Chapter 2 Getting to Know the Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
Introduction
Streaming Infrastructure
Before setting up your new Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200, it is useful to understand the complete overview of live streaming
There are many applications for capturing video into the computer environment that can range from DVD authoring to live webcasting. Regardless of the final use of the video, all can be categorized into three main workflow processes:
•Single video/session capture
–Typically the captured file is then processed and/or authored into its final form for delivery
•Batch video/session capture (archiving, scheduling and storage)
–Multiple source content is to be digitalized
–Device control is needed for unattended source
–Ability to schedule sessions is needed to capture timed events
•Live video capture, processing and delivery (webcasting)
–Can be single or multiple sources
–Live event at a specific time
–Can be a remote or local capture
–Final content is delivered in real time to viewers
Each category has its unique set of requirements that also dictates different user interfaces, functionality and experiences. The Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200 is designed for live video capture, processing and delivery.
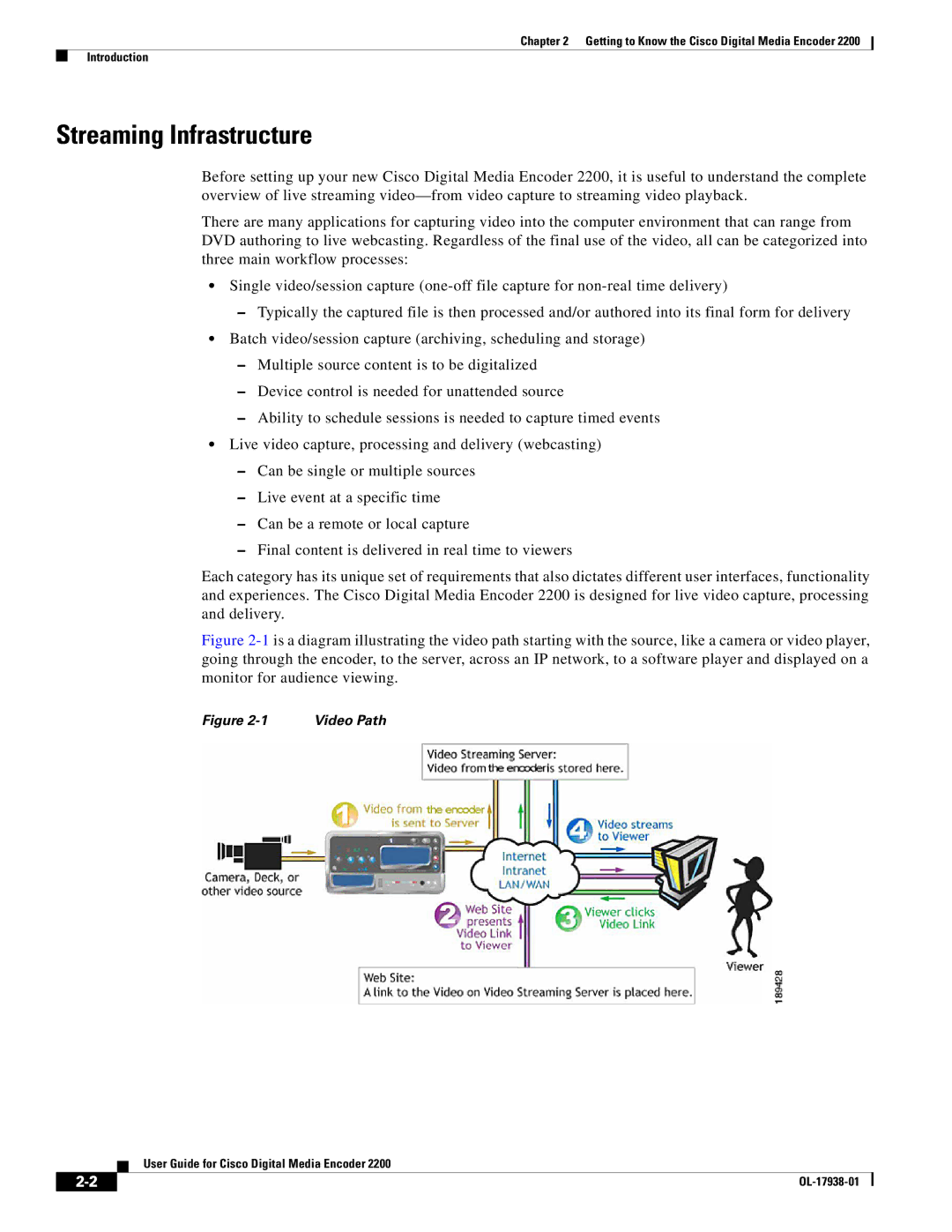
Figure 2-1 is a diagram illustrating the video path starting with the source, like a camera or video player, going through the encoder, to the server, across an IP network, to a software player and displayed on a monitor for audience viewing.
Figure | Video Path |
User Guide for Cisco Digital Media Encoder 2200
| ||
|