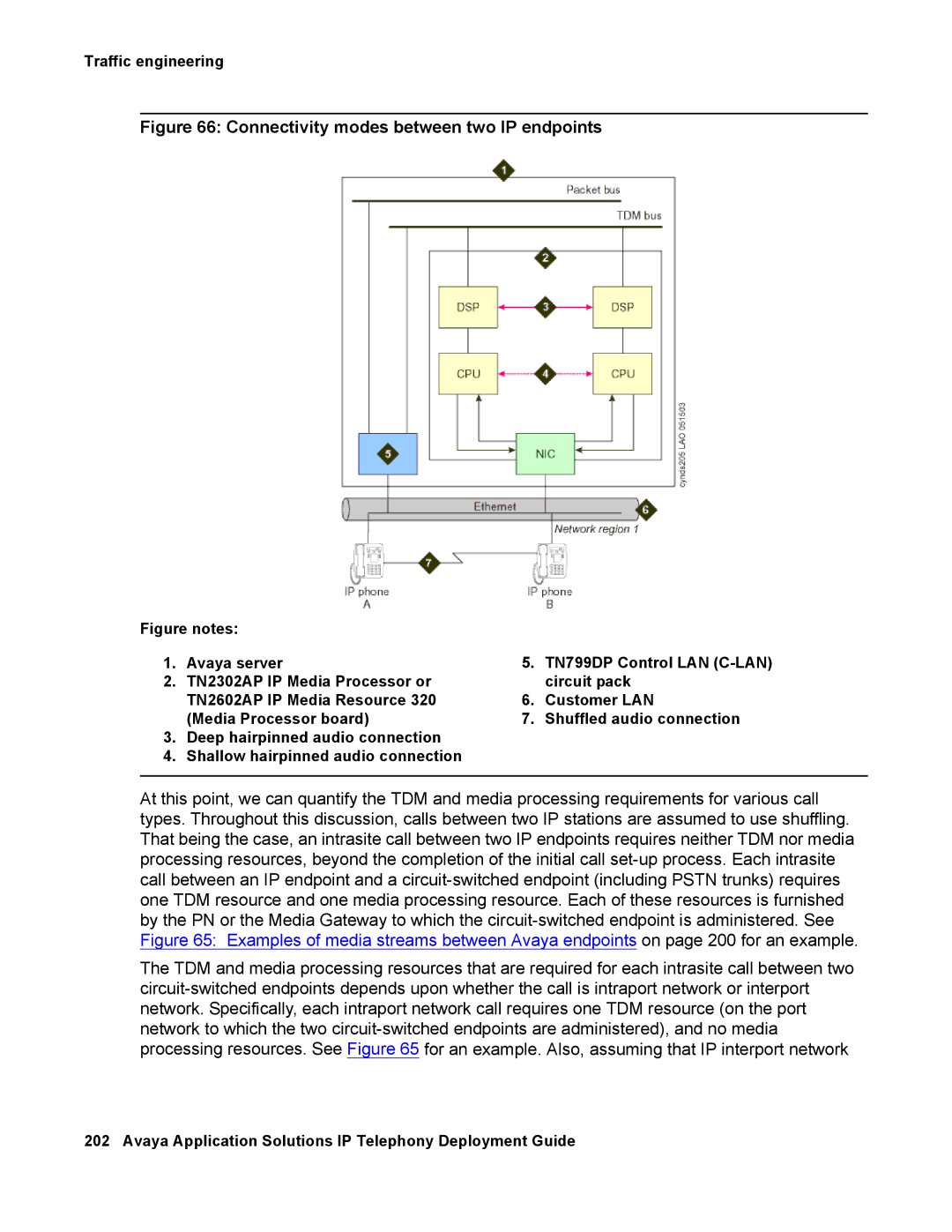
Figure 66: Connectivity modes between two IP endpoints
Figure notes: |
|
| |
1. | Avaya server | 5. | TN799DP Control LAN |
2. | TN2302AP IP Media Processor or |
| circuit pack |
| TN2602AP IP Media Resource 320 | 6. | Customer LAN |
| (Media Processor board) | 7. | Shuffled audio connection |
3.Deep hairpinned audio connection
4.Shallow hairpinned audio connection
At this point, we can quantify the TDM and media processing requirements for various call types. Throughout this discussion, calls between two IP stations are assumed to use shuffling. That being the case, an intrasite call between two IP endpoints requires neither TDM nor media processing resources, beyond the completion of the initial call
The TDM and media processing resources that are required for each intrasite call between two