Chapter 3 Using the Ease Menu and Niagara SCX Web Interface
Niagara SCX Web Interface
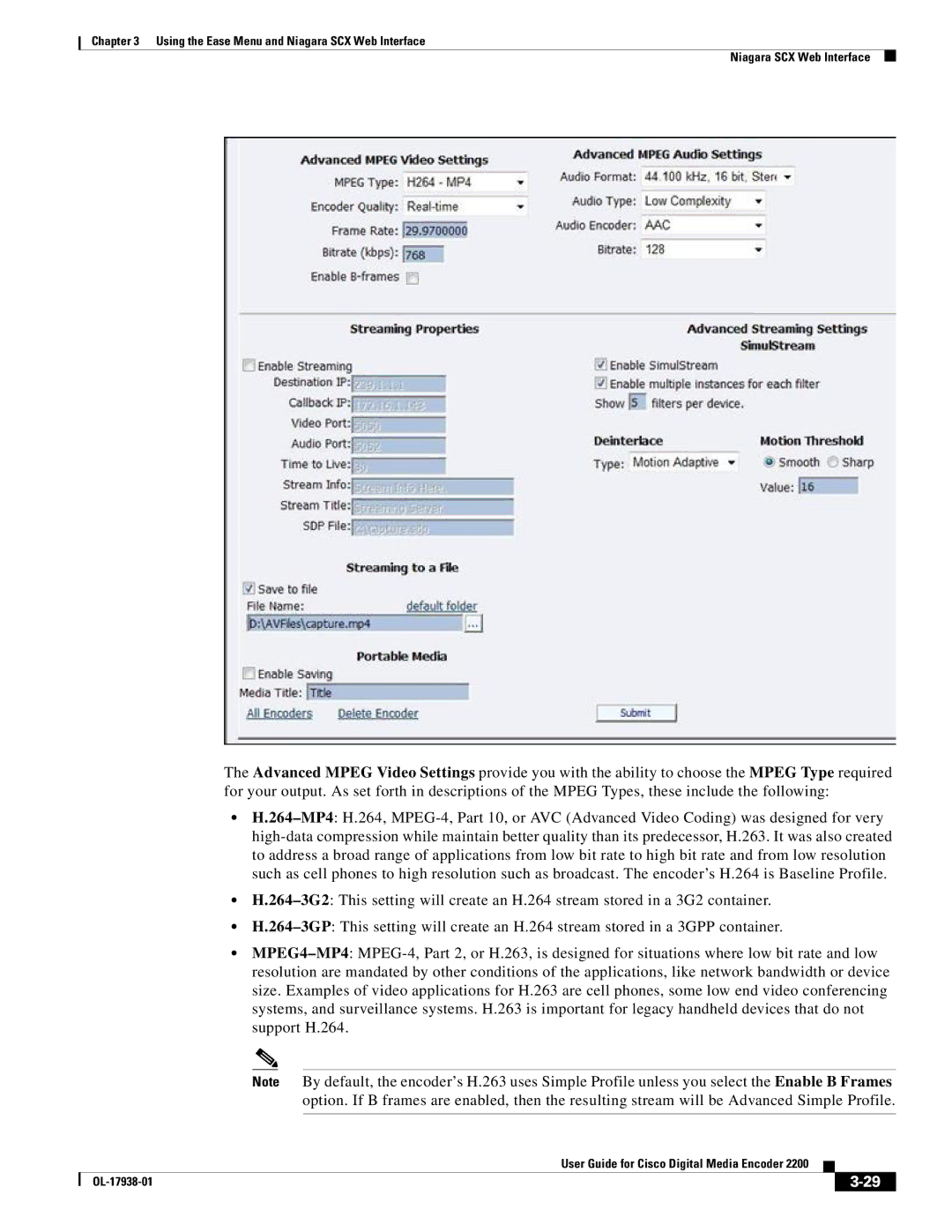
The Advanced MPEG Video Settings provide you with the ability to choose the MPEG Type required for your output. As set forth in descriptions of the MPEG Types, these include the following:
•H.264–MP4: H.264, MPEG-4, Part 10, or AVC (Advanced Video Coding) was designed for very high-data compression while maintain better quality than its predecessor, H.263. It was also created to address a broad range of applications from low bit rate to high bit rate and from low resolution such as cell phones to high resolution such as broadcast. The encoder’s H.264 is Baseline Profile.
•H.264–3G2: This setting will create an H.264 stream stored in a 3G2 container.
•H.264–3GP: This setting will create an H.264 stream stored in a 3GPP container.
•MPEG4–MP4: MPEG-4, Part 2, or H.263, is designed for situations where low bit rate and low resolution are mandated by other conditions of the applications, like network bandwidth or device size. Examples of video applications for H.263 are cell phones, some low end video conferencing systems, and surveillance systems. H.263 is important for legacy handheld devices that do not support H.264.
Note By default, the encoder’s H.263 uses Simple Profile unless you select the Enable B Frames option. If B frames are enabled, then the resulting stream will be Advanced Simple Profile.
| | User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 | | |
| | |
| OL-17938-01 | | | 3-29 | |
| | | |